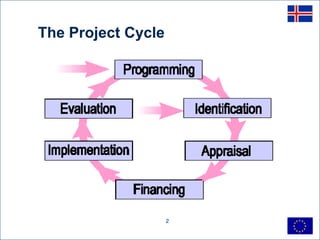
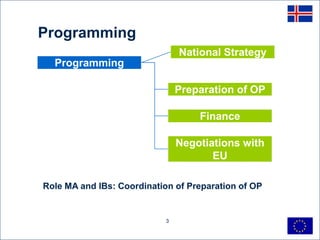
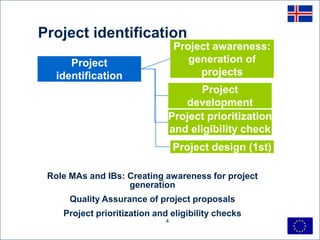
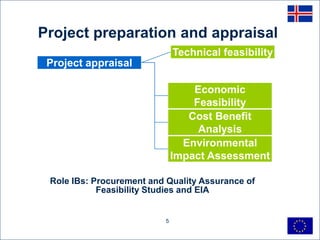
This document discusses project cycle management for sustainable economic development in Iceland. It outlines the key stages in the project cycle including programming, identification, preparation, implementation, evaluation. It emphasizes the roles of managing authorities and intermediate bodies in coordinating project preparation, ensuring quality, and prioritizing projects. Sound project design, management, ownership and sufficient capacity are identified as critical success factors. Quality assurance, risk management, and time management are also highlighted as key elements of effective project cycle management.