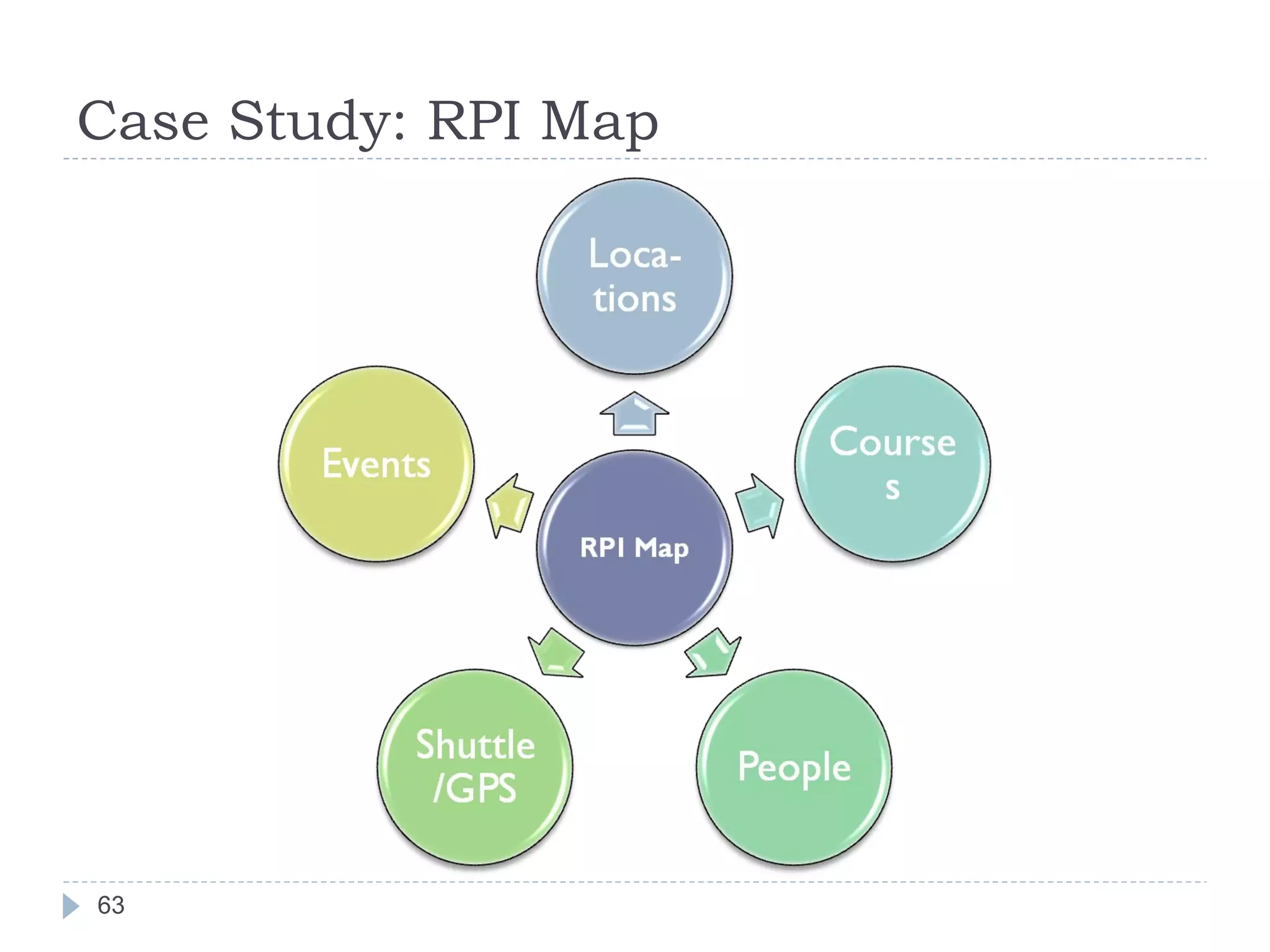
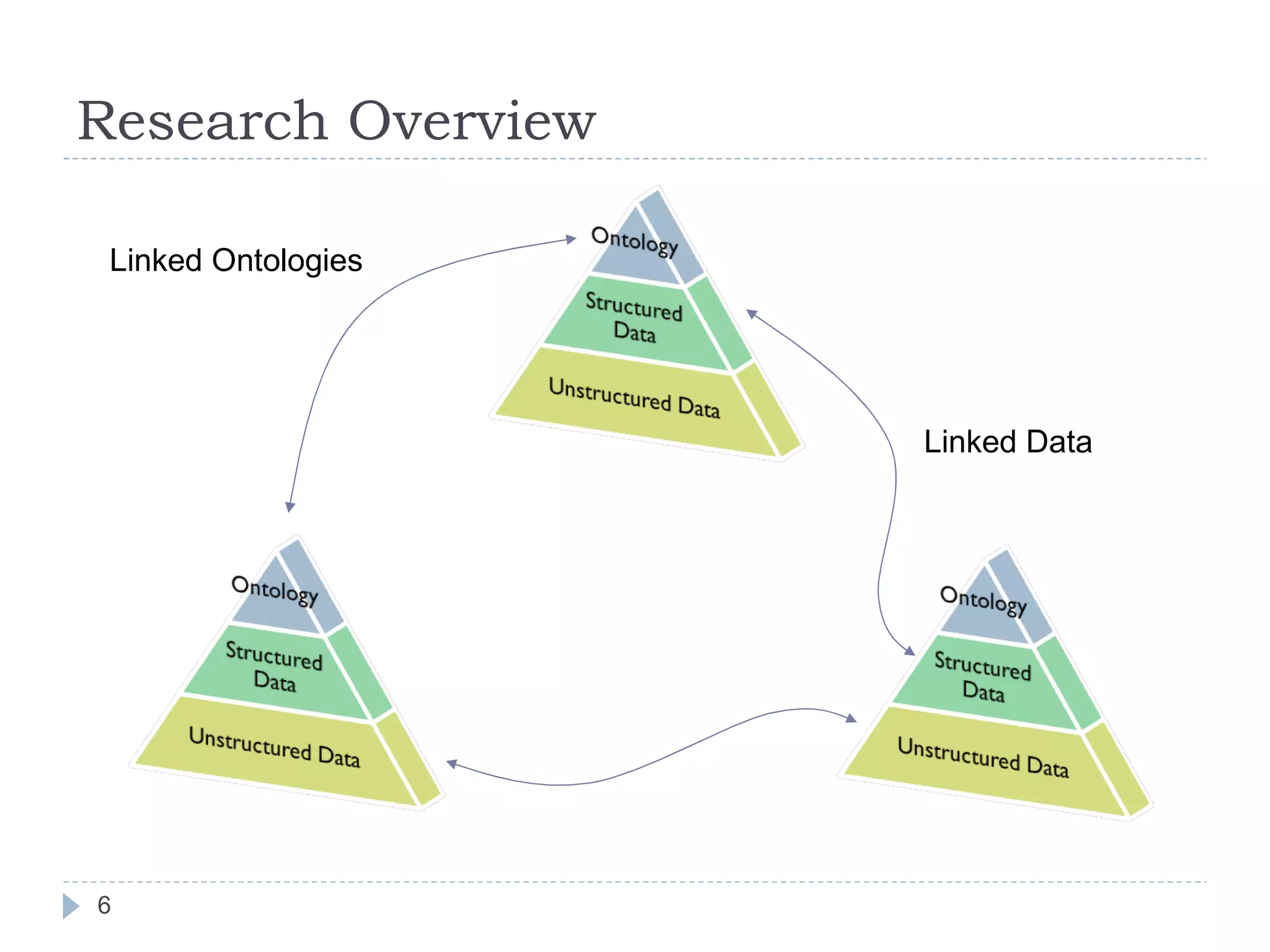
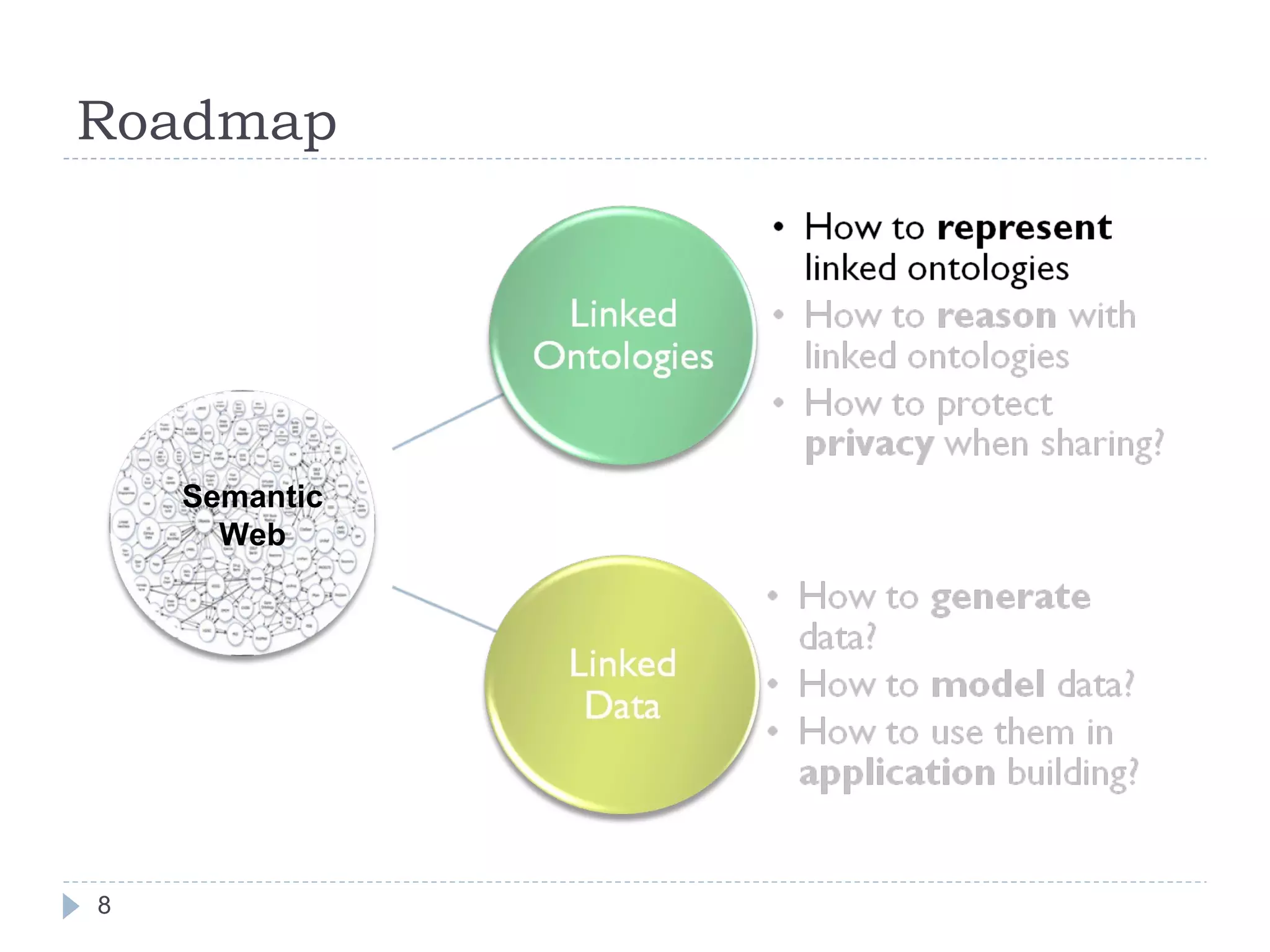
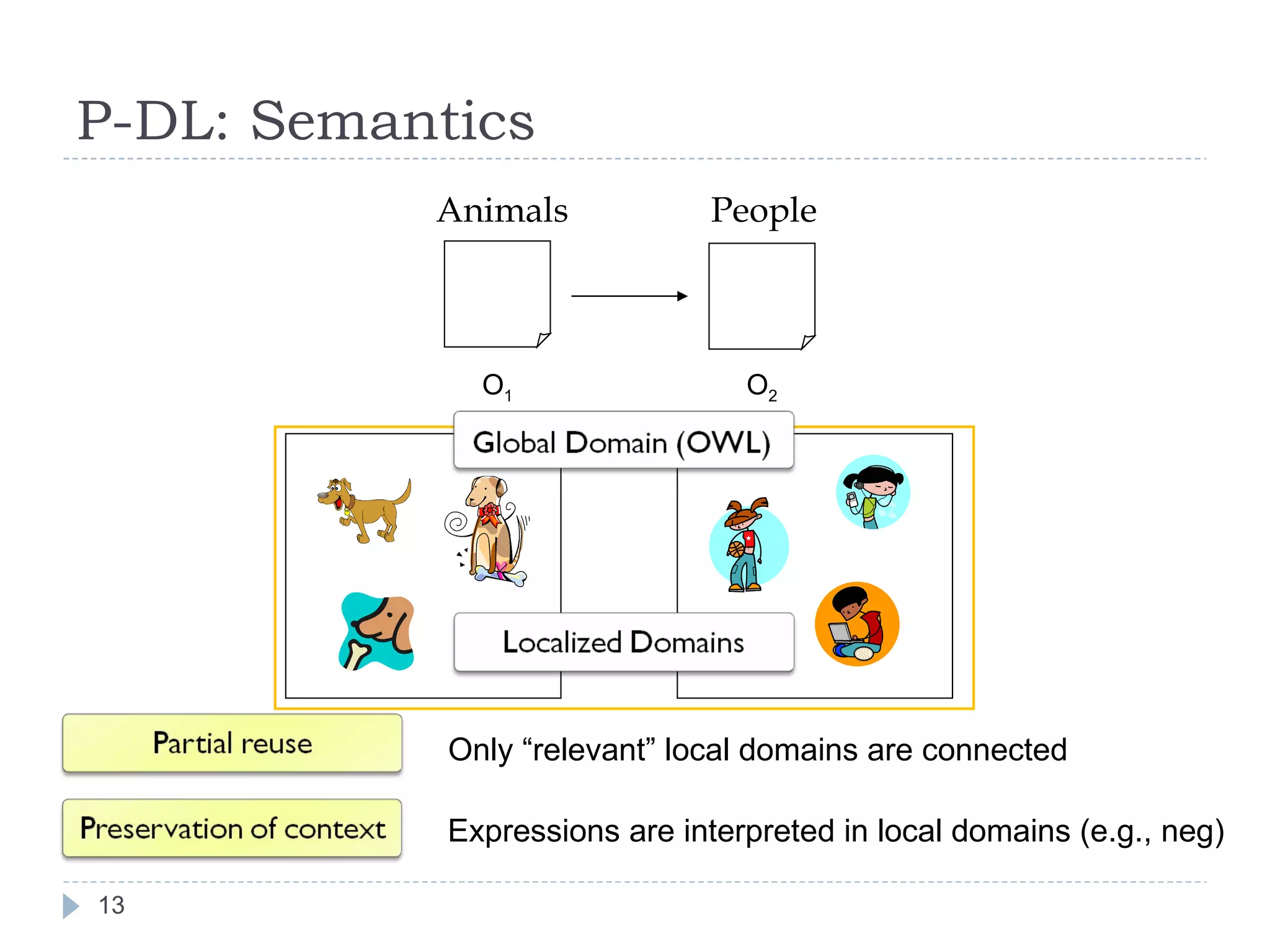
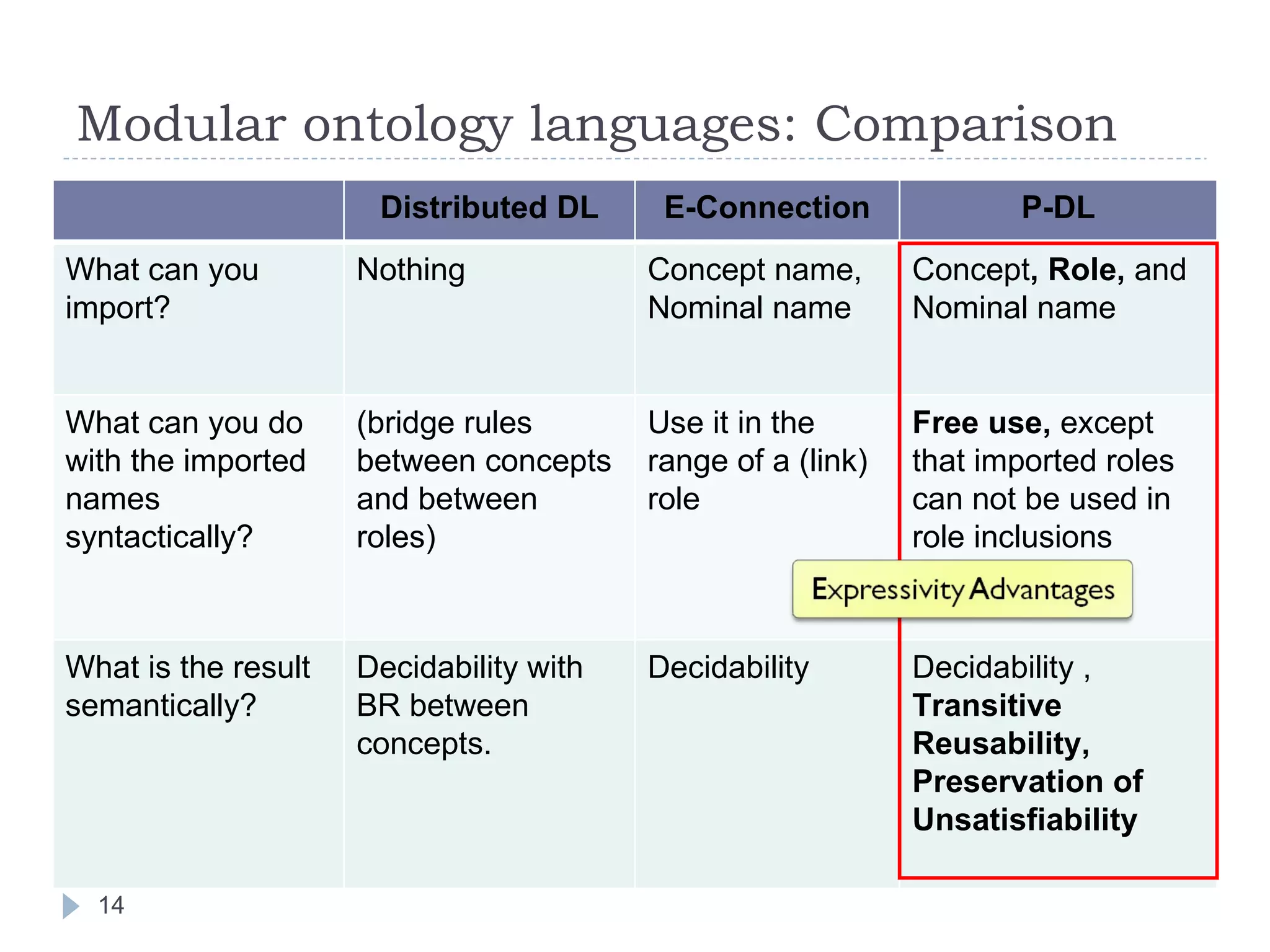
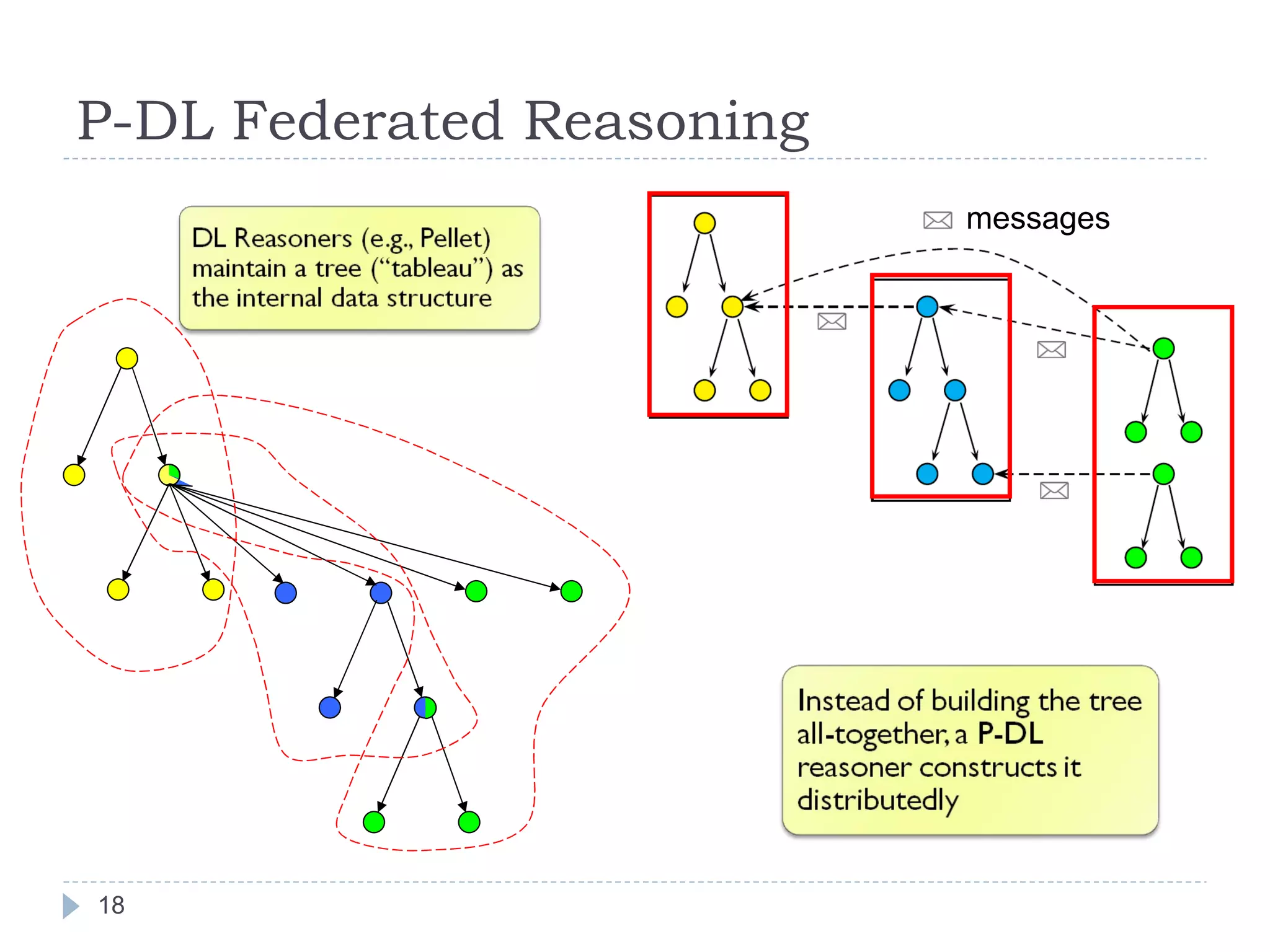
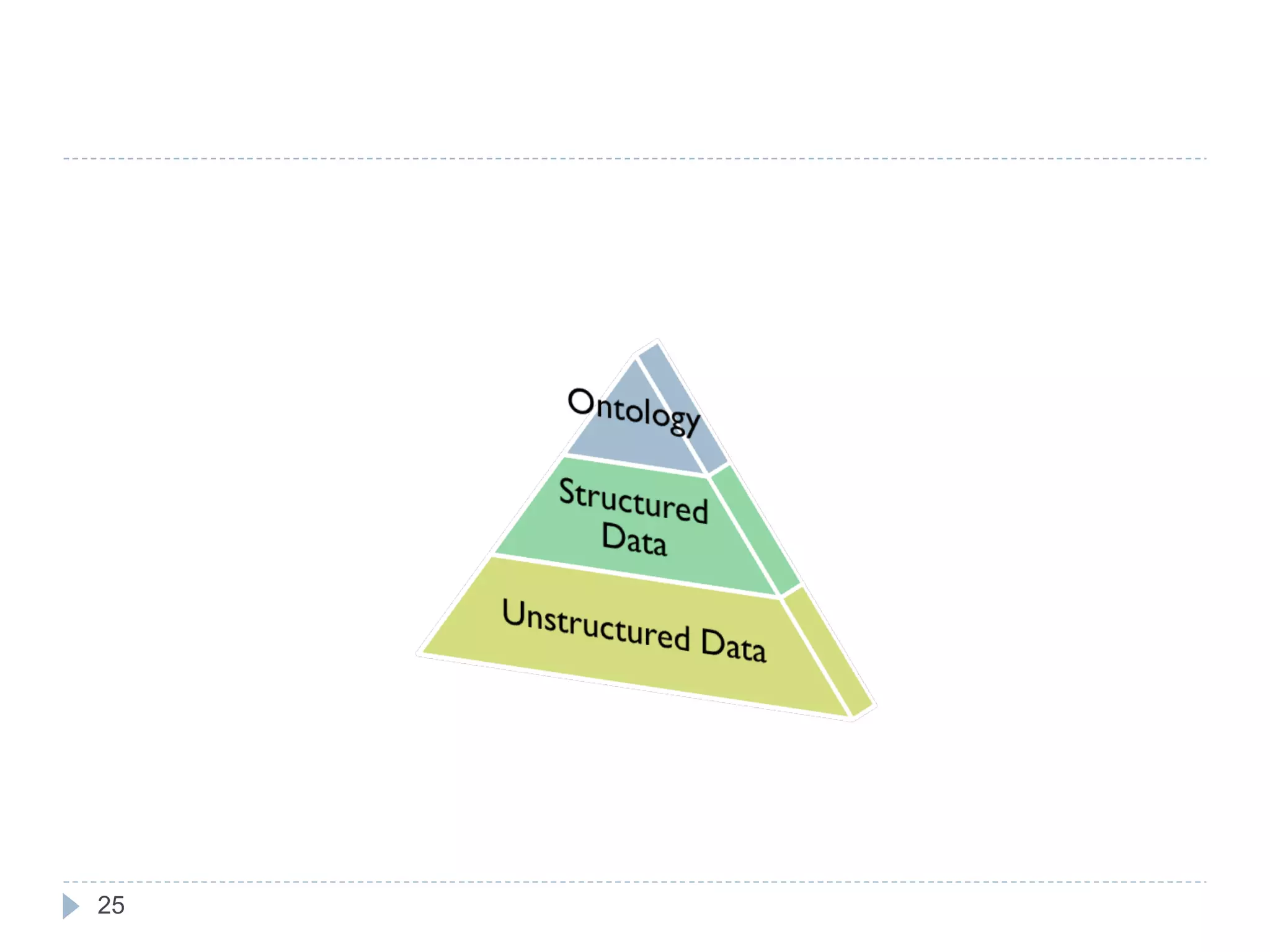
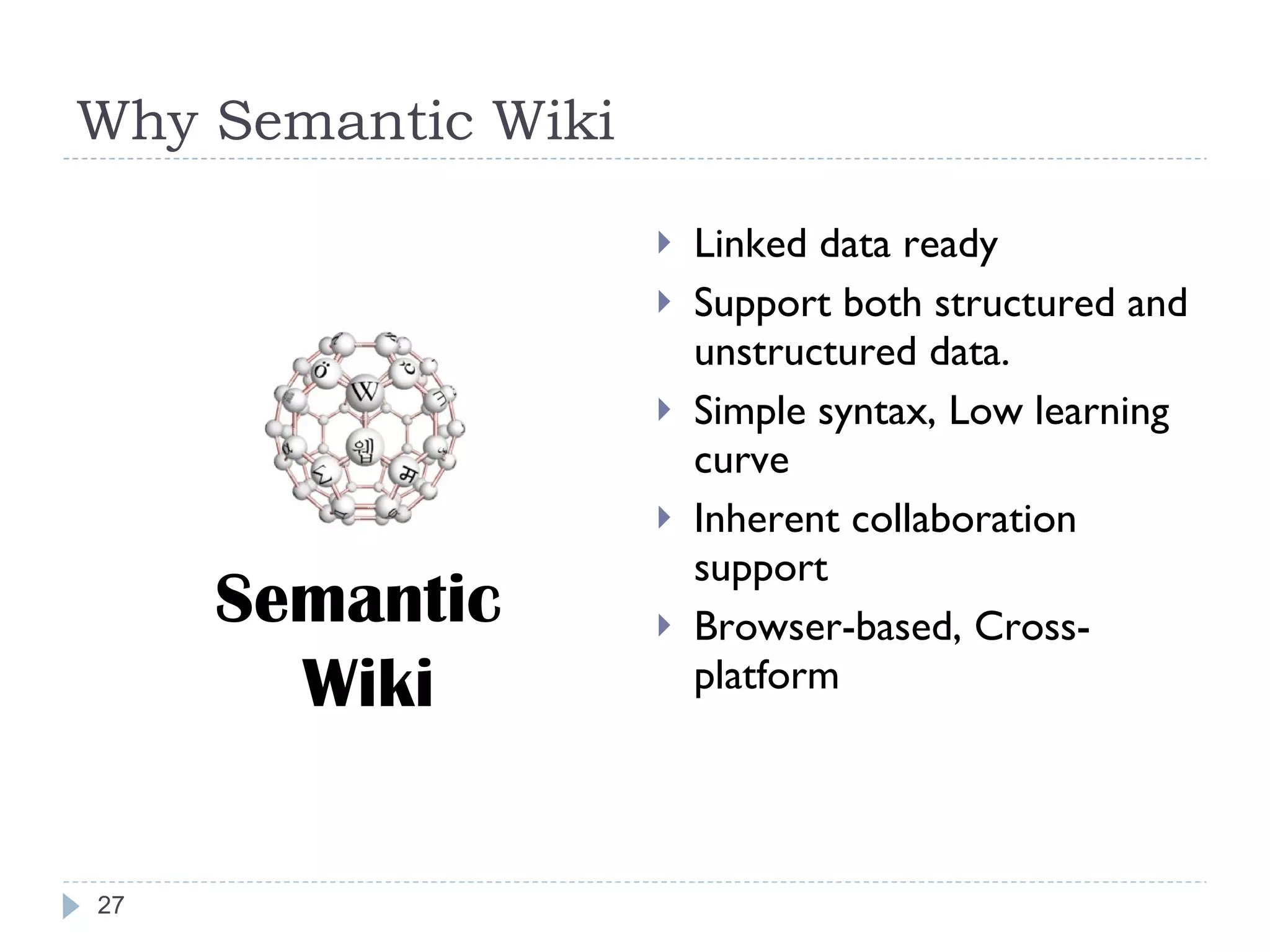
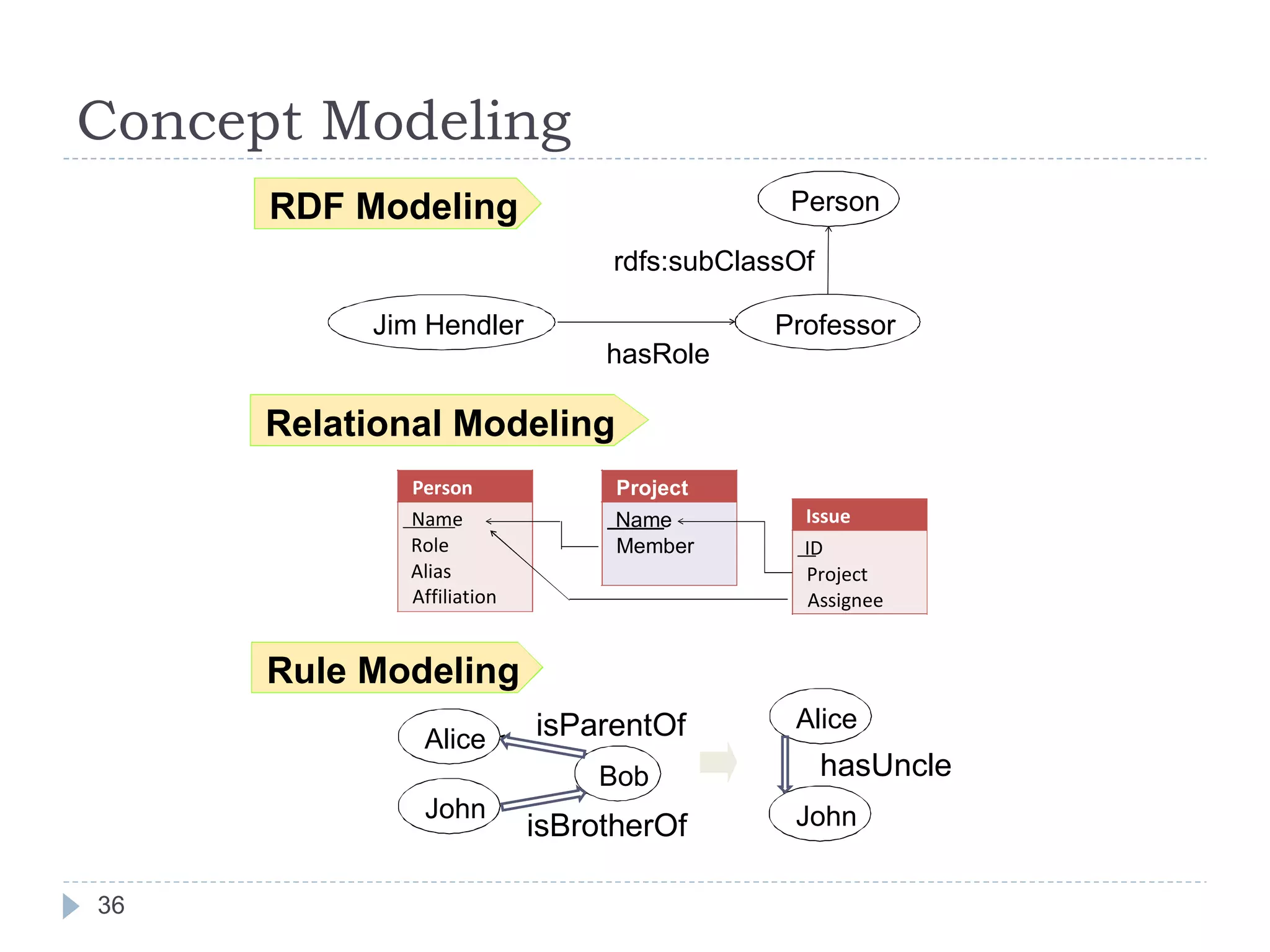
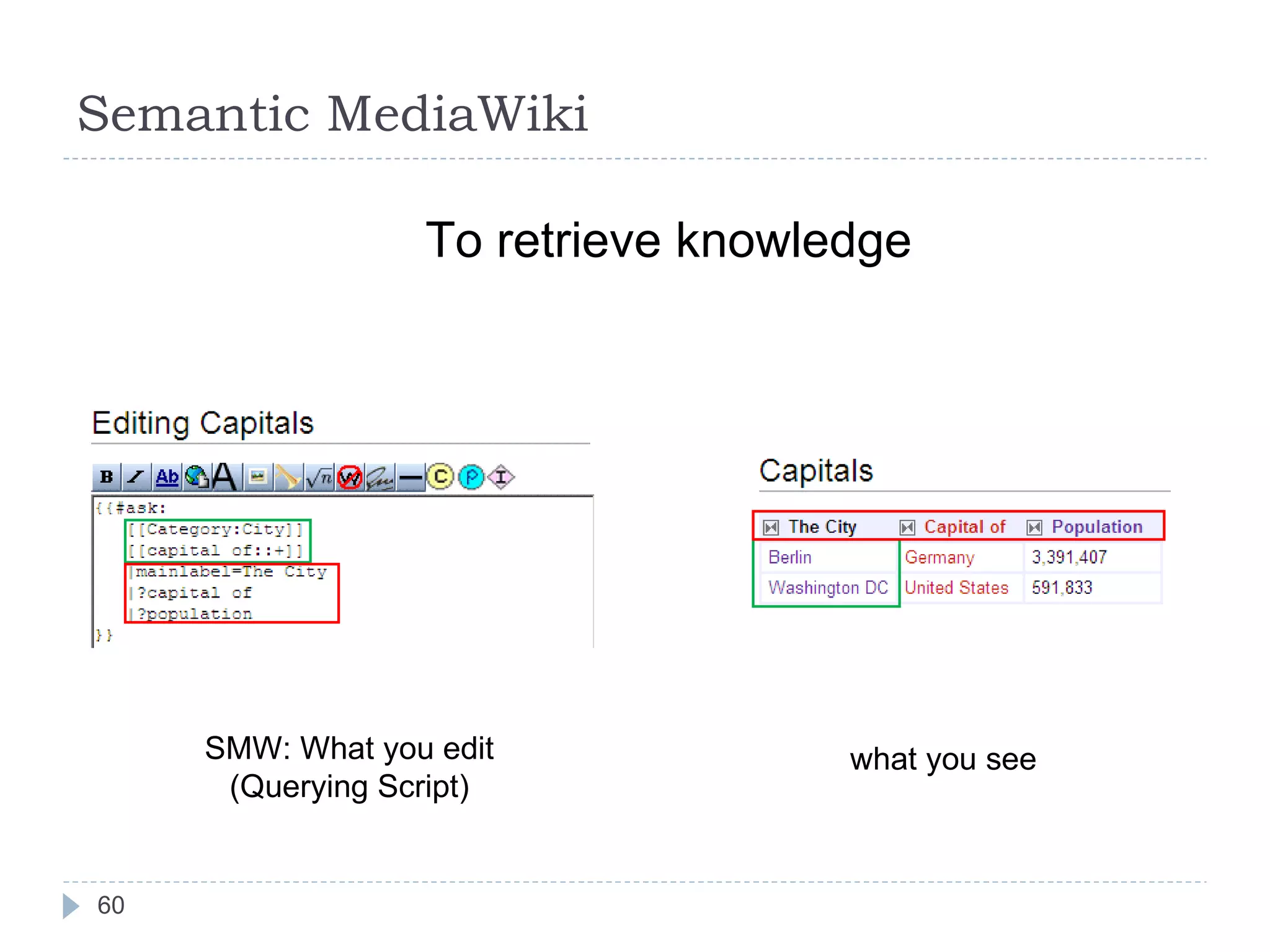
