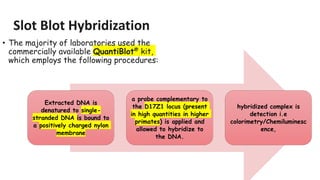
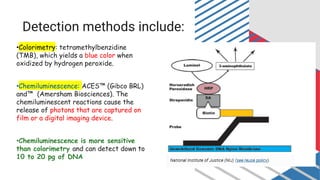
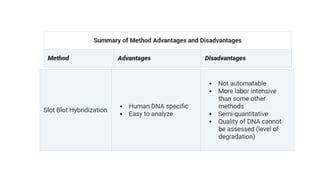
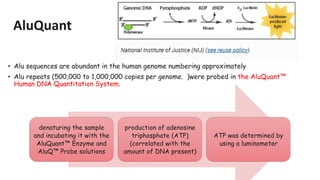
The document outlines various historical and commonly used methods for DNA quantification, including yield gels, spectrophotometry, fluorometry, slot blot hybridization, and AluQuant. Each method has distinct procedures and applications, with specific details on how they measure DNA concentration and quality. This comprehensive overview emphasizes the sensitivity and effectiveness of these techniques in forensic analysis.