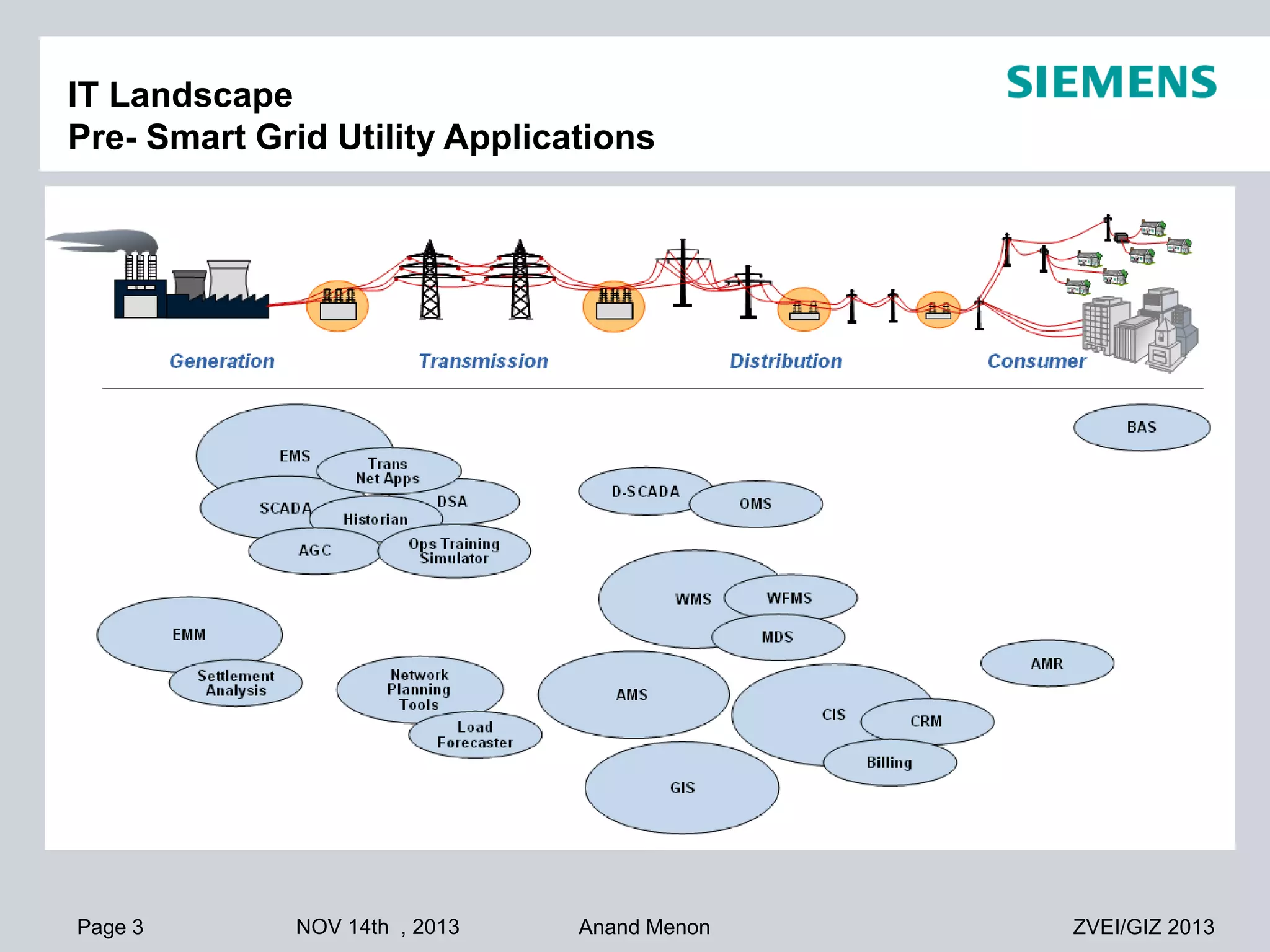
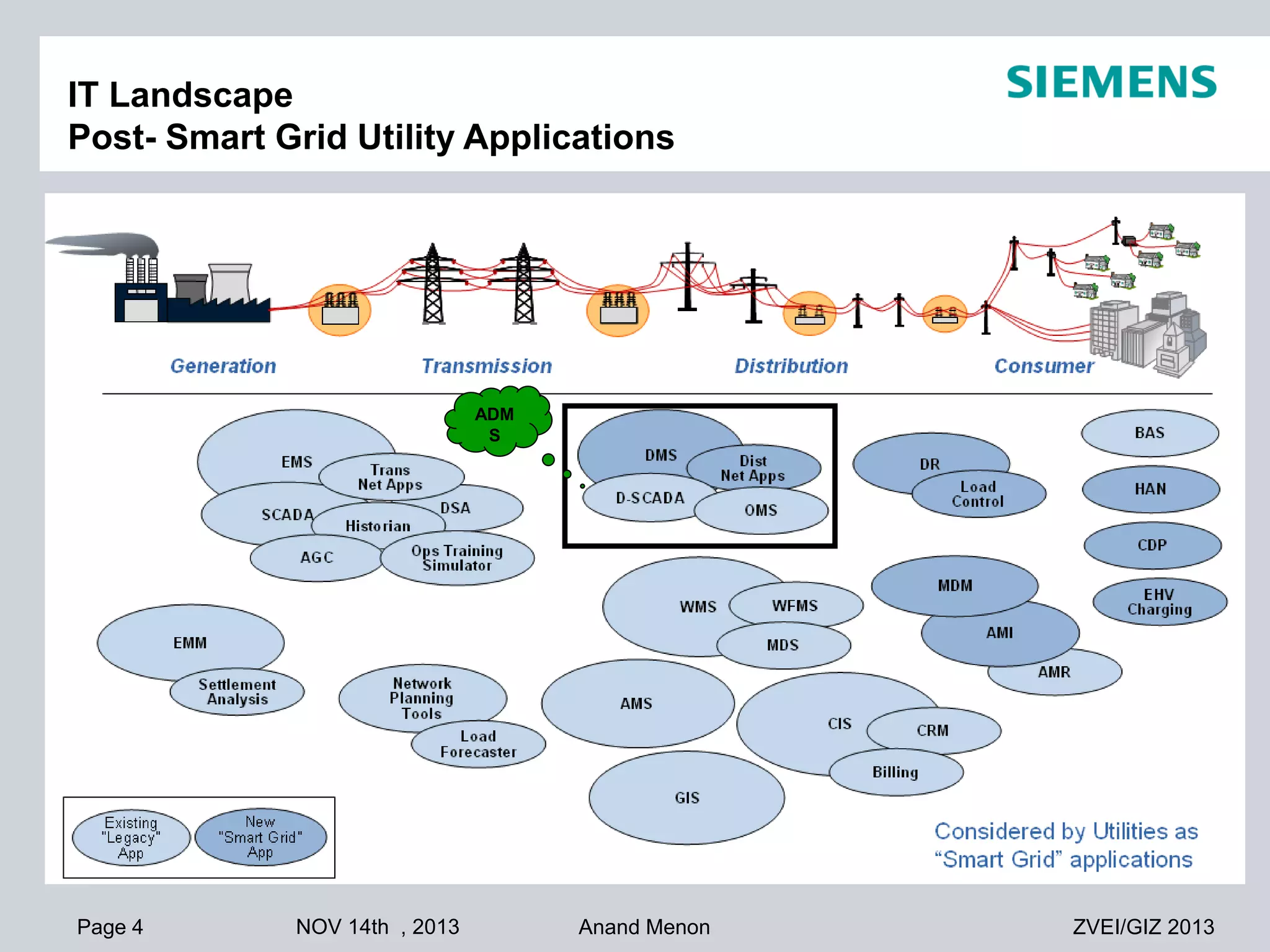
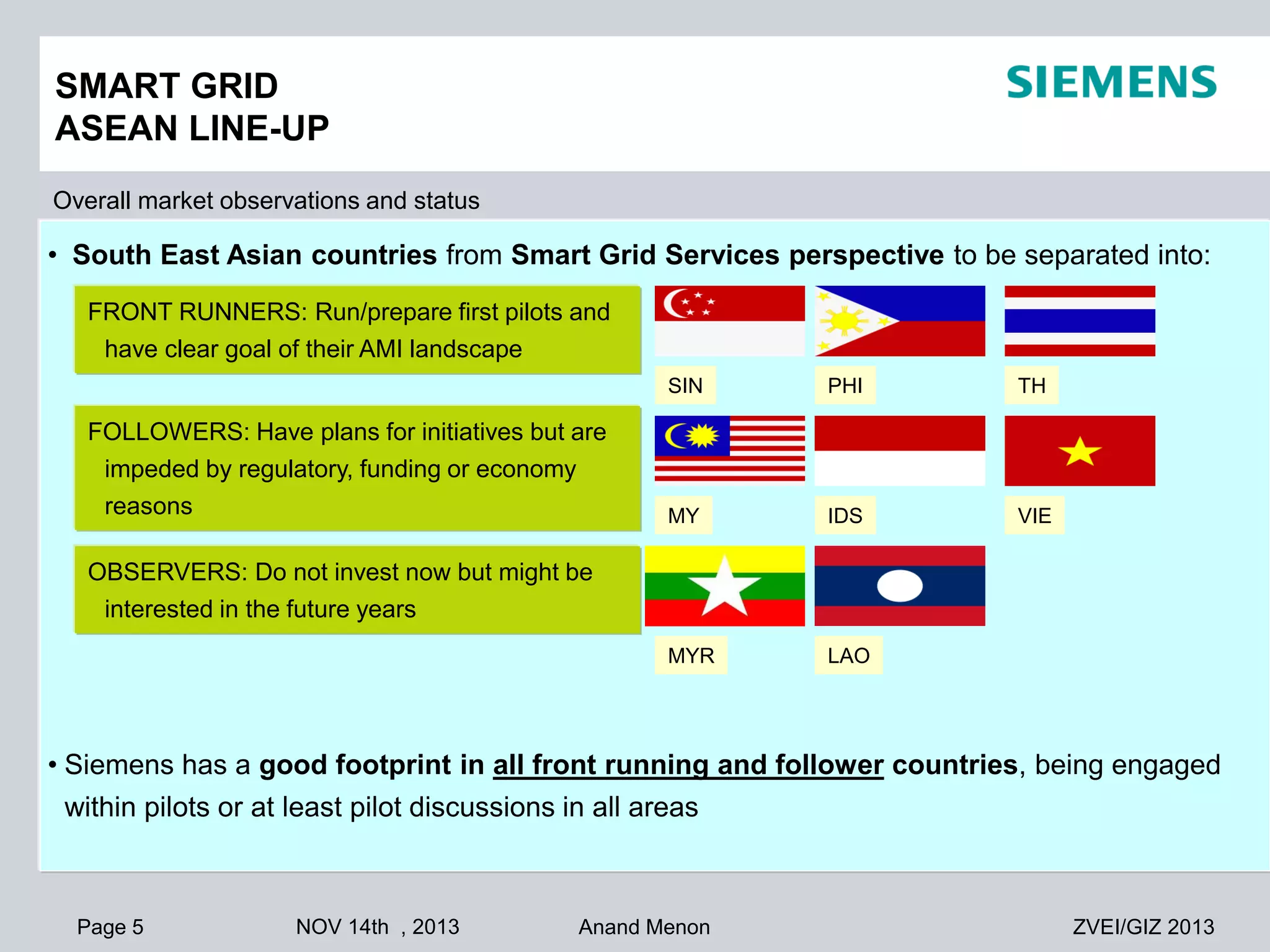
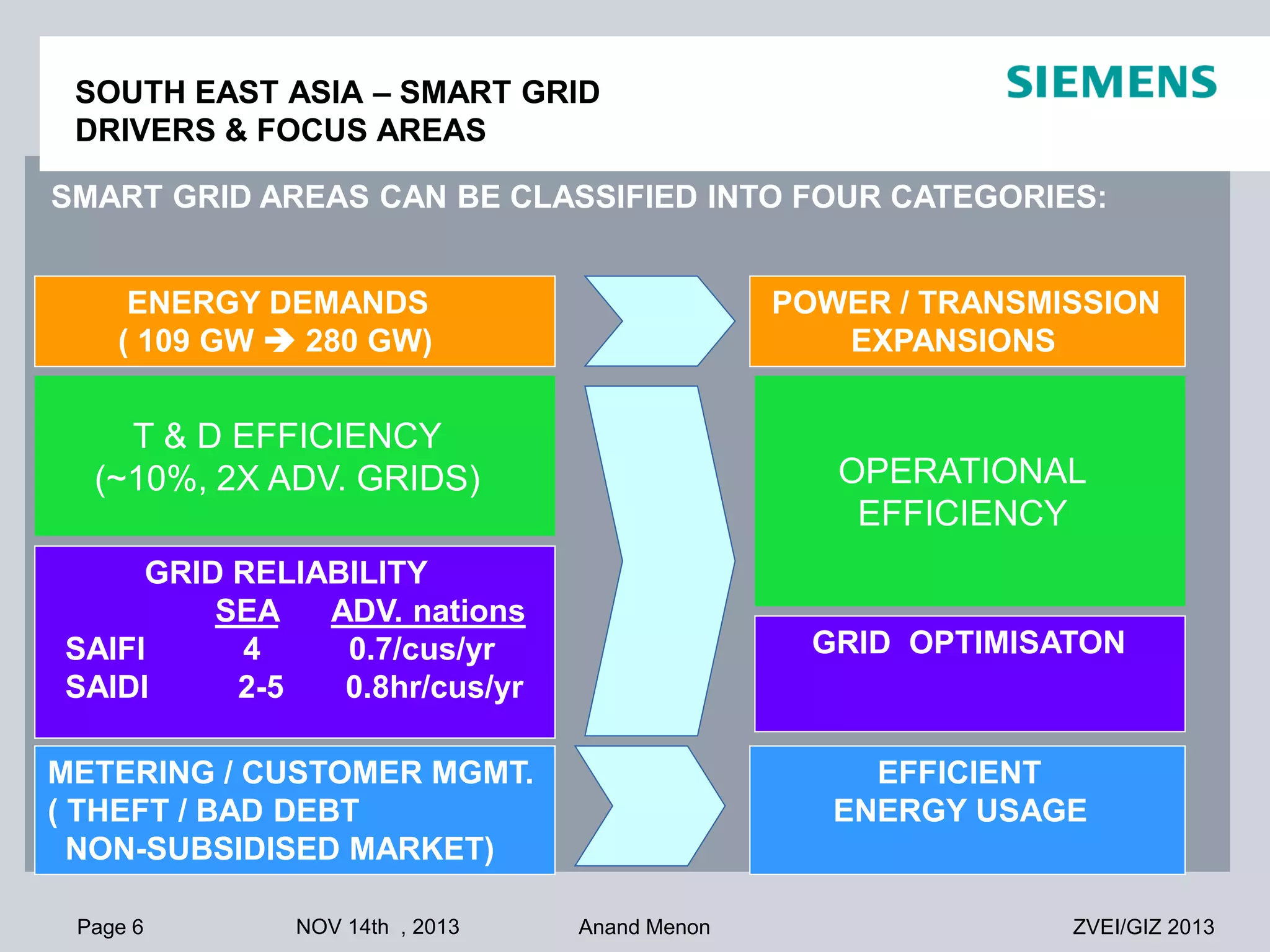