The document outlines Jie Bao's research background and overview, including work on linked ontologies and linked data using semantic wikis. It discusses a modular ontology approach called P-DL that allows importing between ontologies similar to citation. It also describes using a semantic wiki to generate linked data from wiki revision histories and other semantic data. Future work includes applying these techniques to government data and improving scalability.




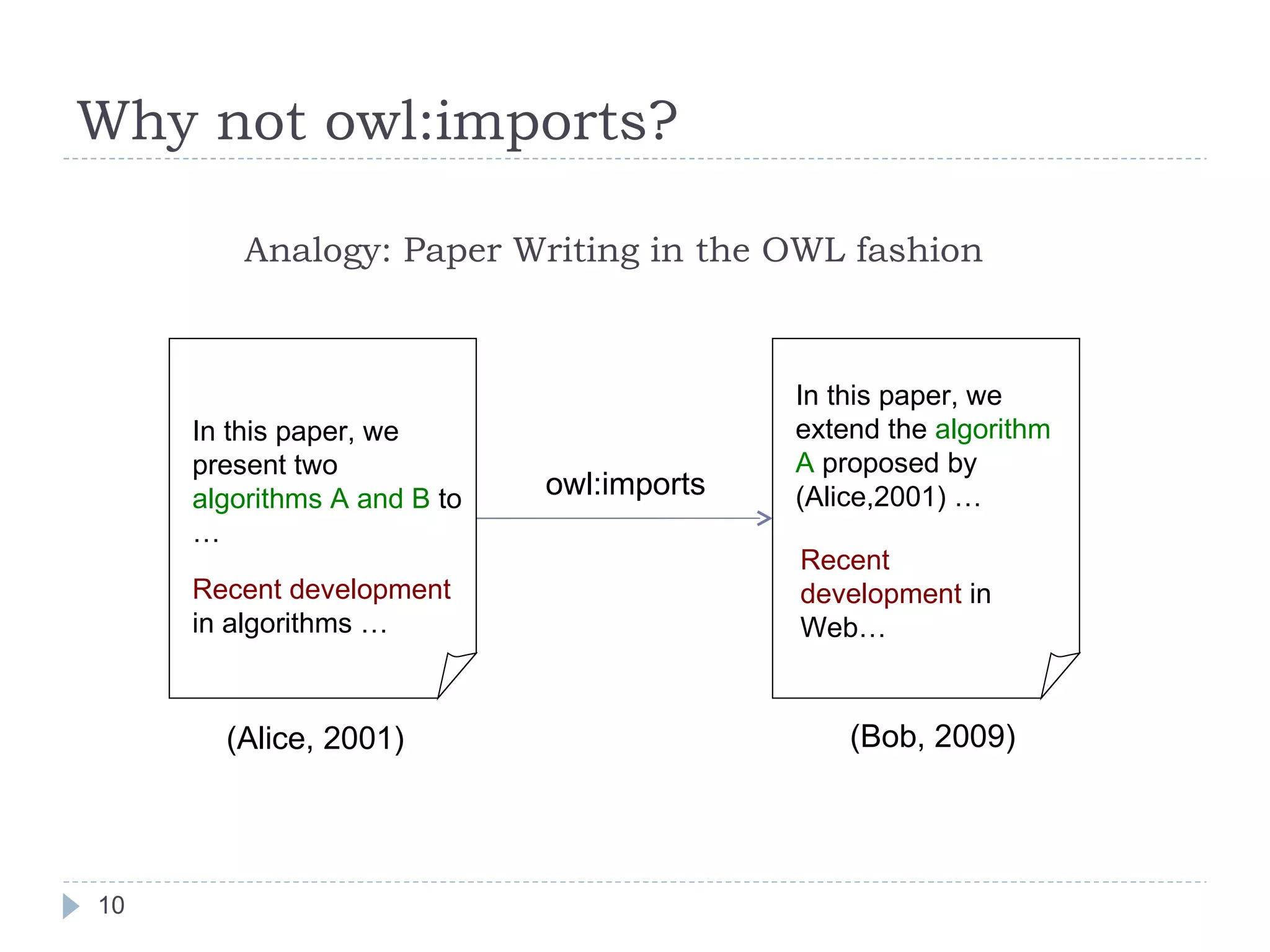
