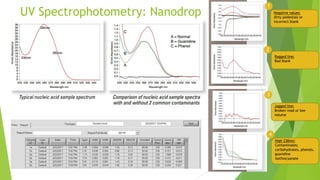
This document discusses various methods for estimating the quantity and quality of DNA and RNA, including UV spectrophotometry, fluorometric quantification, gel electrophoresis, and real-time PCR. UV spectrophotometry using a NanoDrop instrument allows rapid assessment of nucleic acid concentration and purity by measuring absorbance at 260nm and 280nm. Fluorometric methods like PicoGreen and Qubit use fluorescent dyes that bind specifically to DNA or RNA and quantify samples by comparing fluorescence to standard curves. Real-time PCR can quantify and assess DNA quality by monitoring fluorescence during PCR amplification of a target sequence.