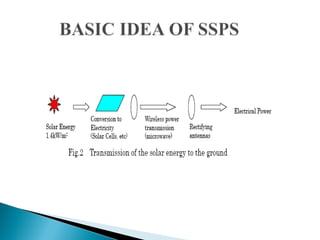
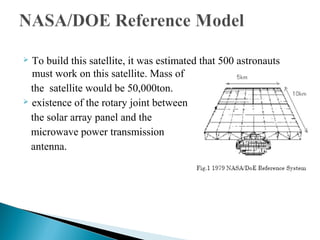
Solar power satellites have been proposed as a way to collect solar energy in space and transmit it to receivers on Earth. In 1968, Dr. Peter Glaser introduced the concept of using large solar panels in geosynchronous orbit to convert sunlight to microwaves and beam the energy back to rectennas on Earth. NASA and the Department of Energy studied the feasibility in the 1970s. In 1999, NASA initiated the Space Solar Power Exploratory Research and Technology program to further design studies. While solar power satellites could provide a continuous source of clean energy without pollution, many technical challenges remain regarding construction, power transmission levels, and thermal management that require more research and development.