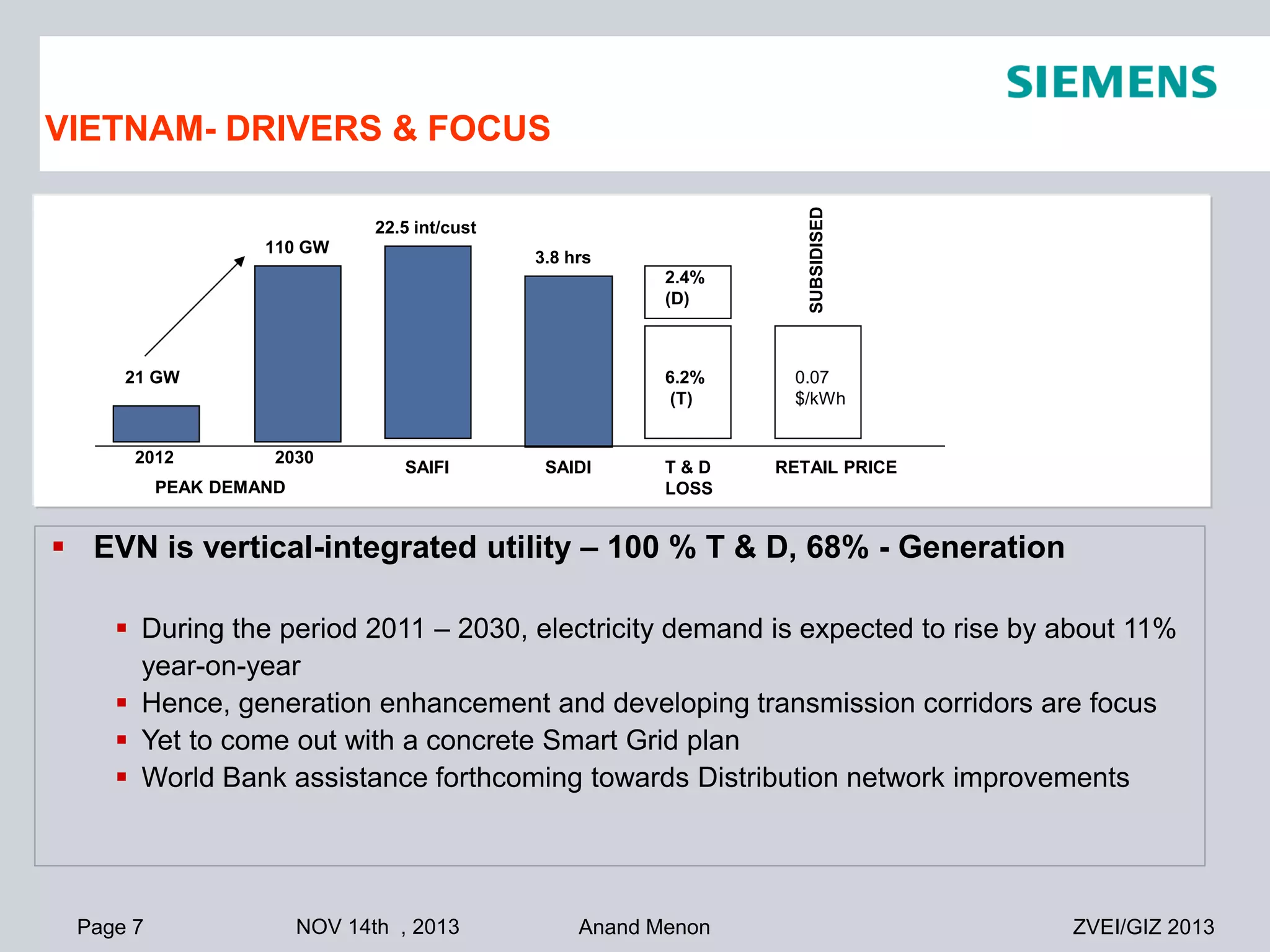
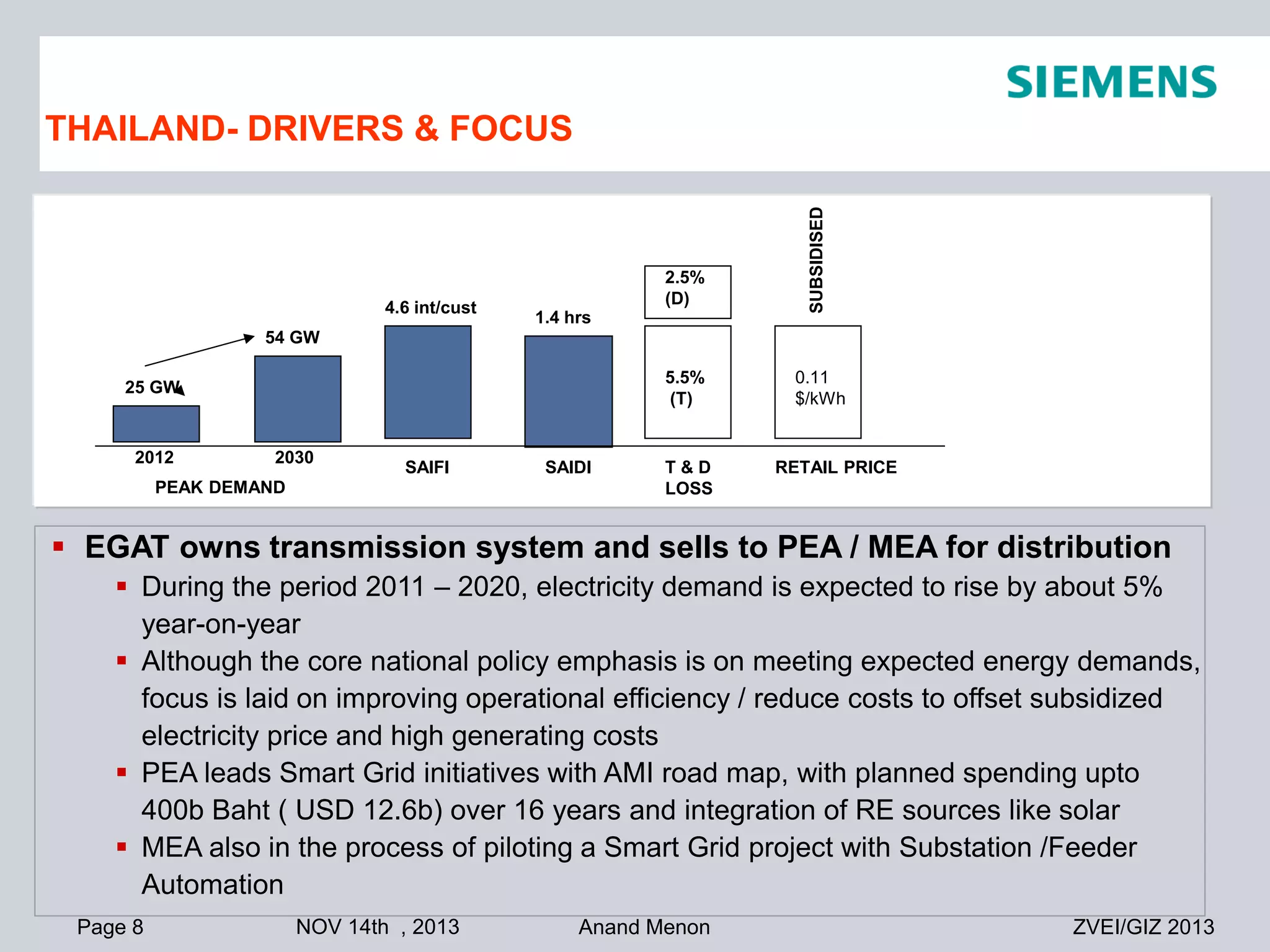
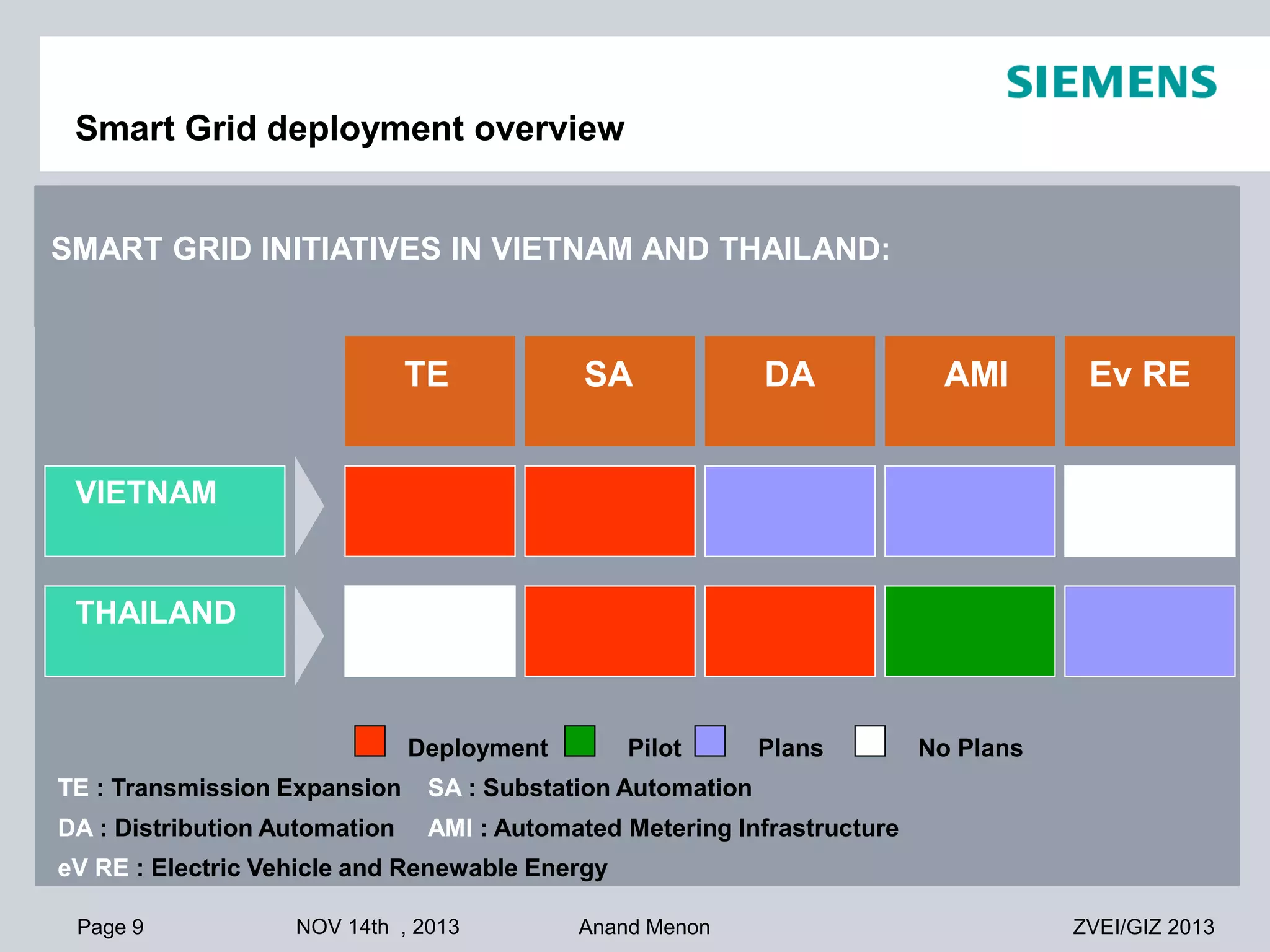
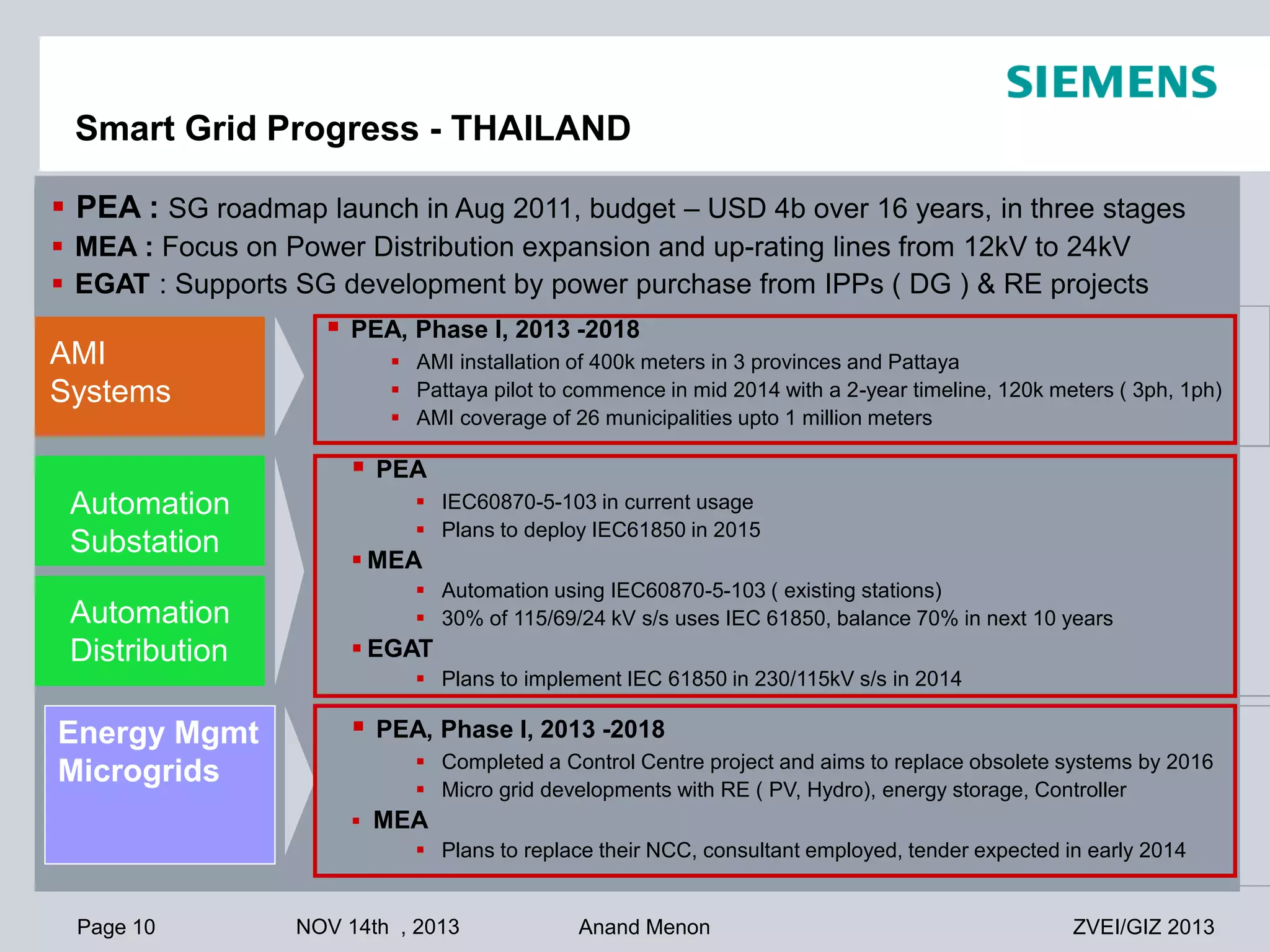
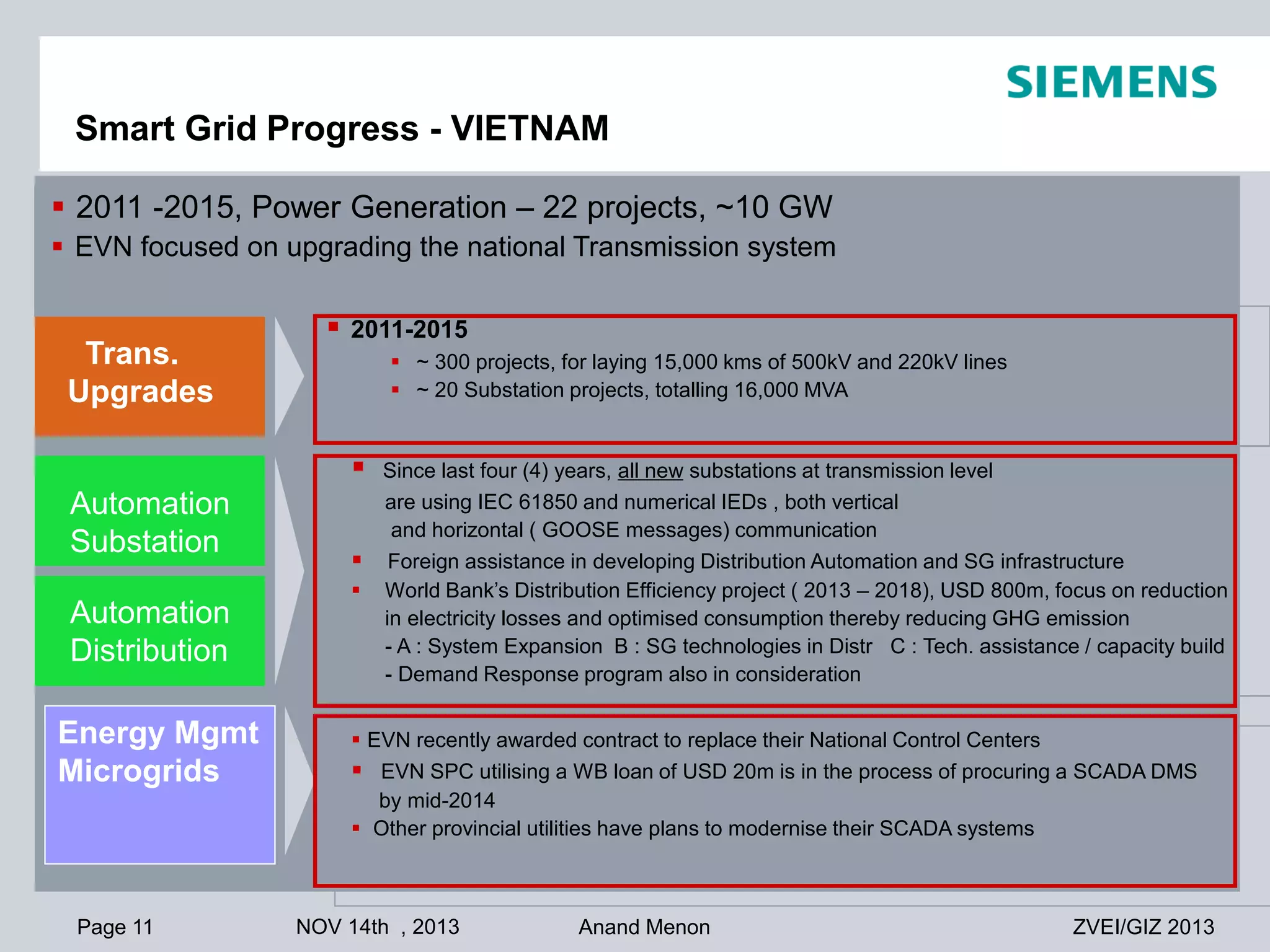
