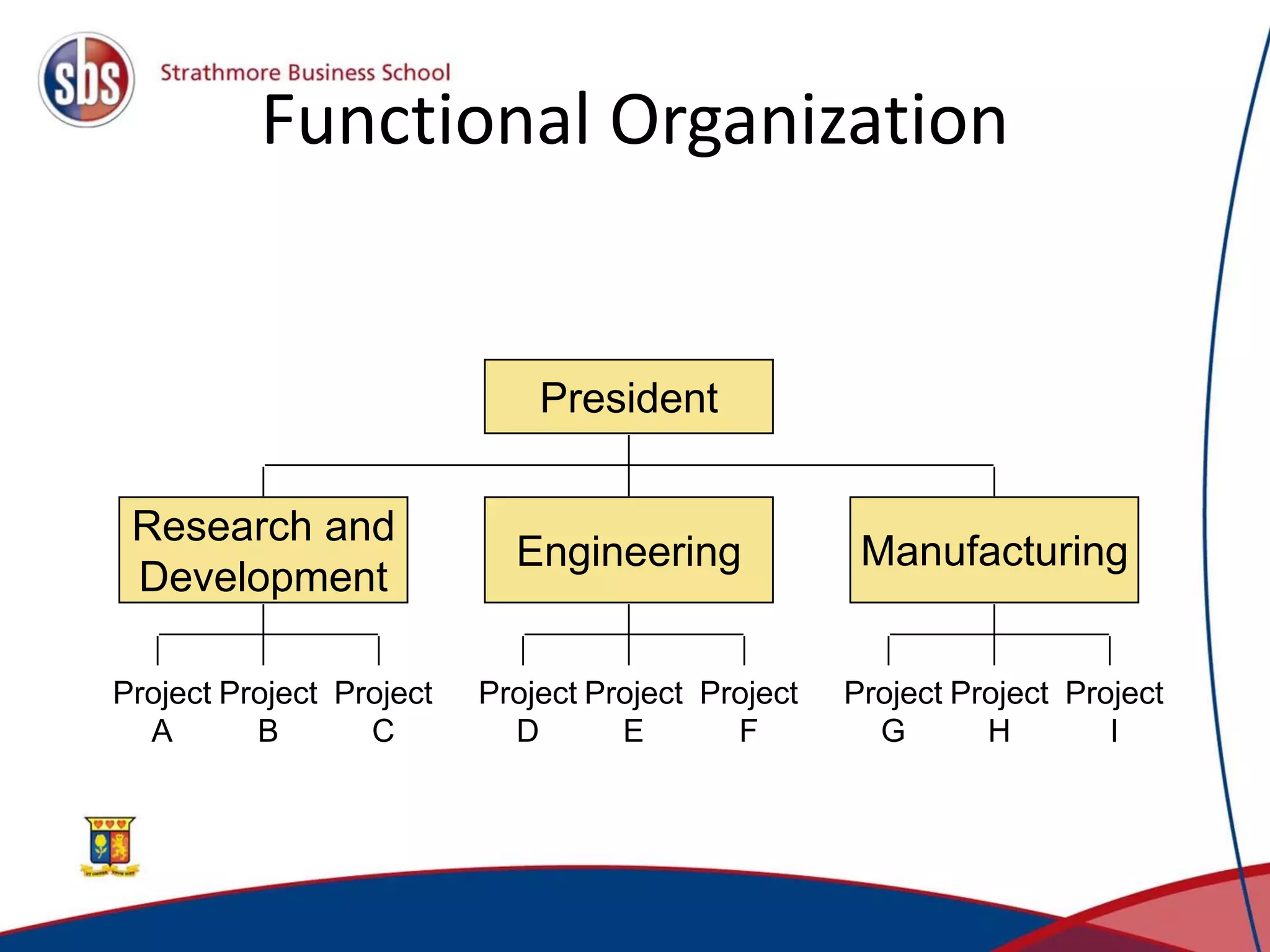
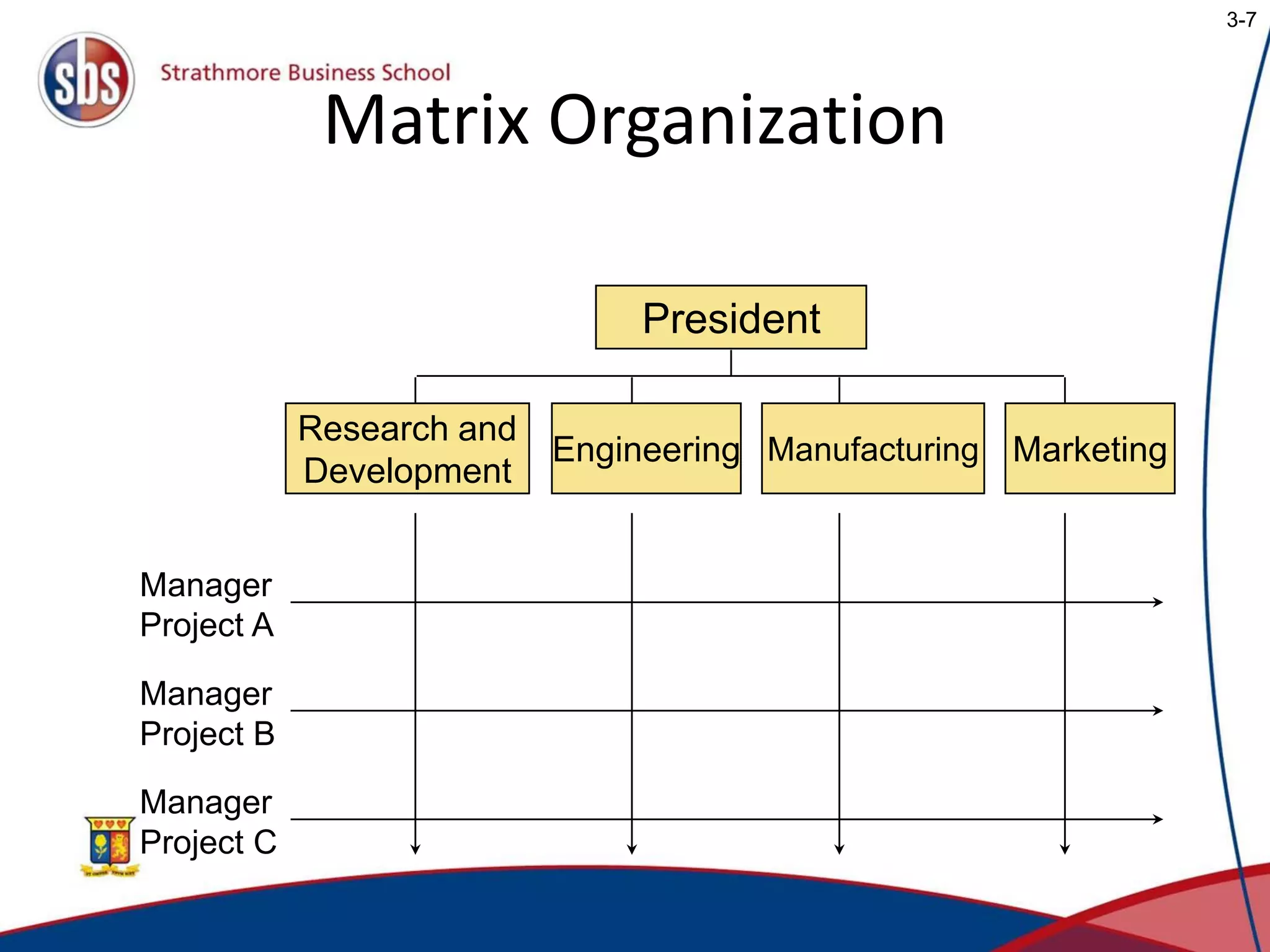
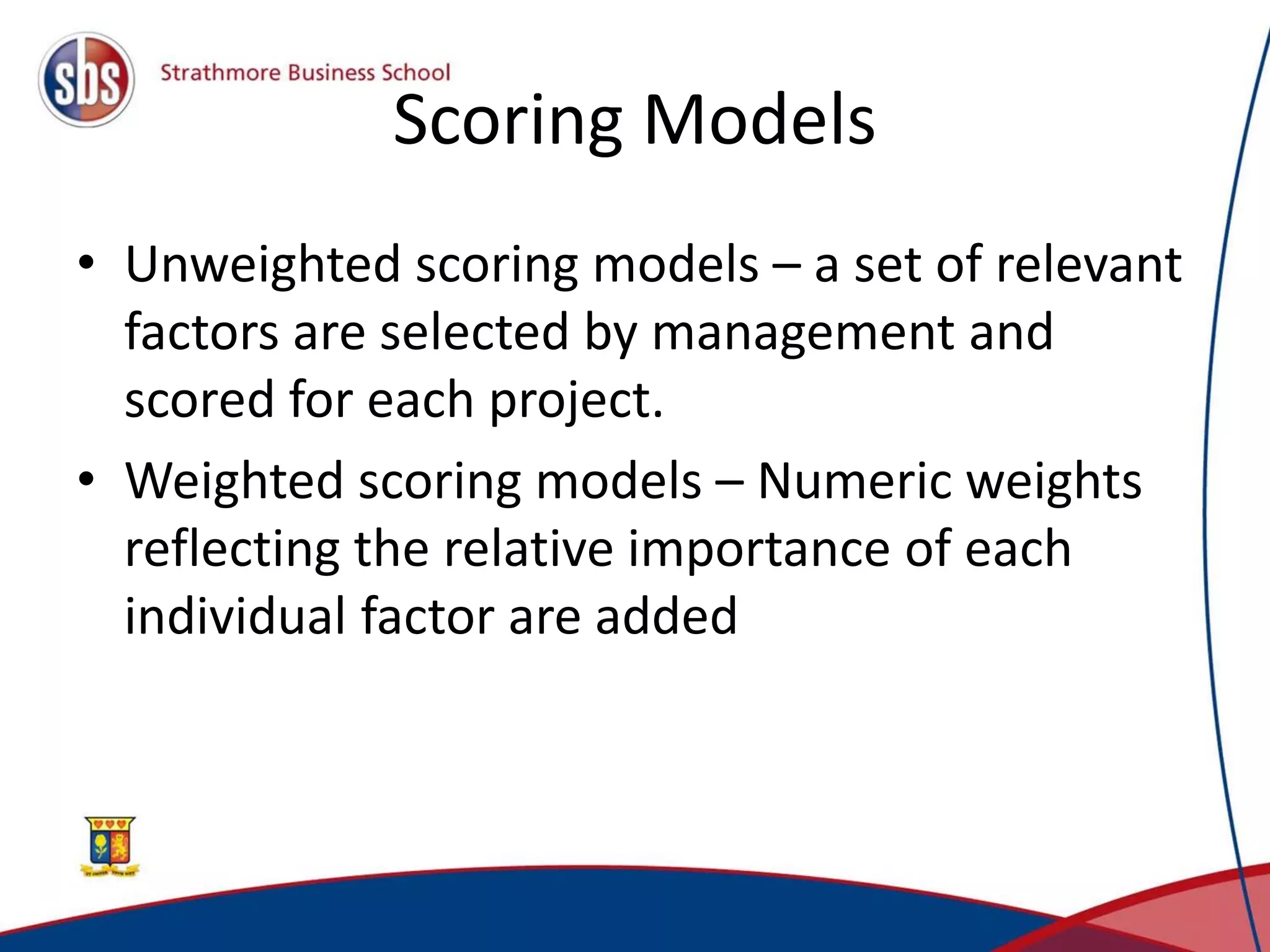
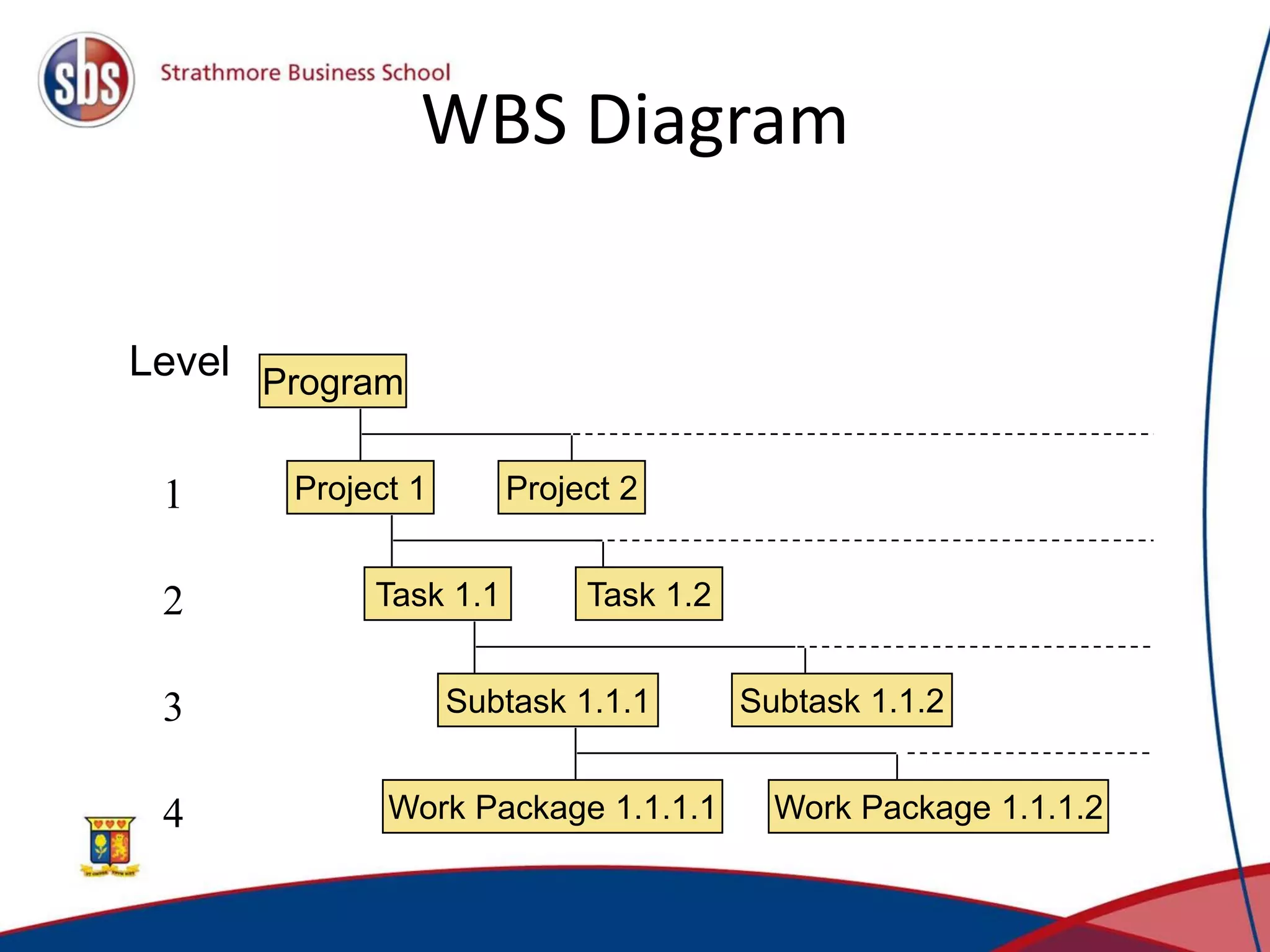
