- Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks. There are 20 different amino acids, some are essential and must be obtained through diet.
- The specific sequence of amino acids determines the 3D shape of a protein and its function. Denaturation occurs when proteins lose their shape due to heat, acid, etc.
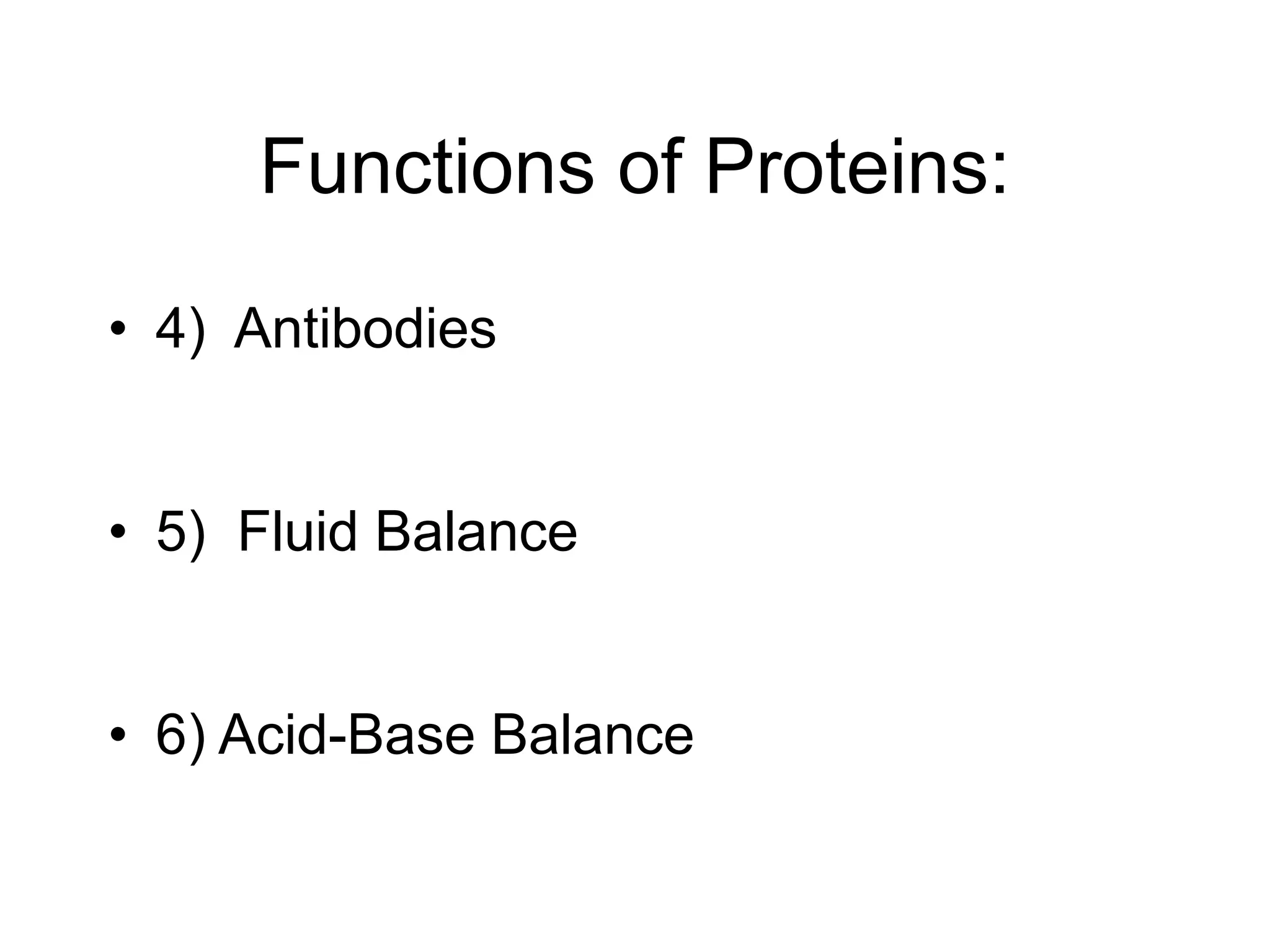
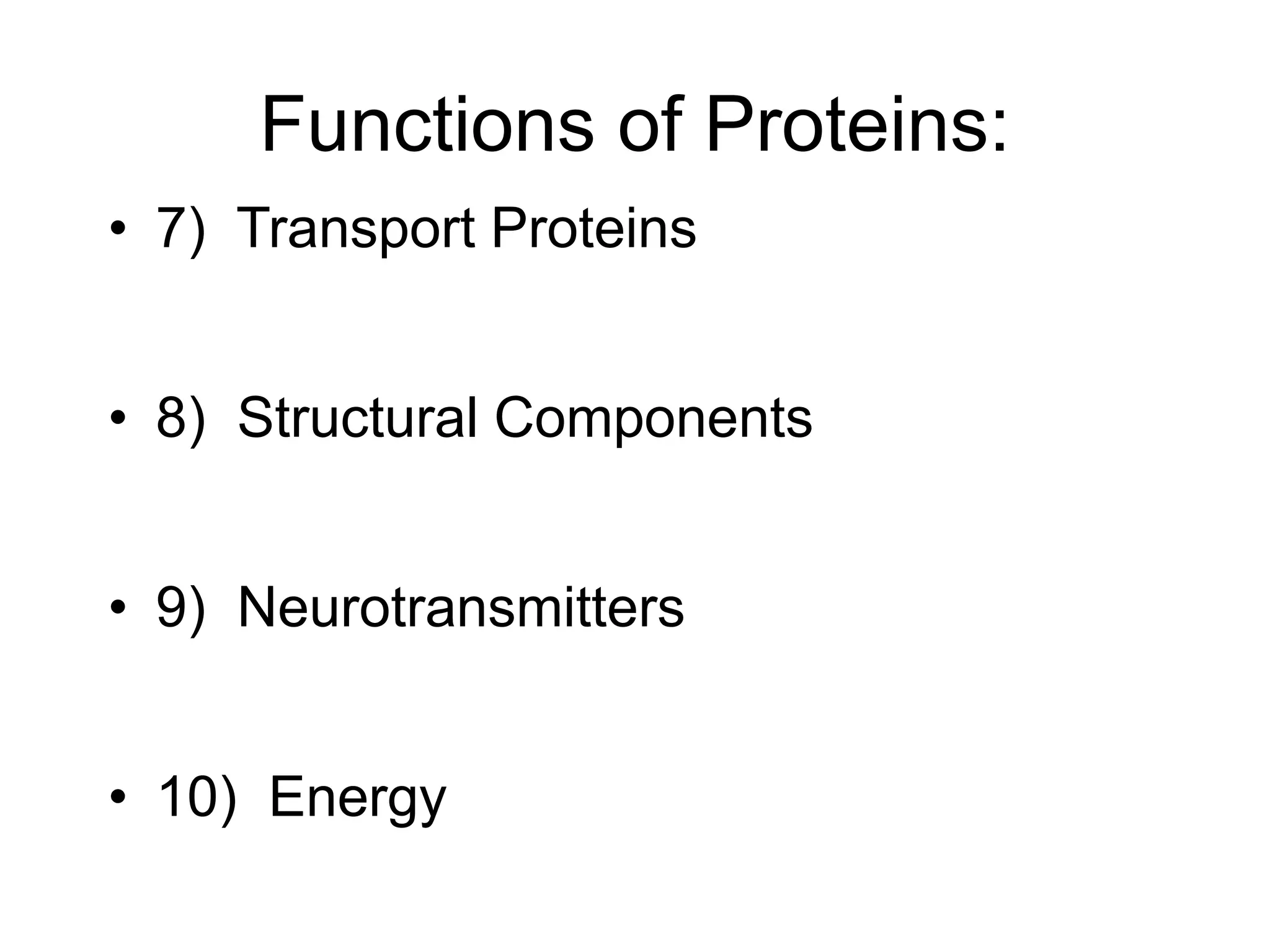
- Proteins serve many important functions in the body including structure, enzymes, transport, hormones, antibodies, and more. An inadequate intake can result in the body breaking down its own proteins to obtain energy.