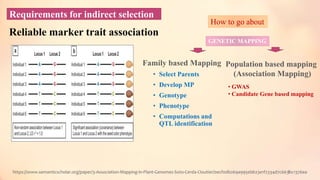
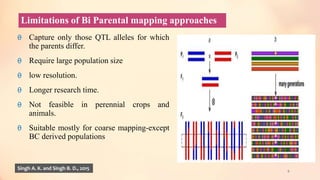
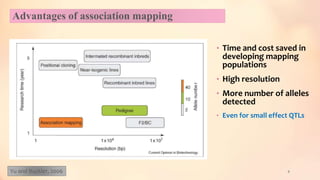
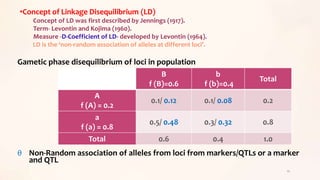
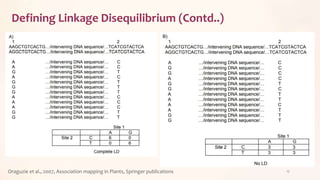
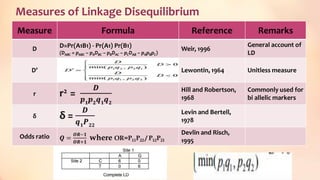
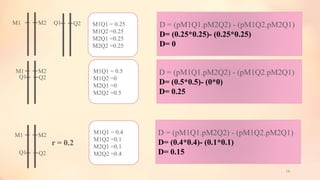
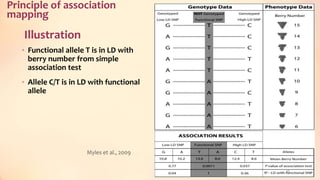
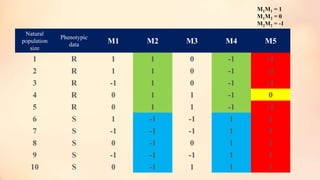
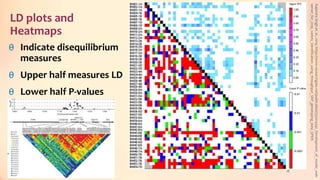
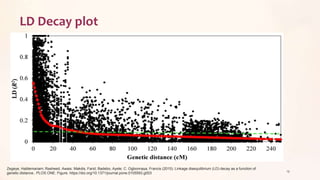
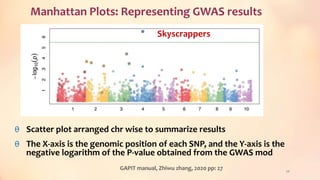
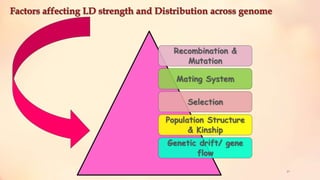
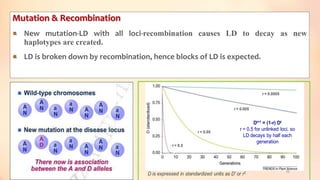
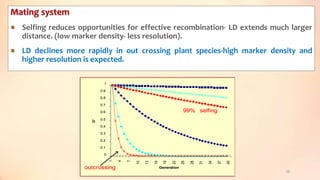
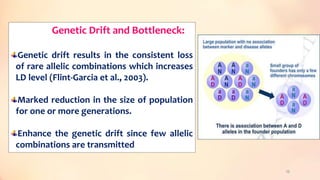
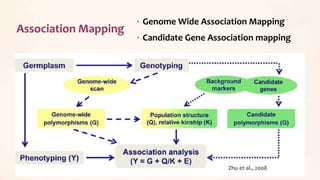
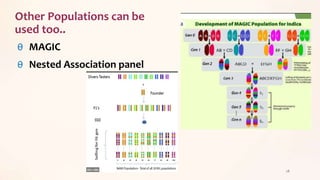
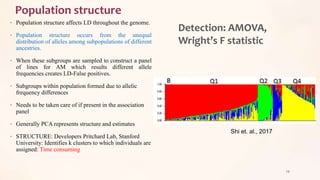
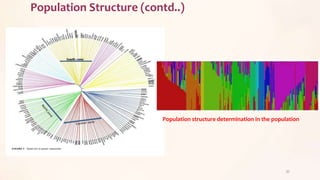
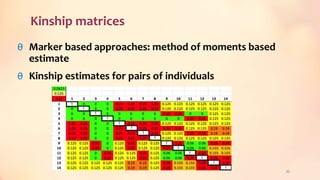
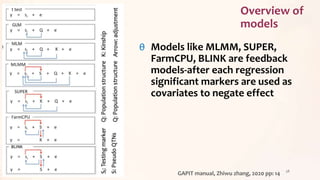
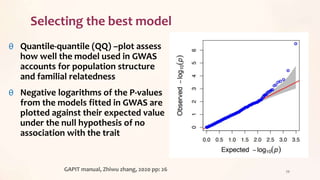
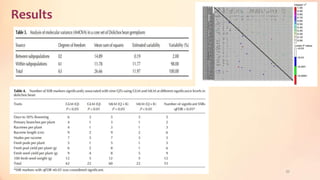
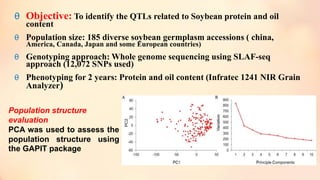
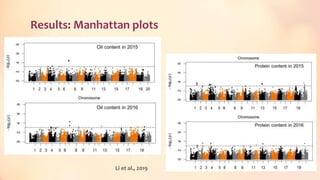
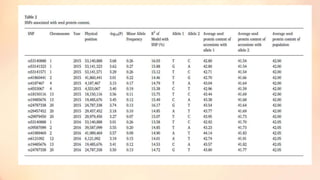
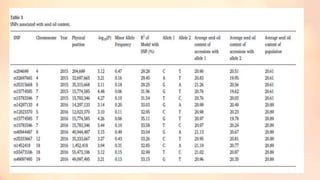
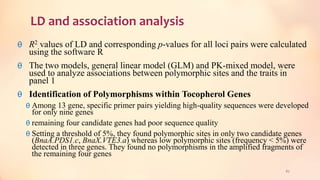
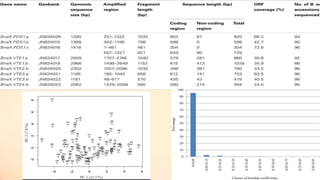
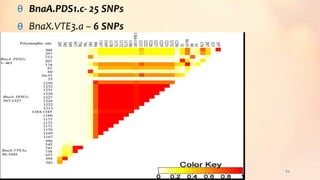
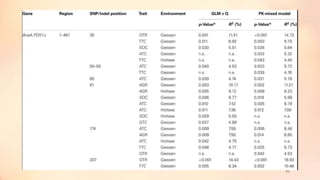
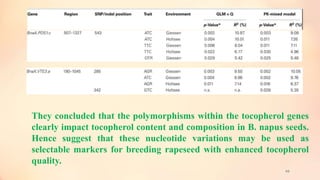
This document discusses association mapping for crop improvement. It explains that association mapping exploits historical recombination events in populations to map quantitative trait loci with greater precision than family-based linkage analysis. Association mapping can be applied to diverse populations and detect more alleles than bi-parental mapping. Genome-wide association studies allow for high-resolution mapping of traits down to the sequence level by leveraging linkage disequilibrium. Statistical methods must account for population structure and kinship to avoid false positives in association analyses.