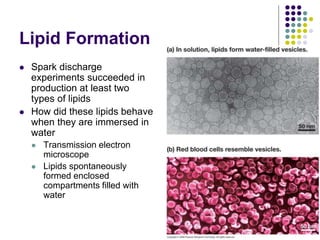
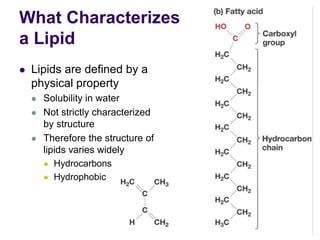
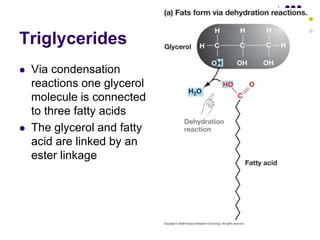
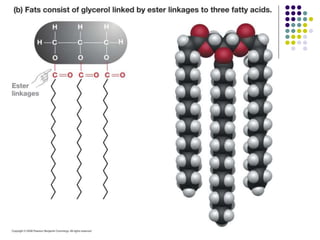
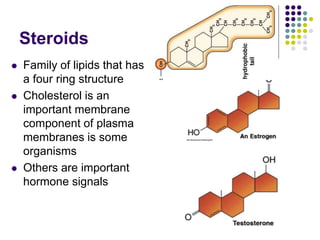
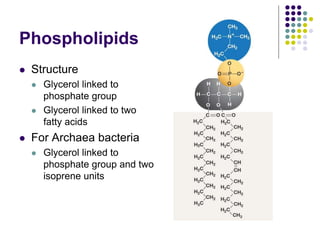
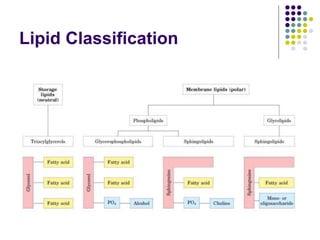
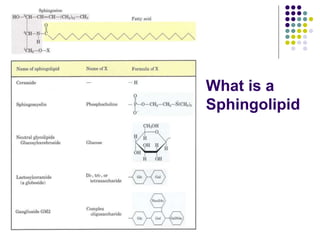
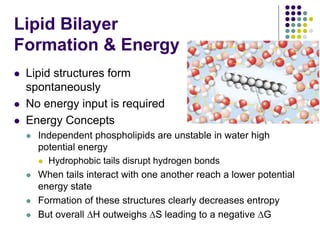
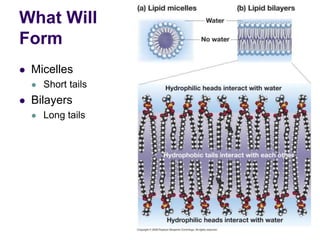
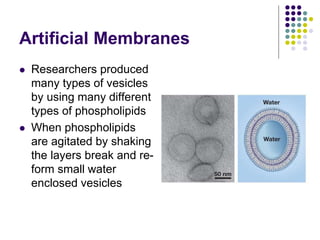
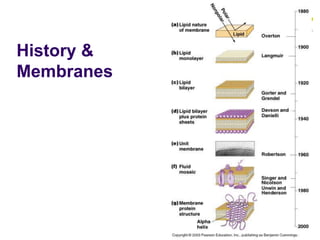
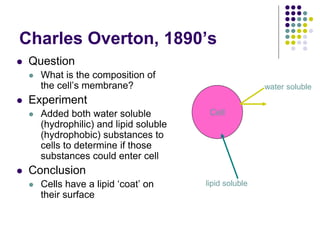
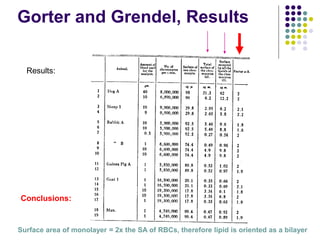
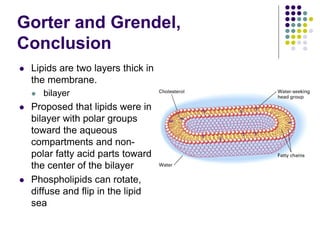
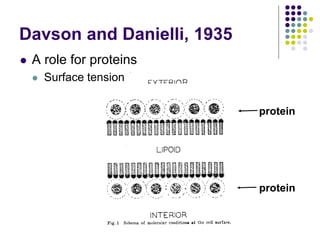
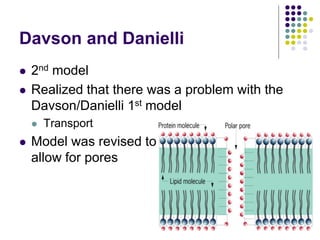
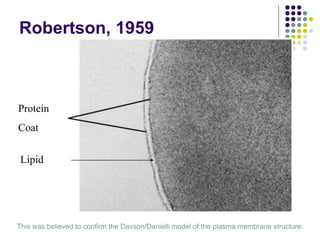
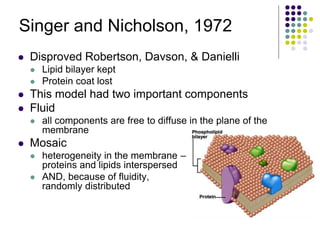
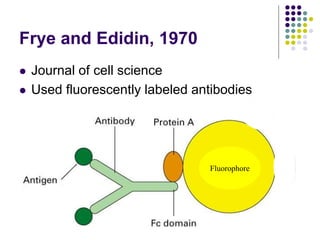
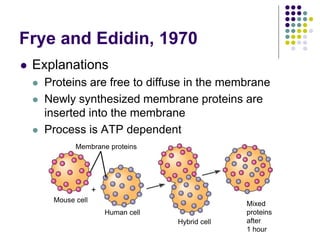
