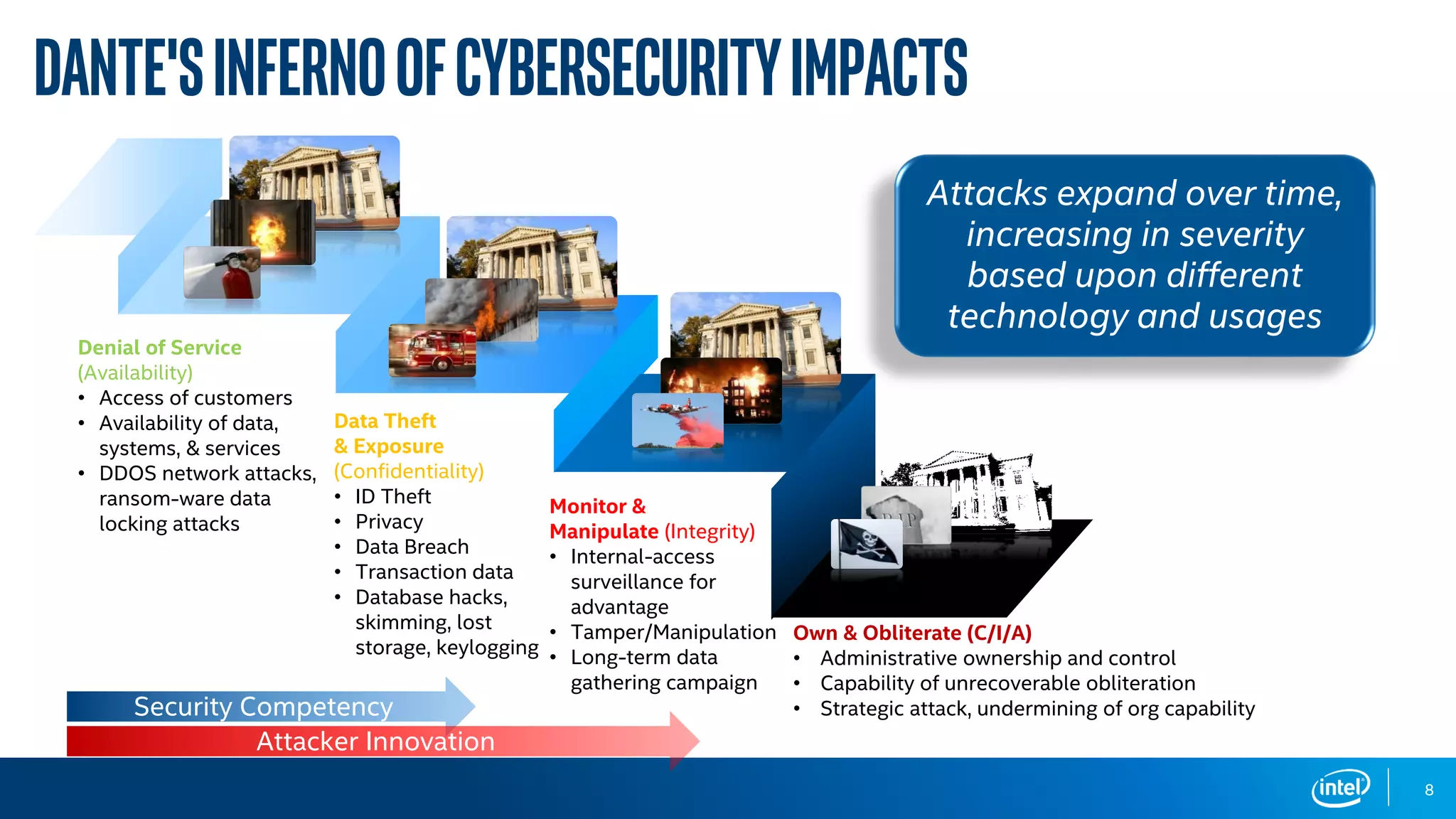
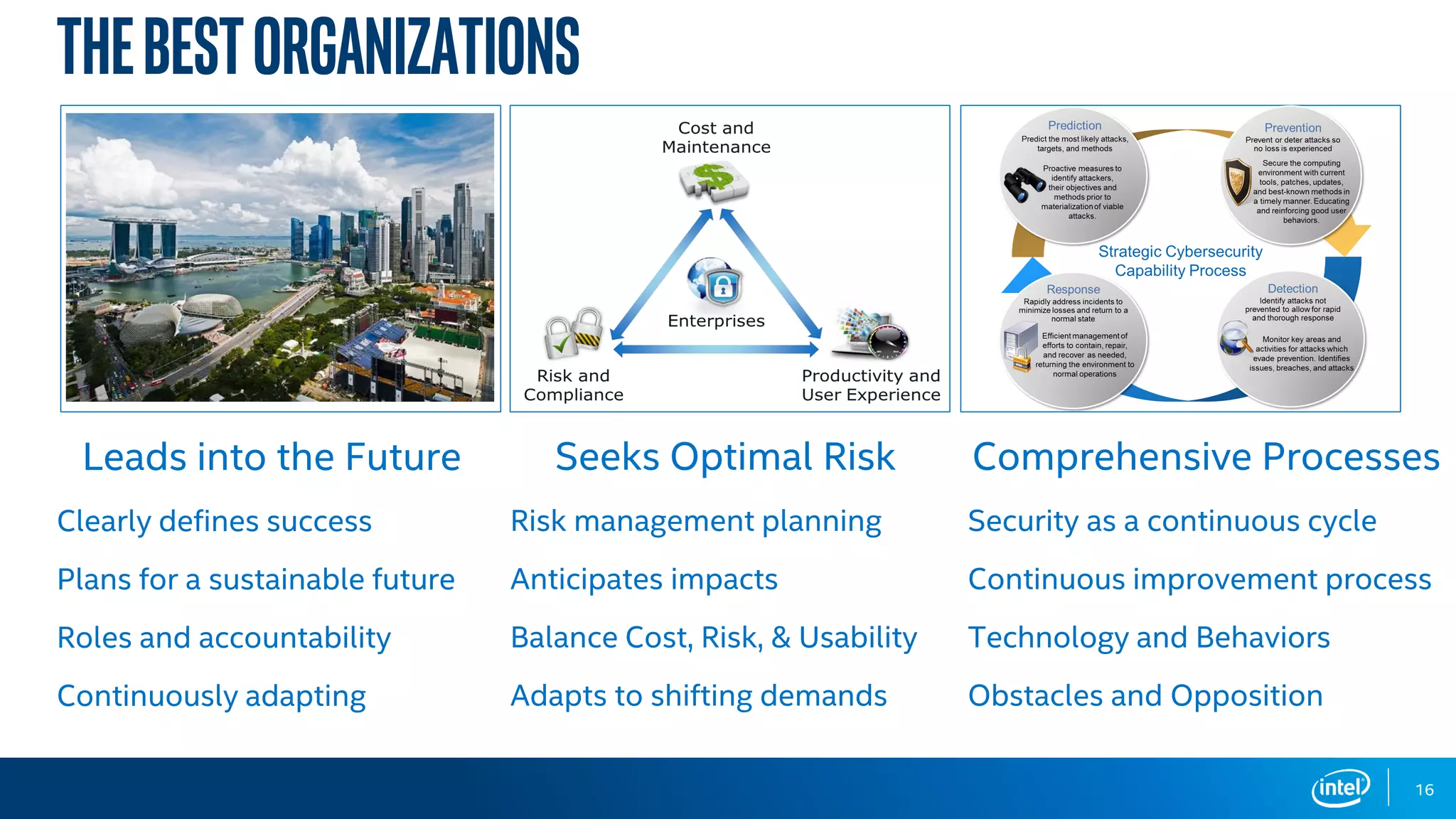
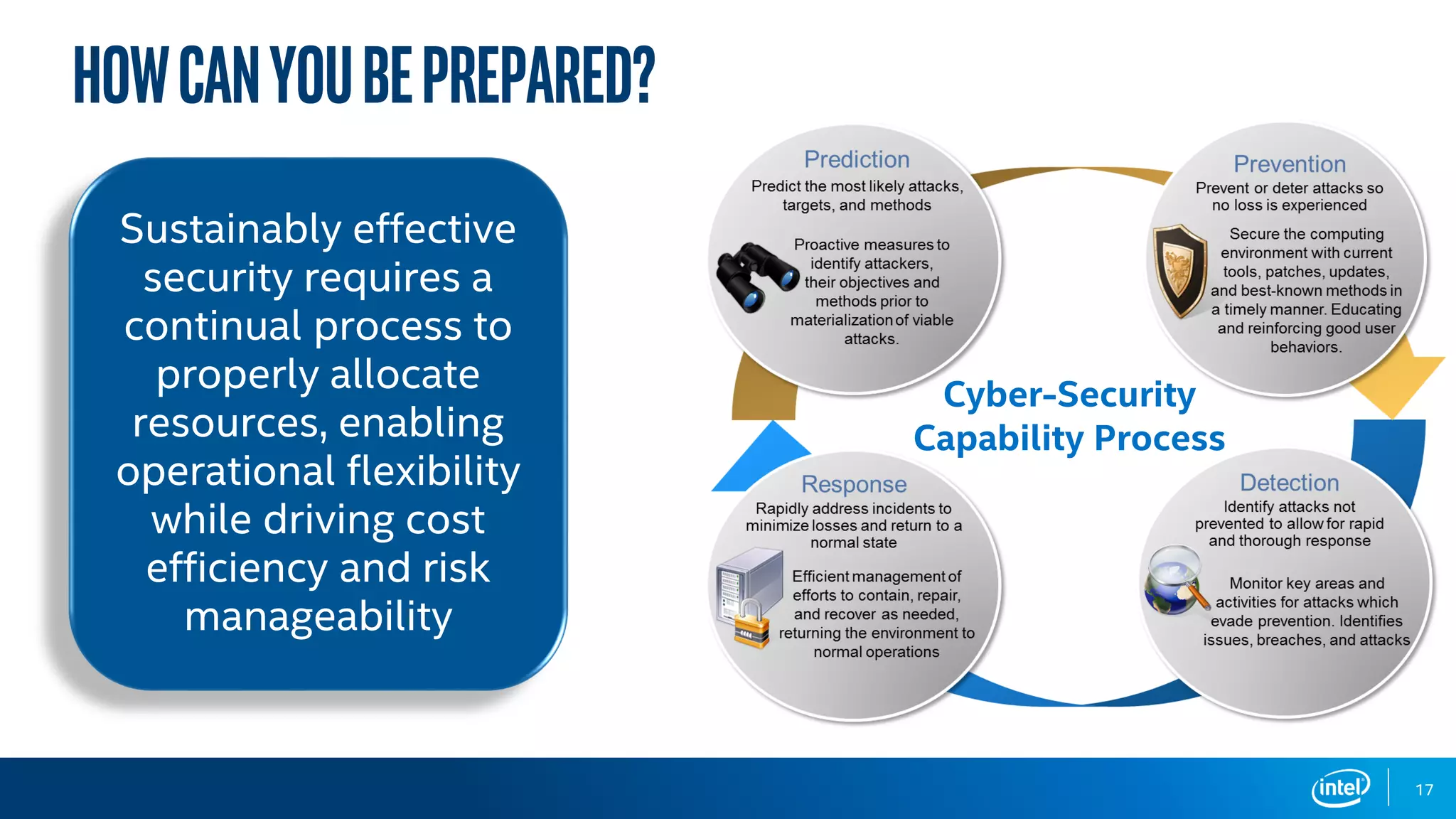
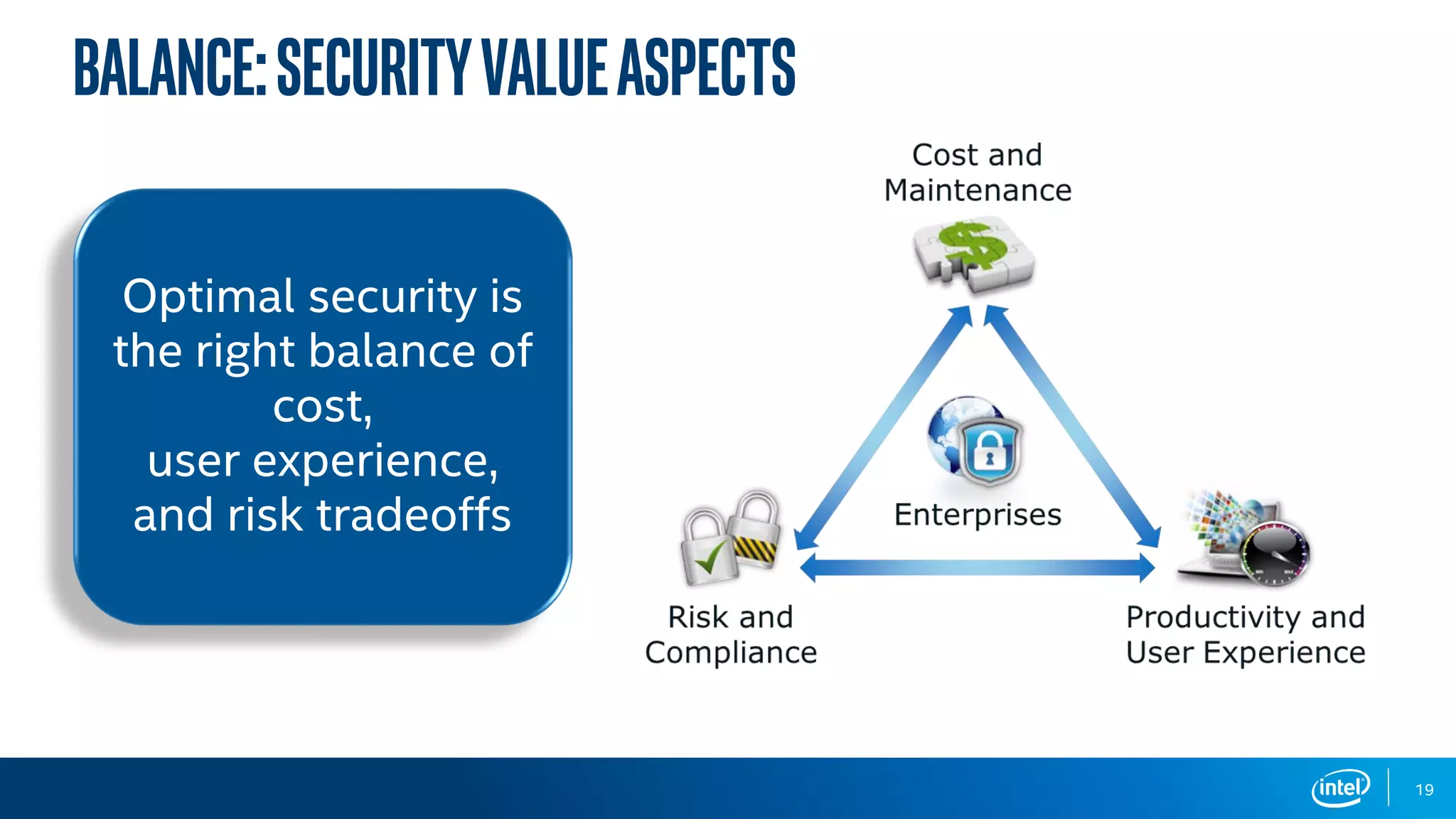
The document discusses the various cybersecurity threats faced by organizations, particularly in the education sector, highlighting the significant risks posed by data breaches, malware, and cybercrime. It emphasizes the need for robust leadership, preparation, and continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices, as well as the importance of adapting to technological advancements and evolving threats. The document concludes by urging organizations to prepare proactively against these threats to avoid crises.