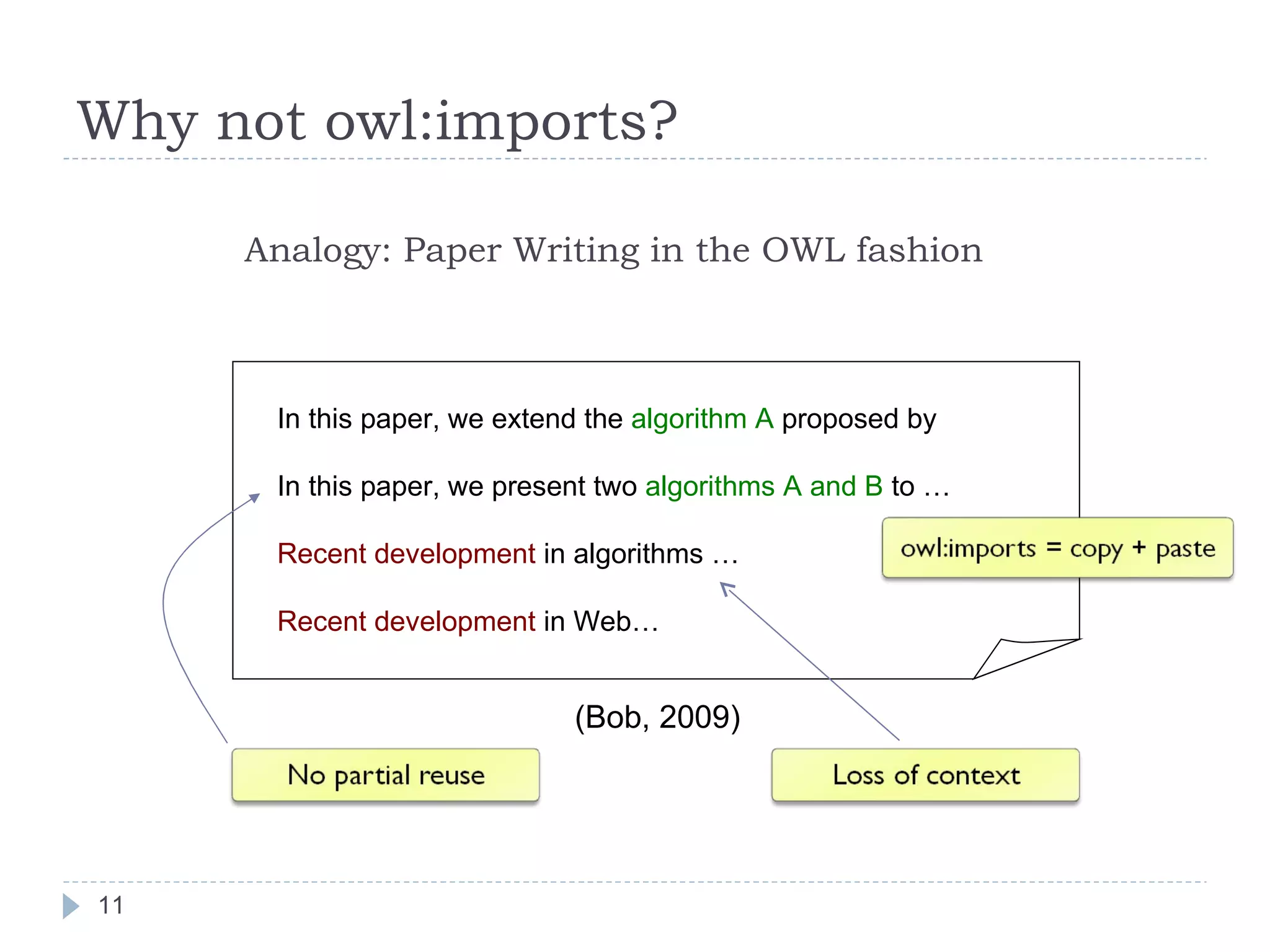
![P-DL: Importing akin to Citation P-DL imports (Alice, 2001) (Bob, 2009) Paper(Bob2009) {Bob2009} ⊑ propose.{AlgC} {AlgC} ⊑ extend.{ AlgA } {Bob2009} ⊑ cite.RecentDev Paper(Alice2001) {Alice2001} ⊑ propose.{ AlgA } {Alice2001} ⊑ propose.{AlgB} {Alice2001} ⊑ cite.RecentDev [ISWC 2006; ASWC 2006; AAAI 2007, AAAI 2008] P-DL = Package-based Description Logics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-12-2048.jpg)