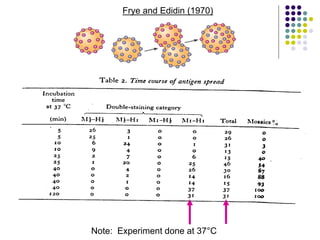
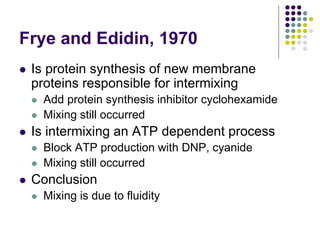
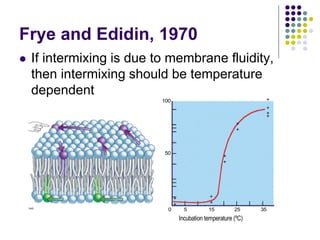
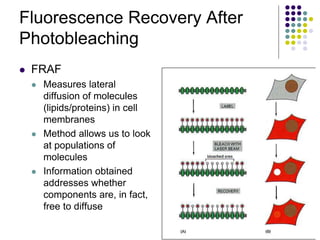
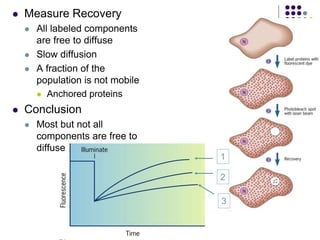
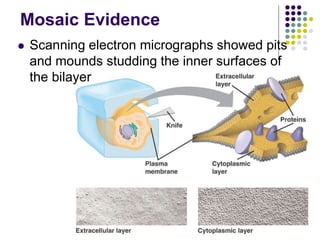
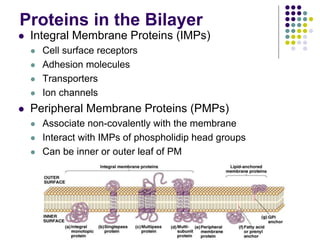
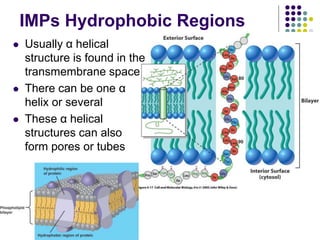
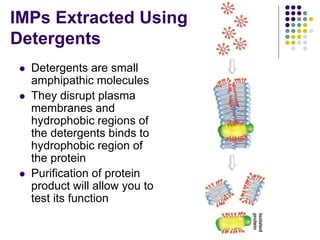
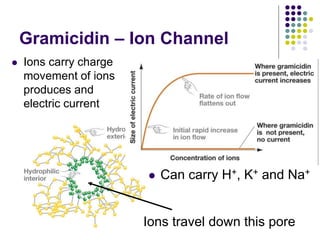
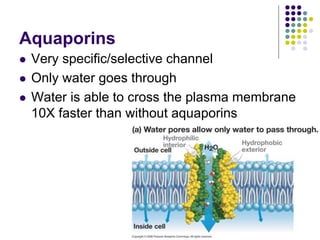
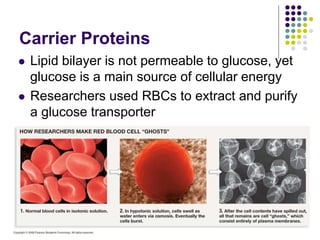
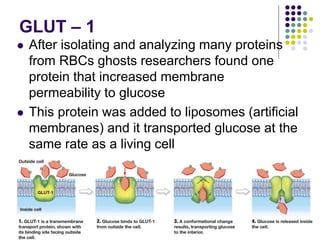
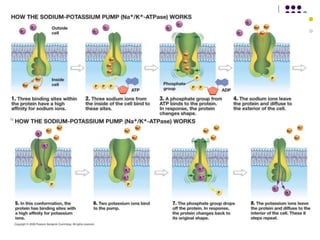
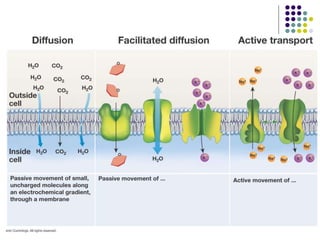
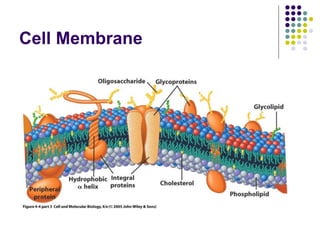
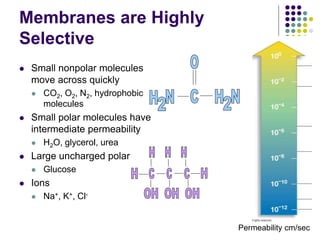
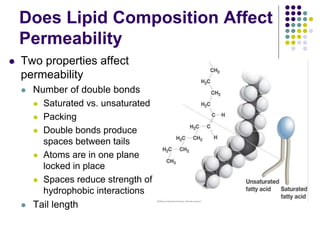
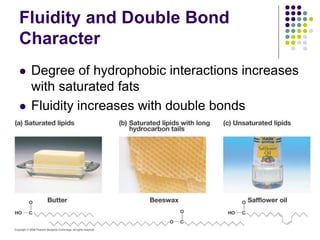
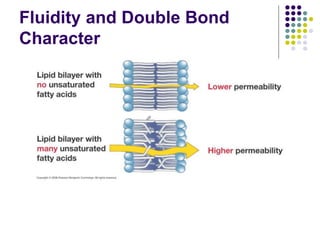
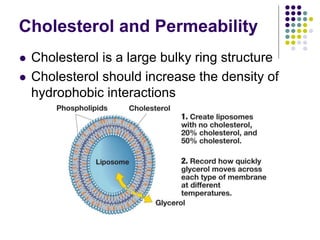