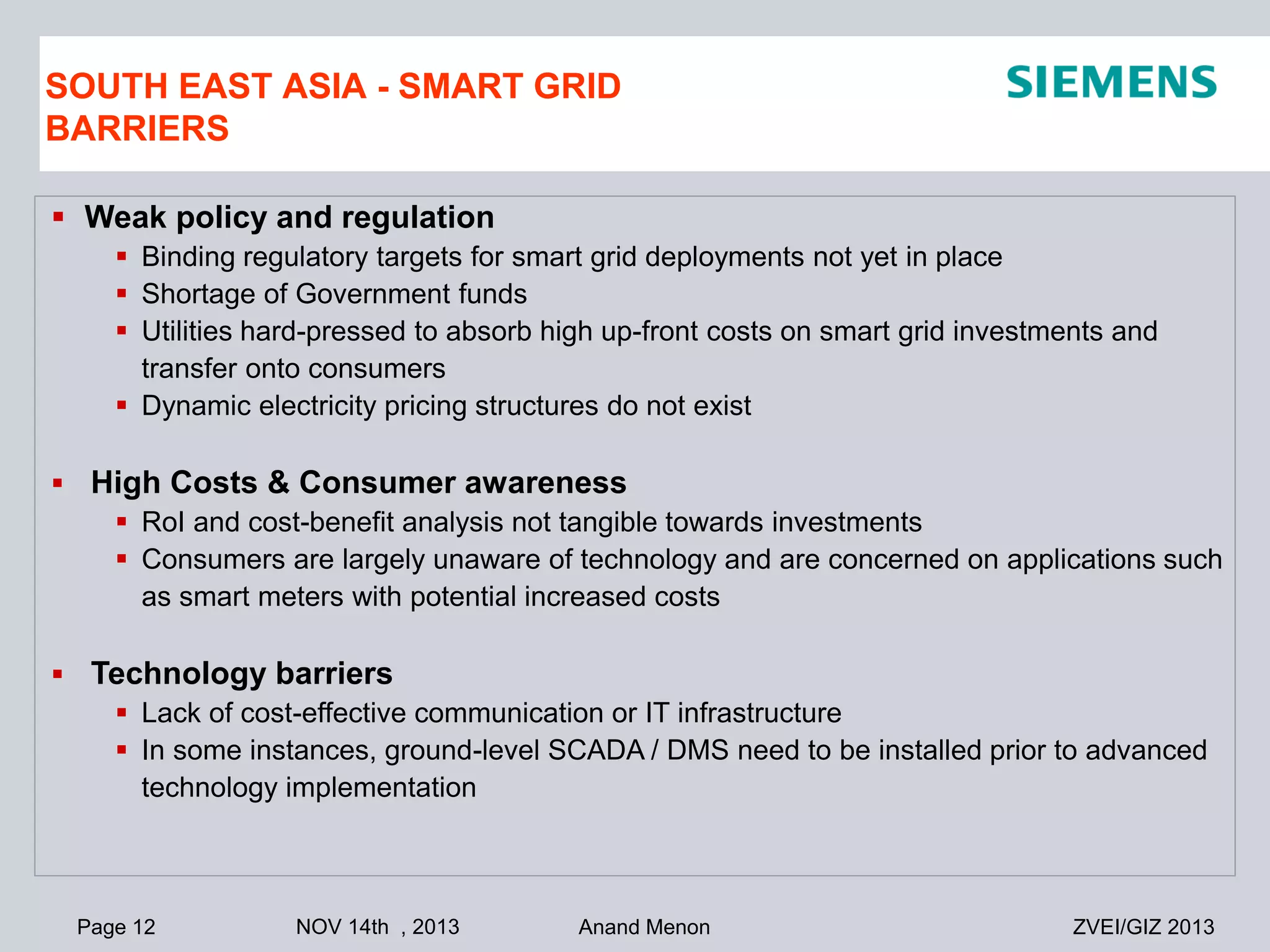
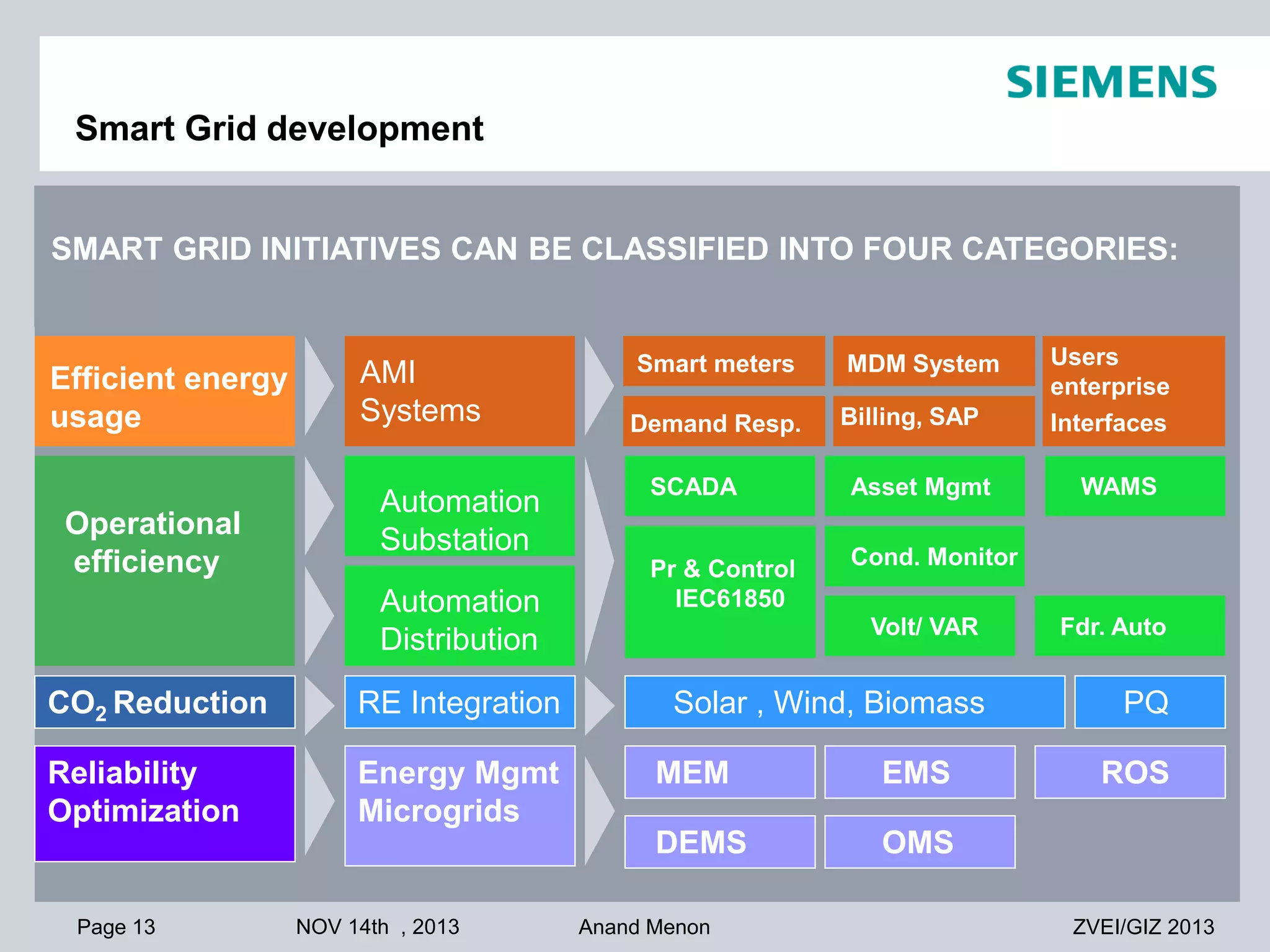
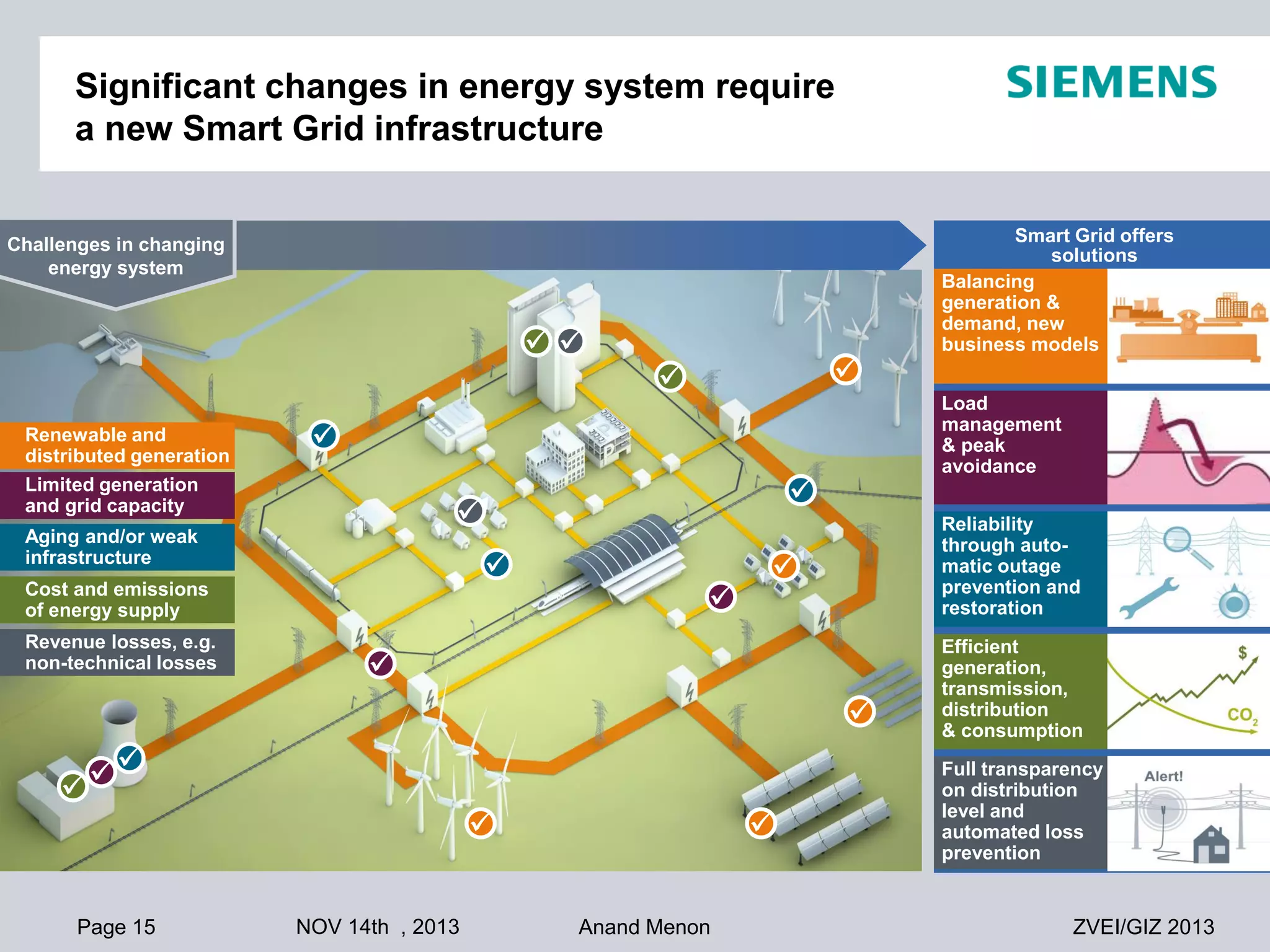
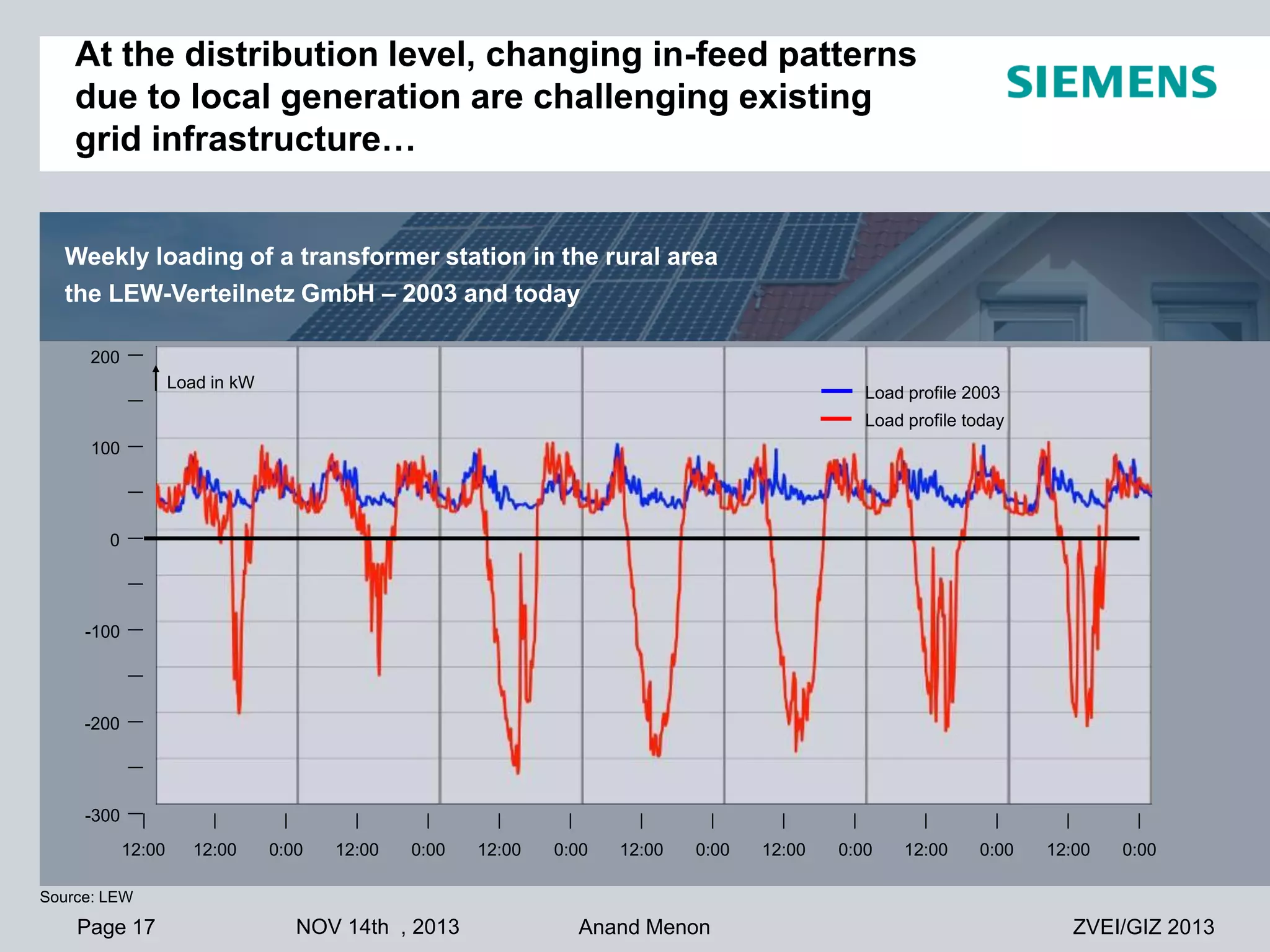
