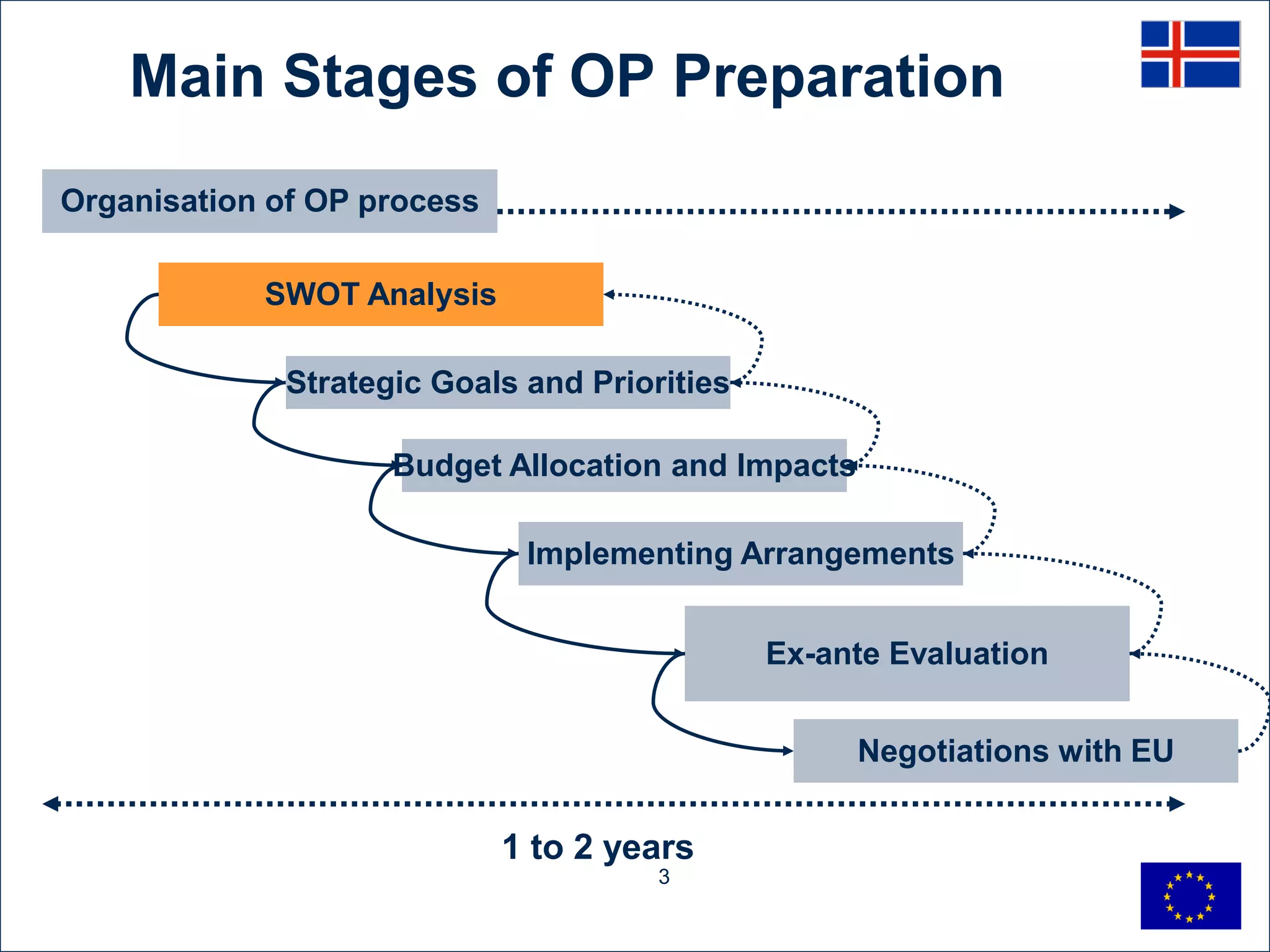
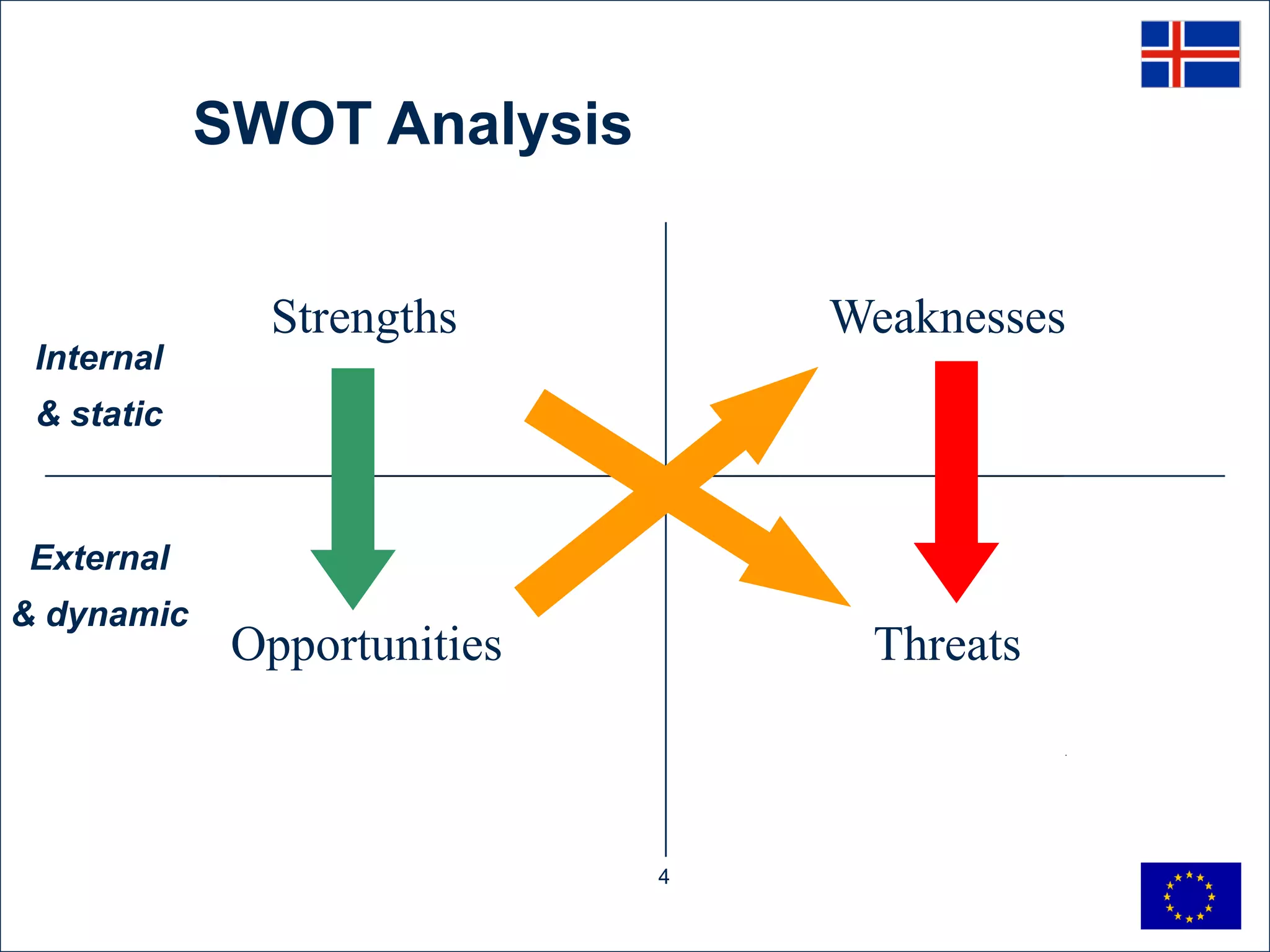
The SWOT analysis identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for the sustainable economic development of the Sudurnes region of Iceland. The region's strengths include its international airport, natural resources, available land, young population, fish industry, and infrastructure. Weaknesses are the low educational level of the workforce, lack of entrepreneurship, need for better connections to the capital area, too many local authorities, and distance from the capital. Opportunities involve developing the airport and natural resources, tourism, and cooperation with other regions. Threats include lack of coordination, potential unemployment increases, skills shortages, changes to fisheries policy, and proximity to the capital area.