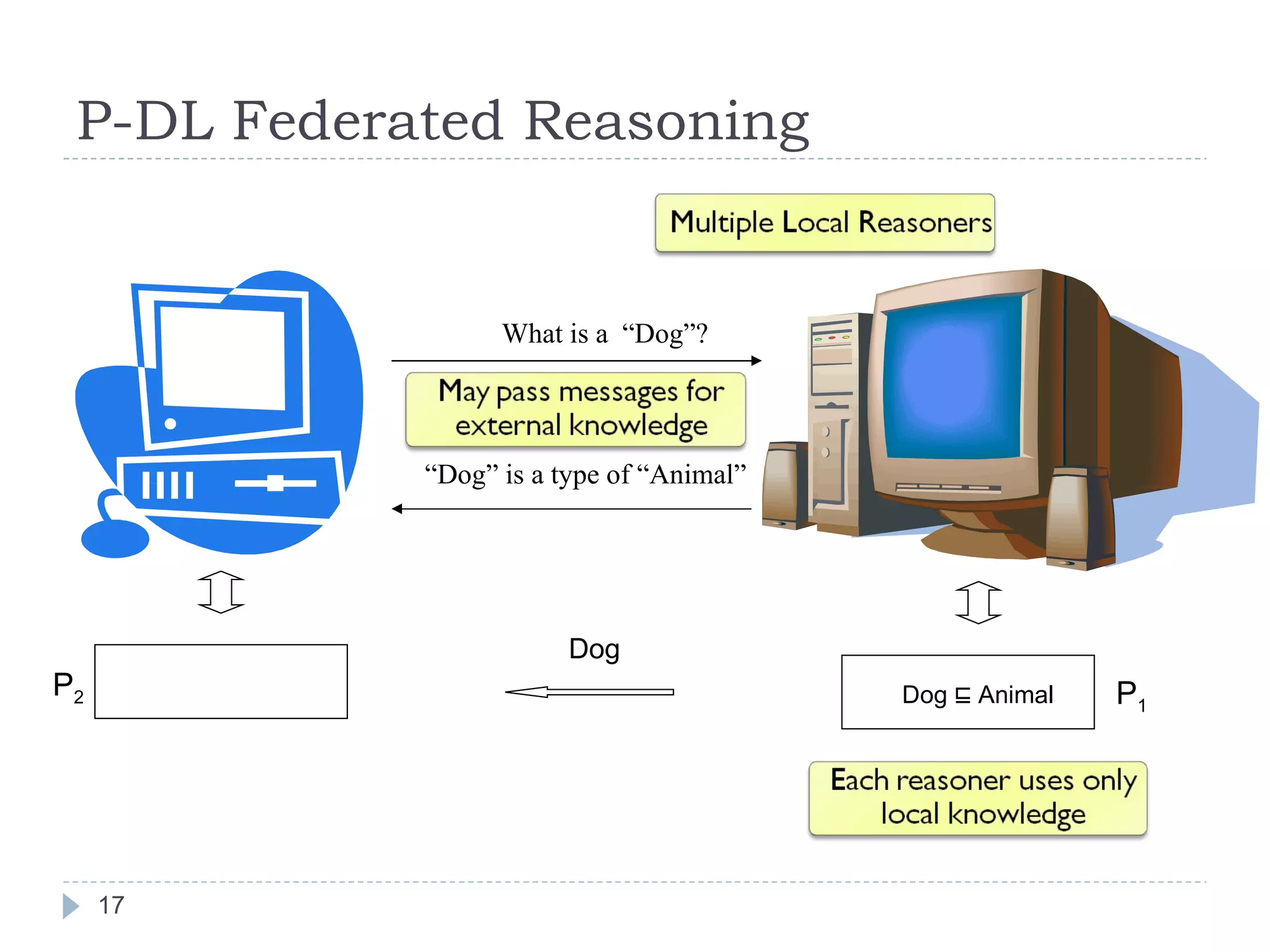
![Reasoning with P-DL Major Considerations [WI 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-16-2048.jpg)
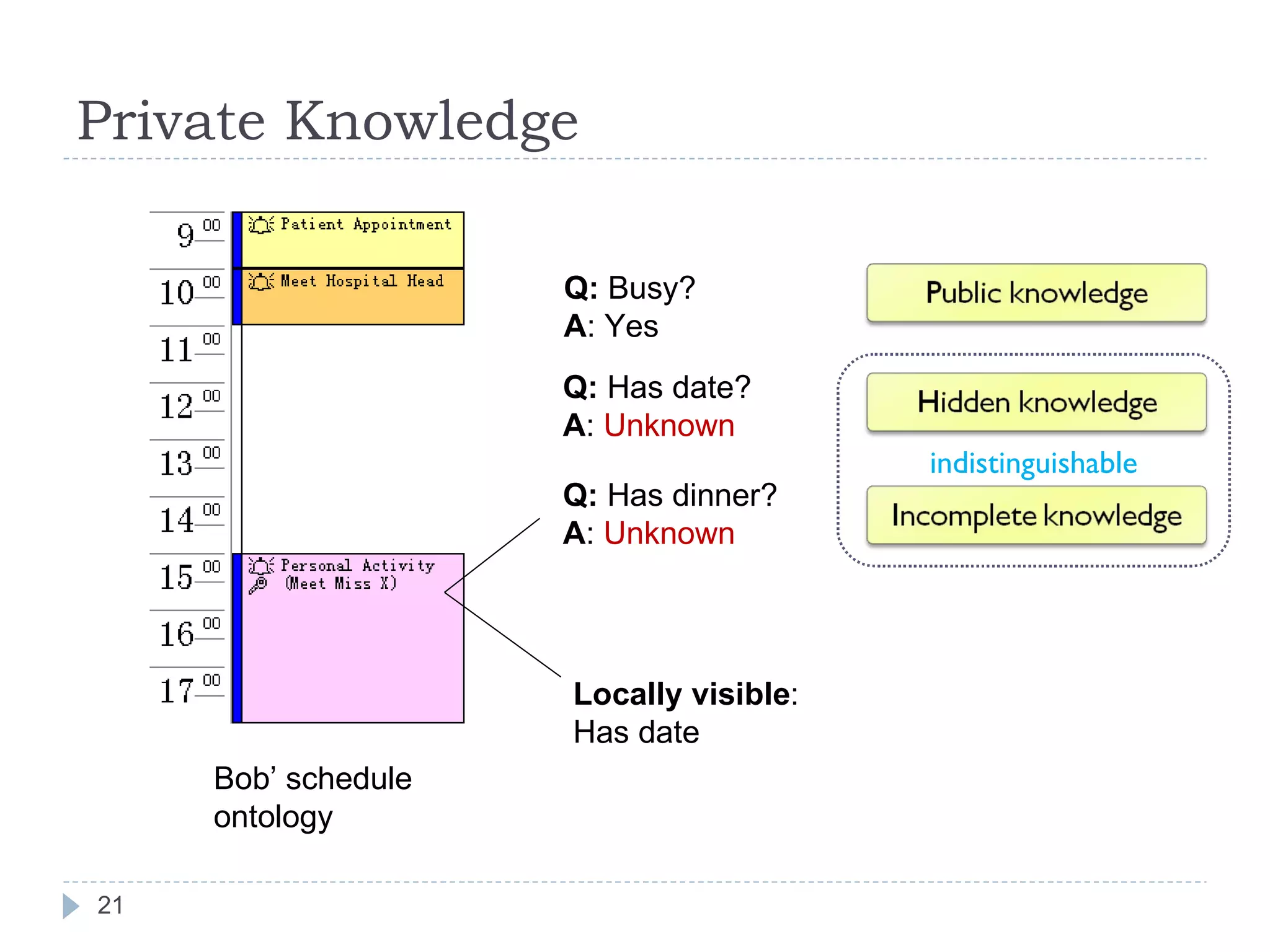
![Privacy Matters A reasoner may pose queries to another reasoner (of a remote ontology) However, not everything is public. [WI 2007]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-20-2048.jpg)
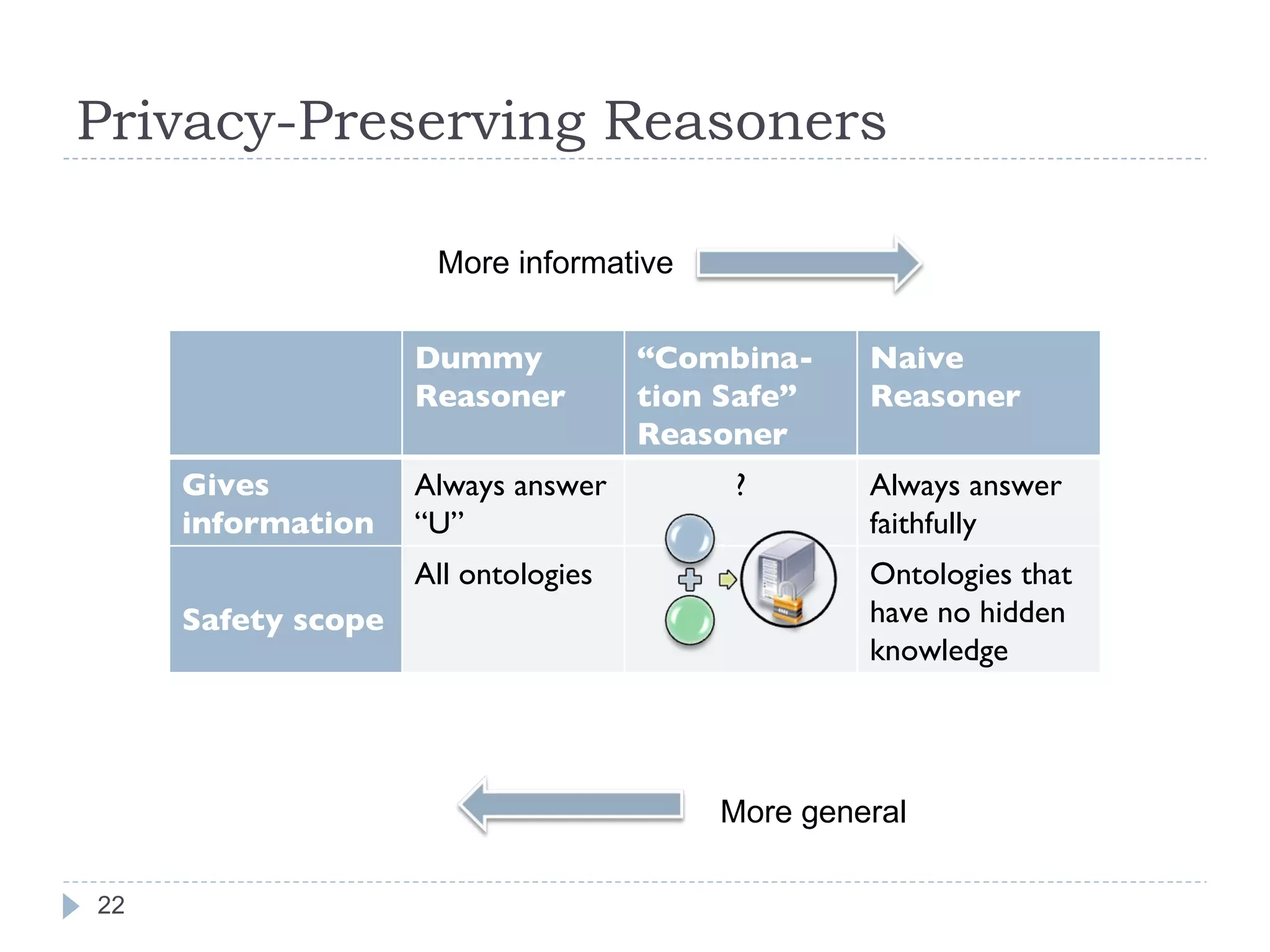