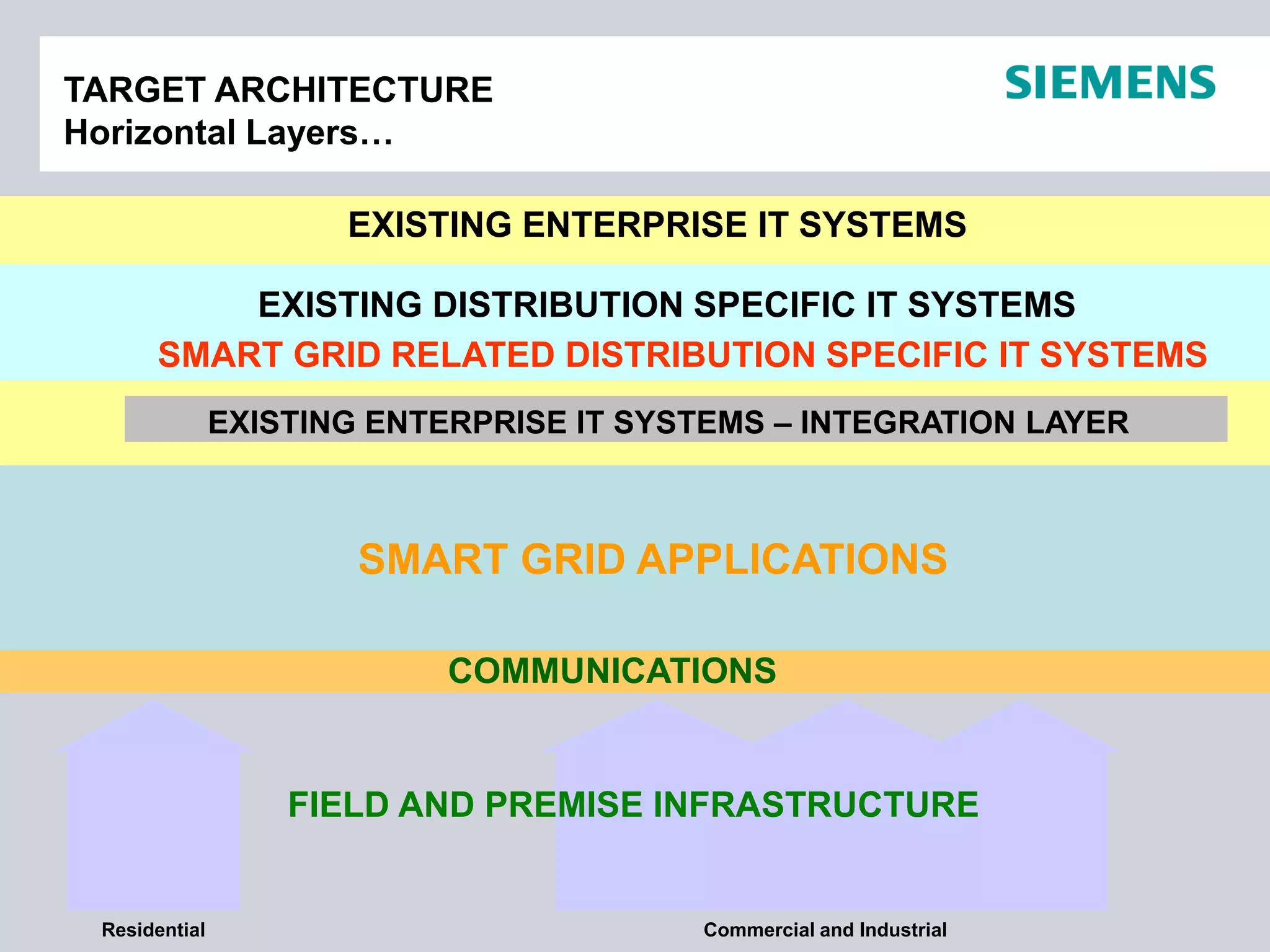
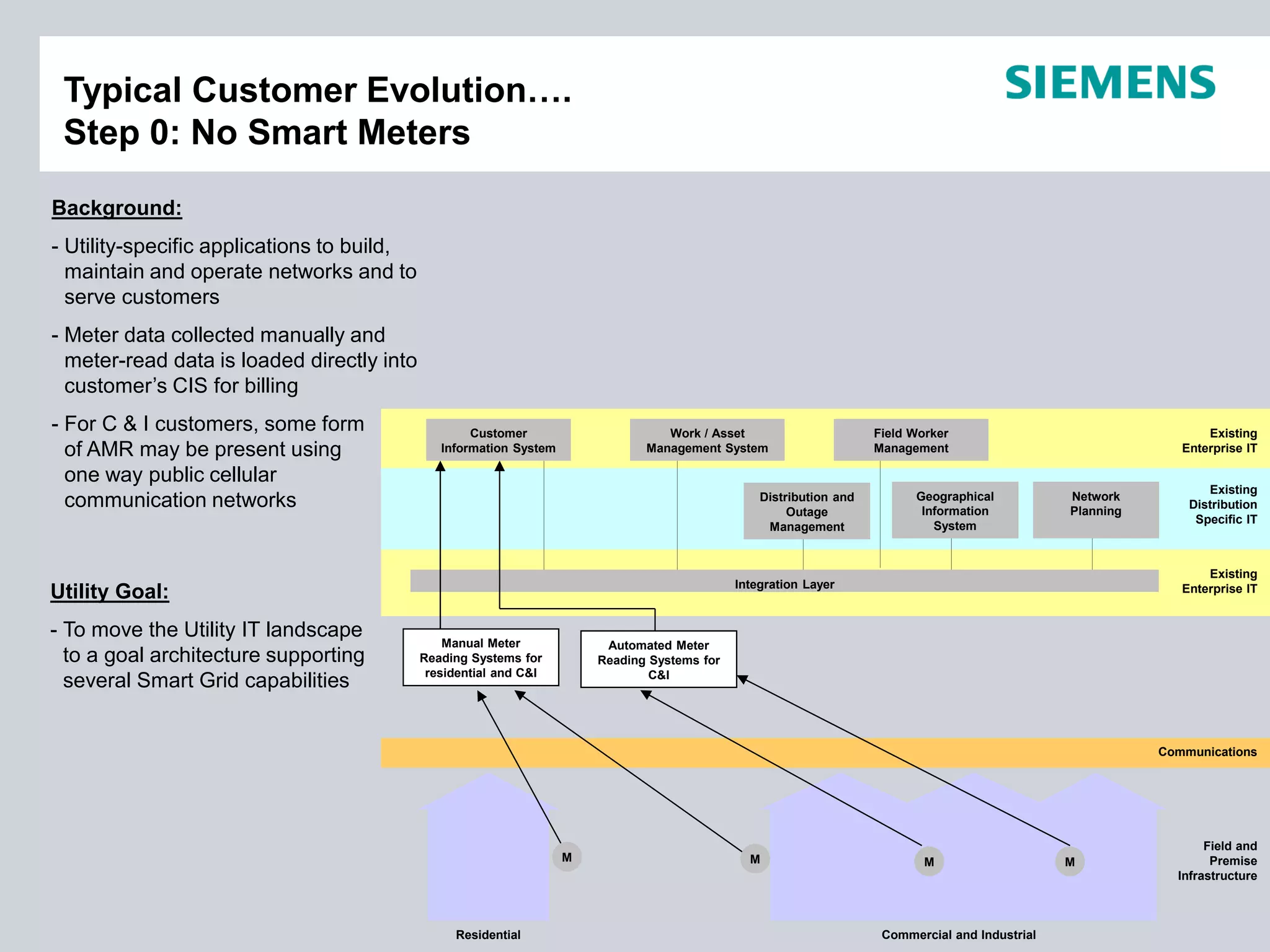
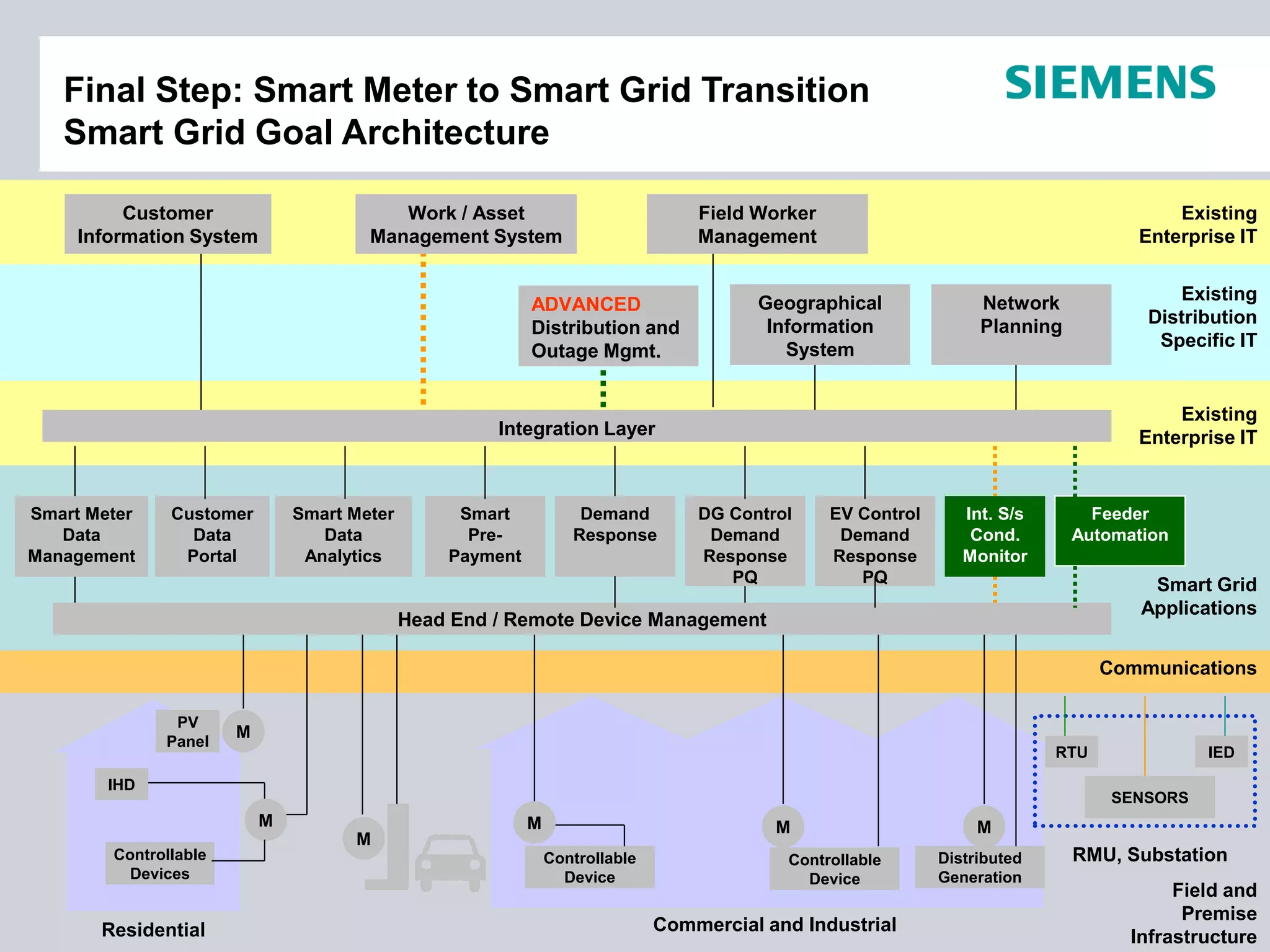
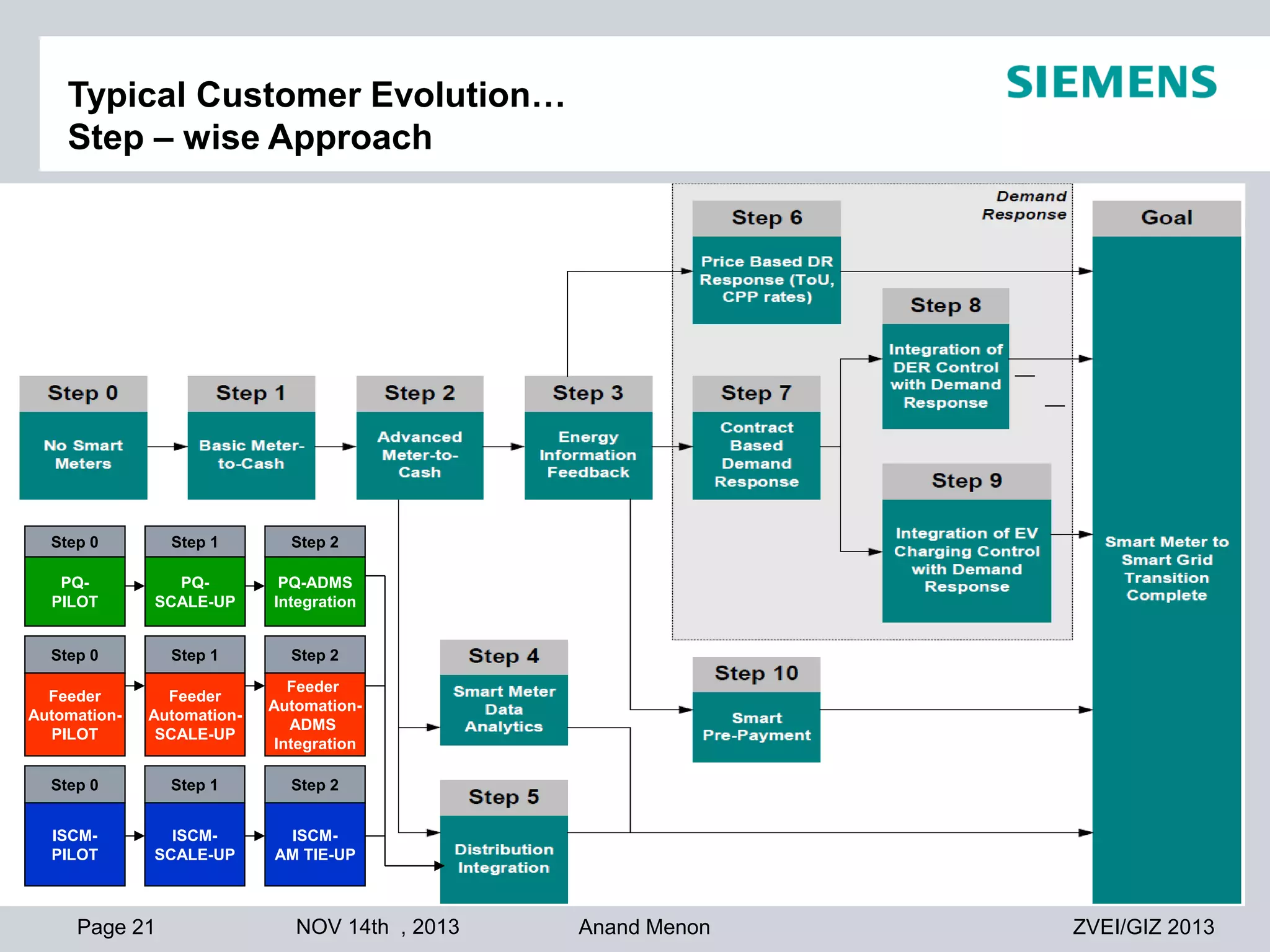
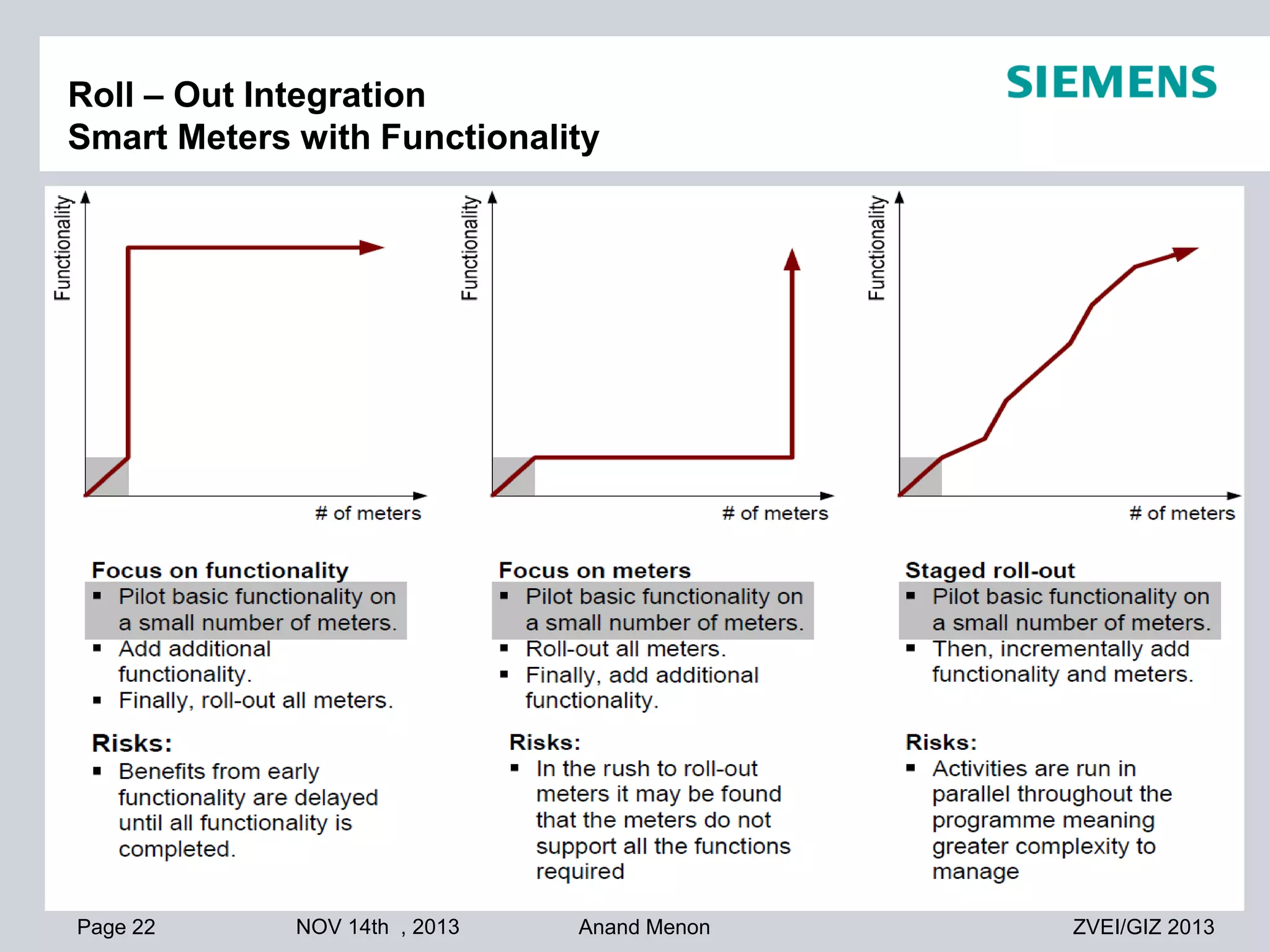
