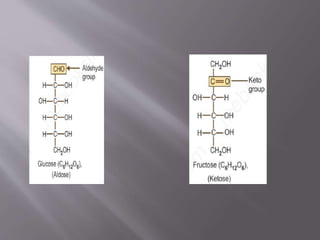
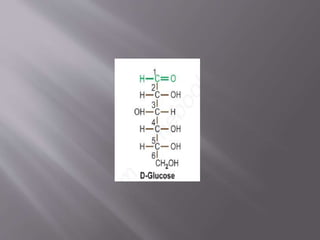
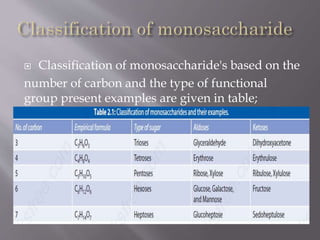
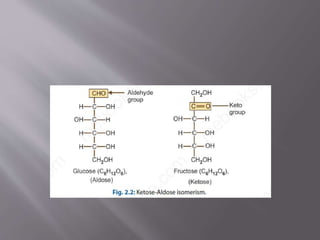
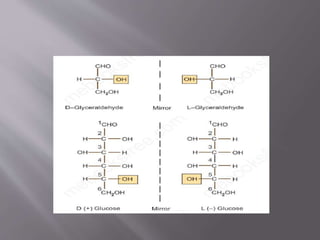
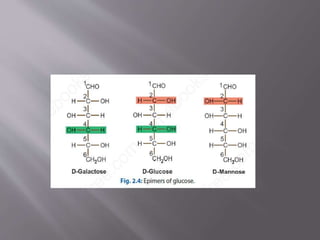
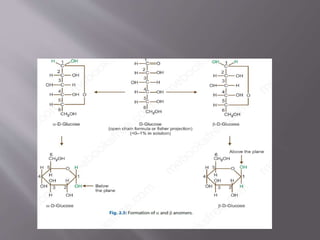
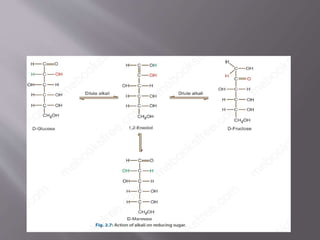
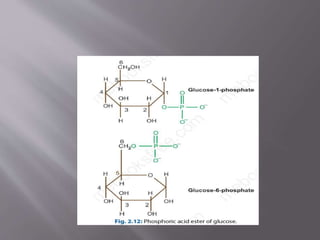
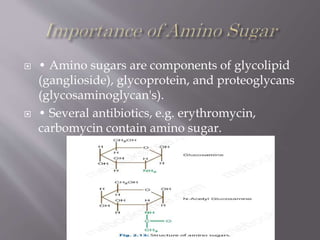
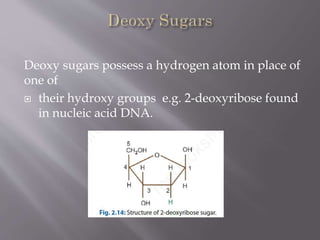
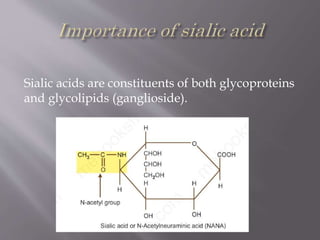
Carbohydrates are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups and are abundant biomolecules that serve various functions, including energy sources and structural components. They are classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides, with examples such as glucose and fructose exhibiting isomerism. Key properties of carbohydrates include their optical activity and reactions such as oxidation and reduction, which result in different sugar derivatives and functional roles in biological systems.