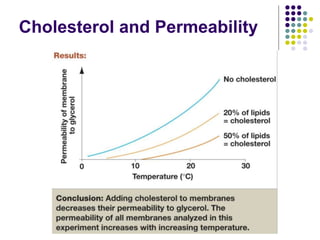
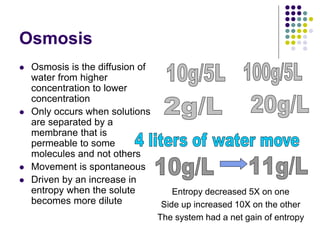
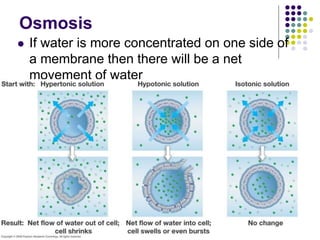
The document discusses the evolution of cell membranes from early RNA molecules clinging to clay particles to the modern fluid mosaic model. Key events include the formation of lipid bilayers that separated internal and external chemistry, allowing more efficient reactions. Experiments showed lipids spontaneously forming enclosed compartments and lipid bilayers with integral membrane proteins that gave membranes a mosaic-like structure. The fluid mosaic model proposes membranes are fluid with lipids and proteins able to diffuse freely within the plane of the bilayer. Transport proteins like channels and carriers allow selective permeability while pumps use ATP to transport molecules against gradients.