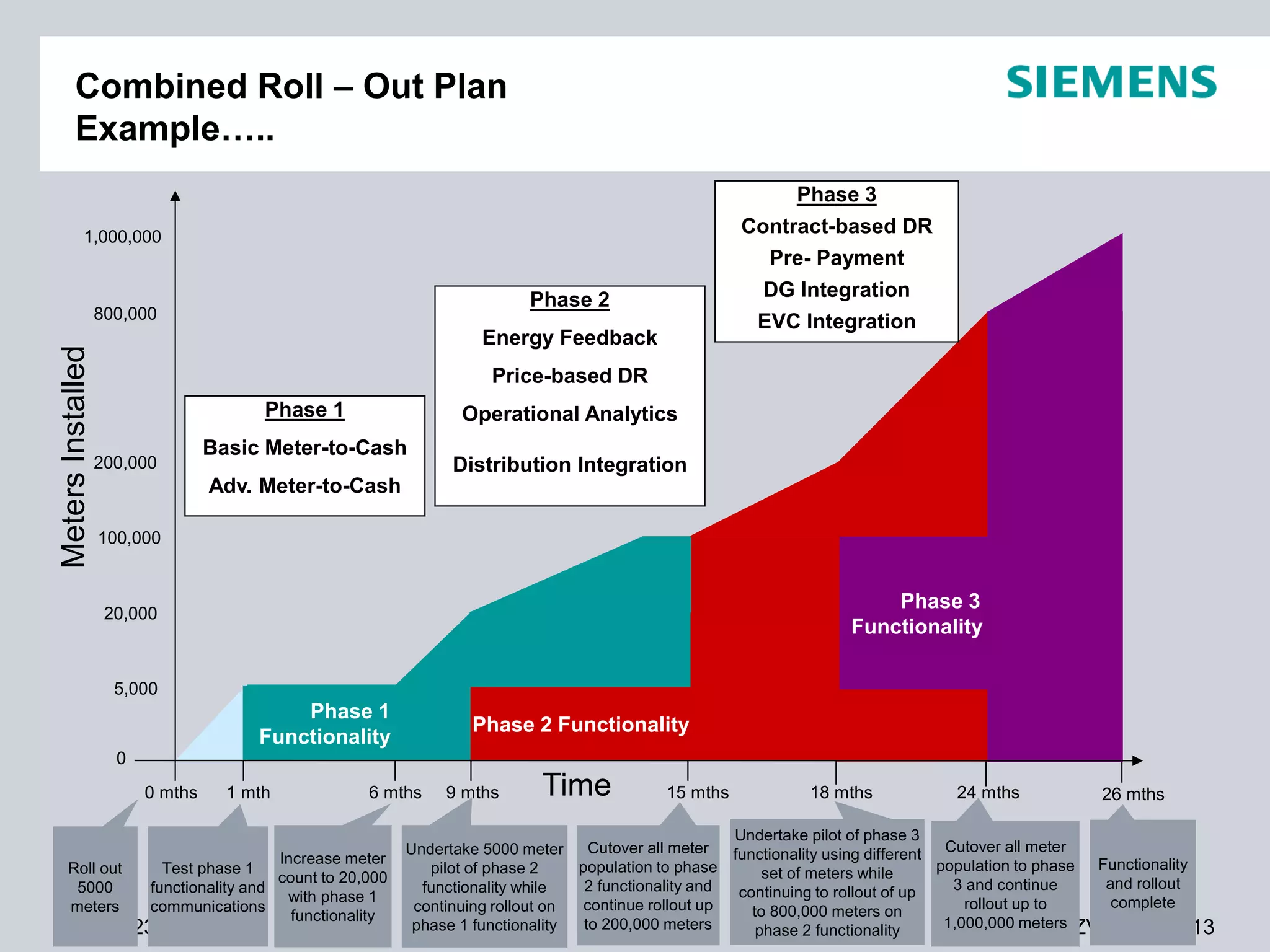
This document summarizes smart grid initiatives in Vietnam and Thailand. It finds that both countries are focused on meeting increasing energy demands through transmission expansions and improving operational efficiency. Thailand's PEA leads smart grid initiatives with a roadmap including AMI deployment. Vietnam lacks a clear smart grid plan but is working to upgrade transmission infrastructure with foreign assistance. Barriers to smart grid development include weak policies, high costs, and lack of technical infrastructure. The document outlines typical approaches to phased smart grid deployments integrating meters, distribution automation, and enterprise systems.