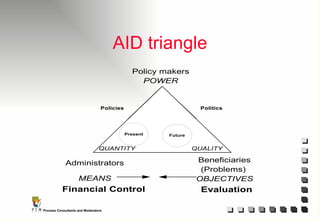
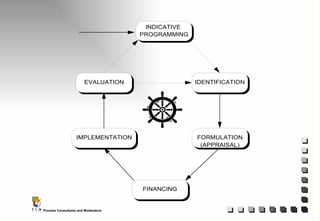
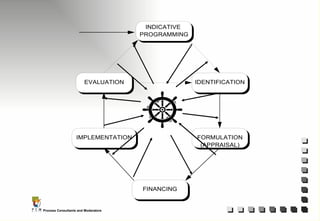
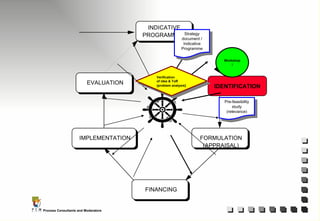
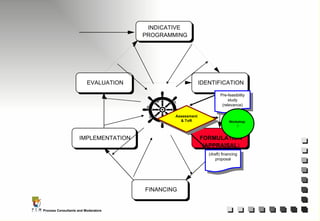
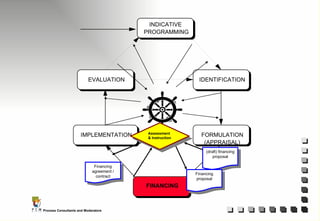
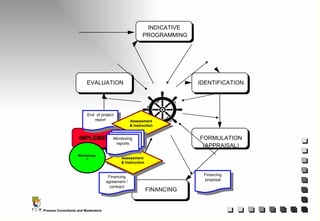
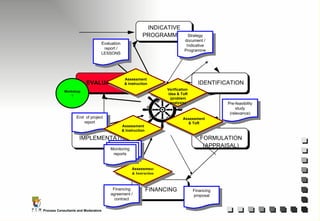
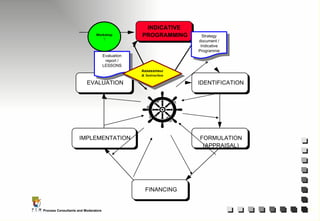
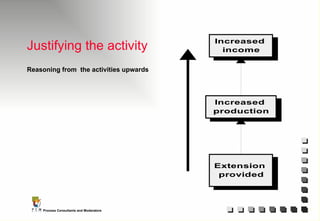
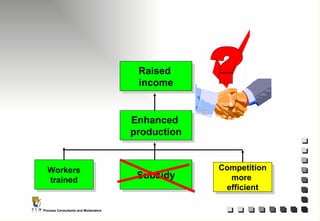
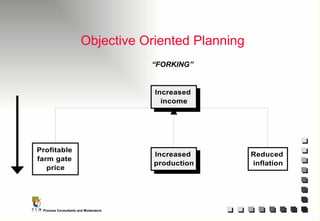
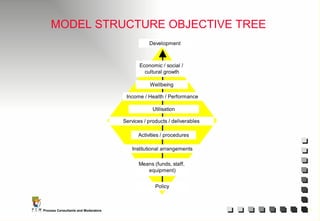
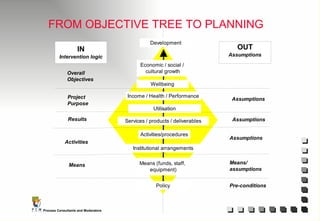
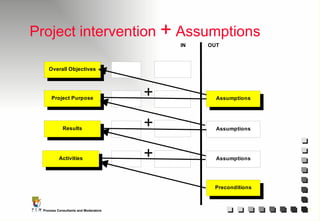
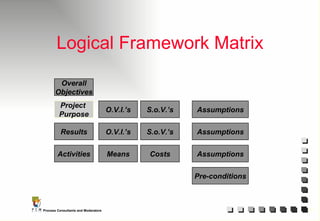
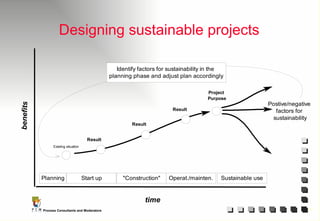
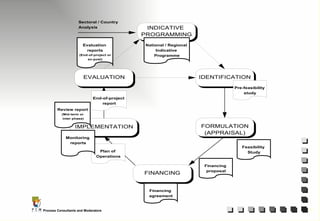
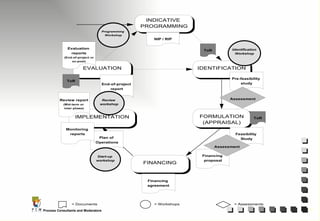
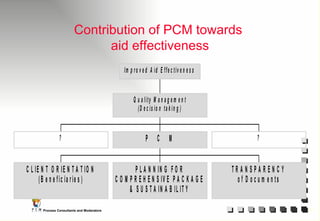
The document outlines the principles and practices of Programme Cycle Management (PCM), emphasizing the importance of improving project management to reduce confusion and enhance stakeholder involvement. It details the various phases of PCM, from identification and financing to implementation and evaluation, while highlighting the significance of sustainability and transparency throughout the process. The document also encourages the adoption of common methods and standards to increase aid effectiveness and support project objectives.