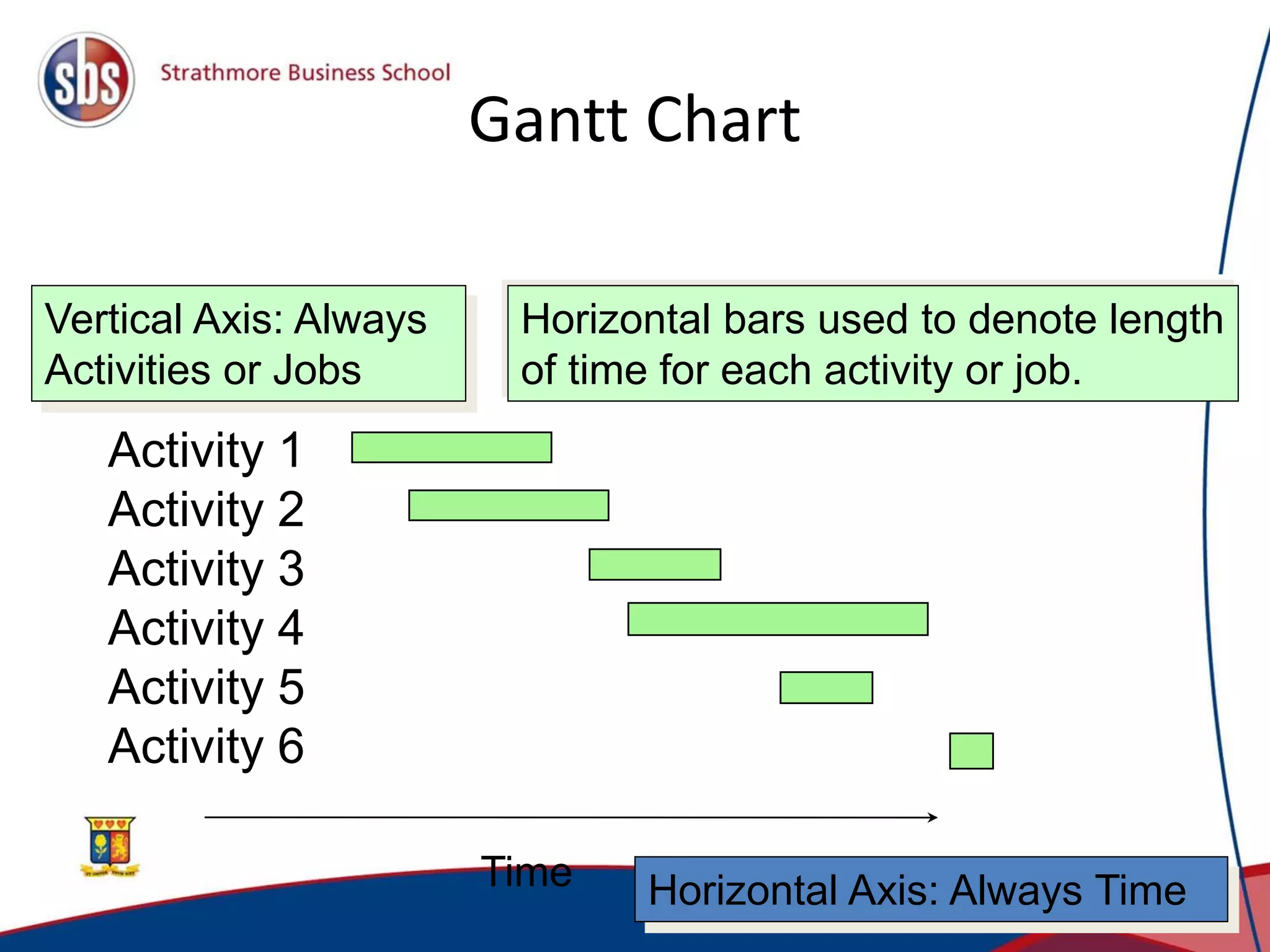
Project management involves planning, directing, and controlling resources to complete projects on time and within budget. There are three main types of project organization structures: pure project, functional project, and matrix project. A matrix project blends aspects of pure and functional projects by utilizing resources from different functional areas while allowing the project manager to decide tasks and timing. Key project management techniques include work breakdown structures to plan tasks hierarchically, network models to identify critical paths, and Gantt charts to schedule activities visually over time.