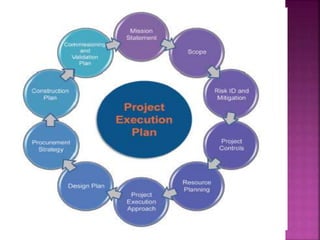
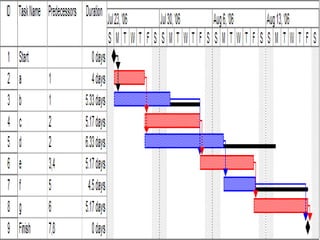
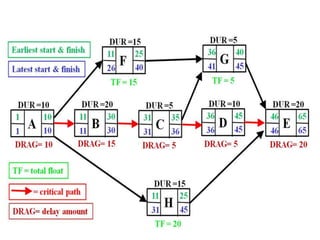
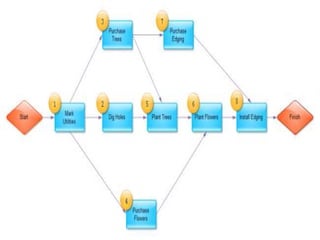
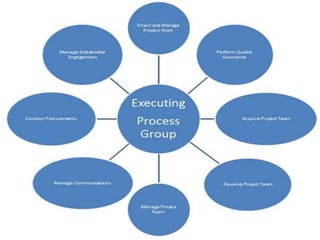
The project execution plan (PEP) establishes how projects will be executed, monitored, and controlled. It communicates project objectives and how they will be achieved. The major elements of a PEP are scope definition, goal statements, quality/technical specifications, resource allocation, and project scheduling. Scope definition clearly defines the project goals. Goal statements list deliverables, milestones, and risks. Quality specifications use precise definitions and measurable standards. Resource allocation identifies needed staff, money, and time. Project scheduling divides work into chunks and sets time-bound milestones, accounting for risks and exceptions to plans.