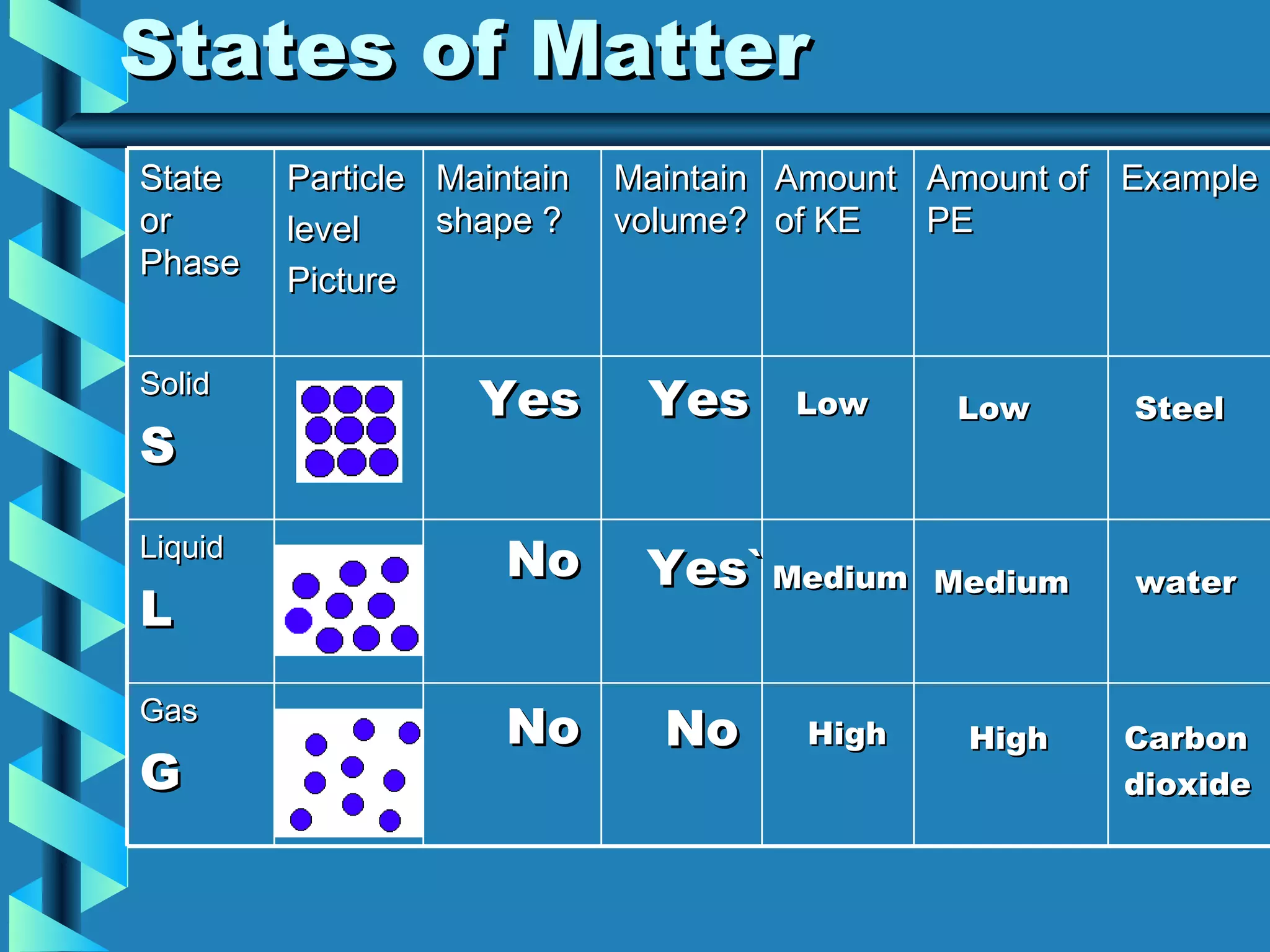
The document discusses the five states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It explains that all matter is made up of particles in constant motion, and the rate of motion determines the temperature and state. Solids maintain their shape and volume, while liquids maintain their volume but not their shape. Gases have no definite shape or volume. Plasma is a high-energy state where matter becomes ionized, like the surface of the sun.