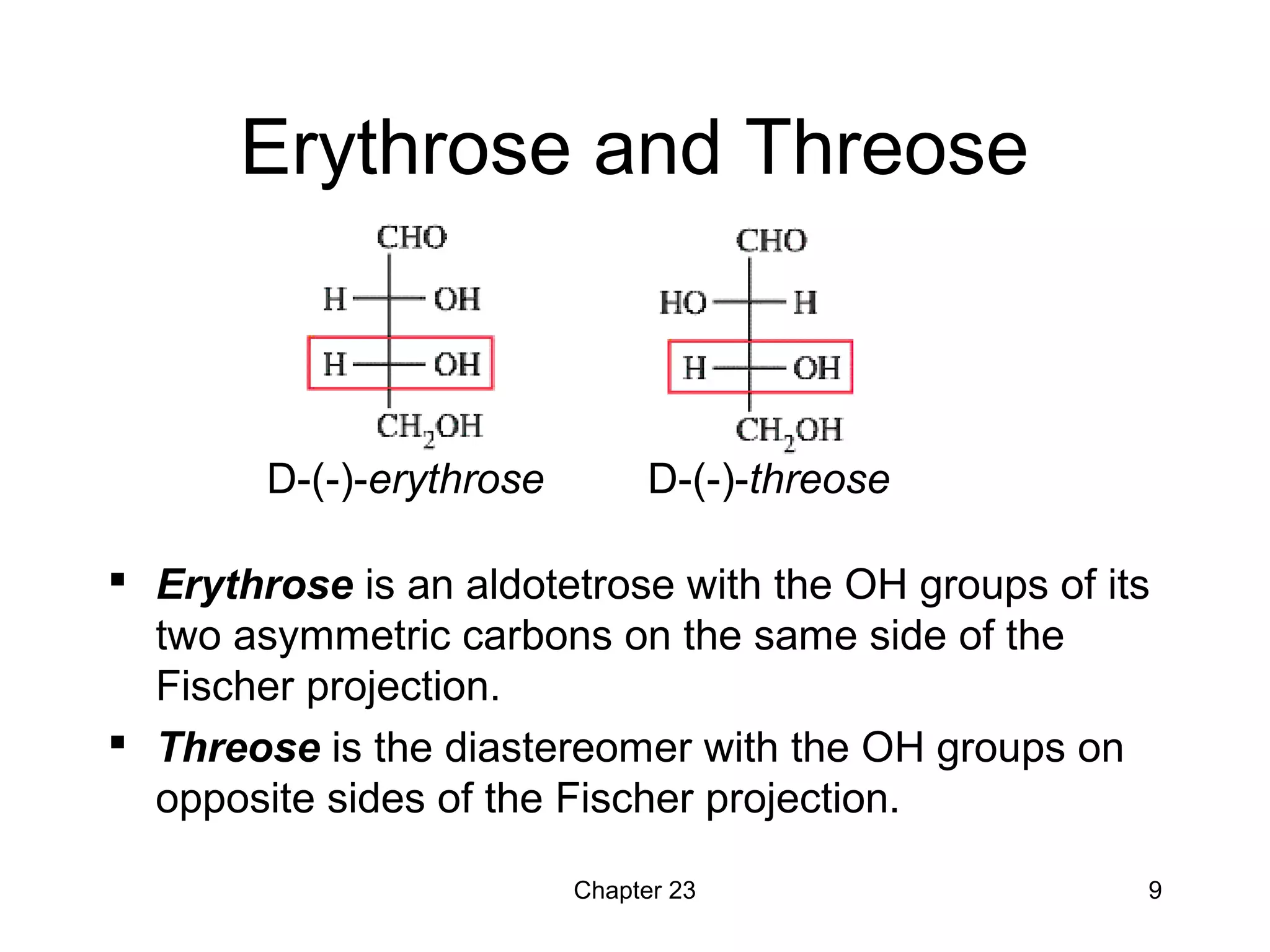
This chapter discusses carbohydrates and nucleic acids. It begins by describing how carbohydrates like starch and cellulose are synthesized by plants from glucose. Carbohydrates are then classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides based on whether they can be hydrolyzed into one, two, or many glucose units. The chapter also covers nucleic acids like RNA and DNA, which are polymers of ribose or deoxyribose linked by phosphate groups and bonded to nitrogenous bases. DNA consists of two antiparallel strands bonded through base pairing between complementary bases.