![Privacy-Preserving Reasoners Reasoner I: iff a statement is hidden, answer “unknown”. Reasoner II: iff a statement may be used in inferring a hidden statement, answer “unknown”. Reasoner III: it will NOT give more knowledge (except the public knowledge) about the signature of the hidden KB. Using the notion of “Locality” in DL. (See [WI 2007] for formal definitions) More informative More general](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-23-2048.jpg)


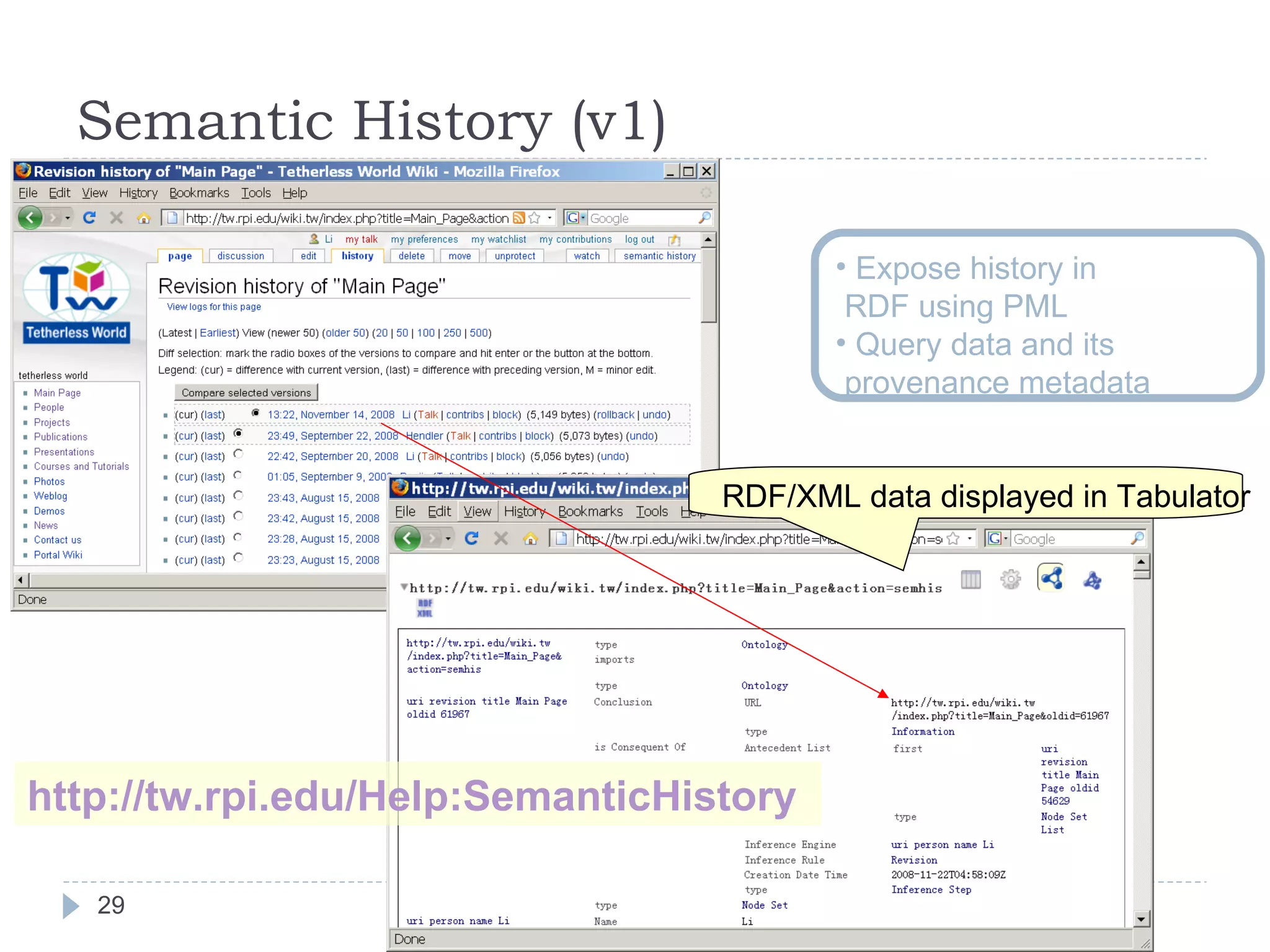
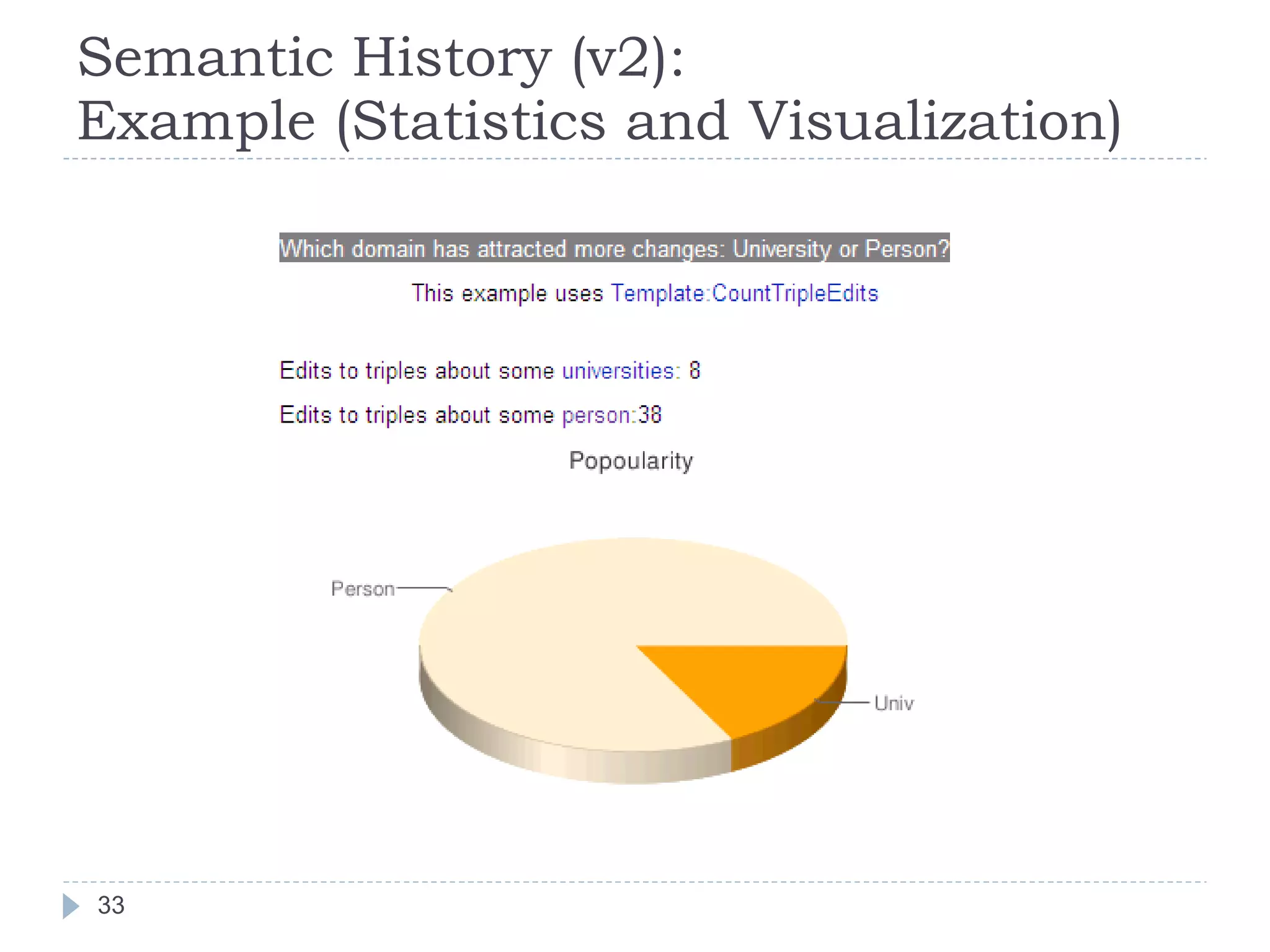
![Semantic History (v2) [SDOW 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-30-2048.jpg)
![Rules: Logic Programs RightHanded(x):-Person(x), not LeftHanded(x). {{LP Rule |body= 1::Person; 1:not:LeftHanded |head= RightHanded }} Example : every person is by default right-handed, unless that person is known to be left-handed: See details at: http://tw.rpi.edu/proj/cnl/Template:LP_Rule [ACITA 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-37-2048.jpg)
![Semantic Wiki: Application Workbench [ASWC 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-40-2048.jpg)
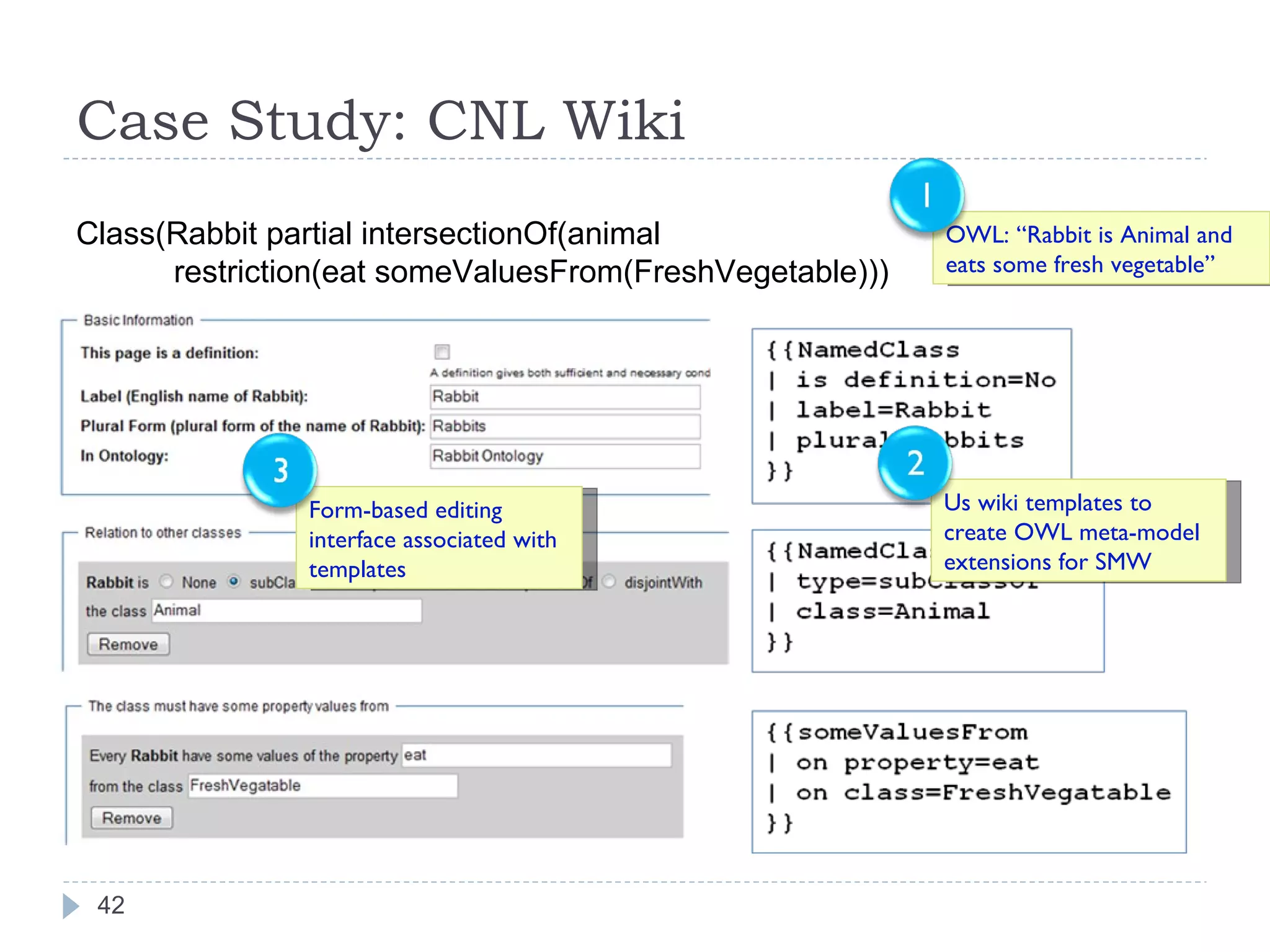
![Case Study: CNL Wiki A Wiki-based ontology editor Supports ontology representation in Controlled Natural Languages (CNL). http:// tw.rpi.edu/proj/cnl [CNL 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-41-2048.jpg)










![SMW Semantics and Complexity (Theory) See proofs in [TW-2008-42] Recall that L NL P NP SMW RDF Modeling Language Translatable into positive logic programs NL-complete NP-complete; P-complete for grounded graph [Bruijn and Heymans 2007] Query language Translatable into positive logic programs P-complete; In L without subqueries (SPARQL) P-complete [Perez et al 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-61-2048.jpg)
![Formalize SMW Query (Theory) {{#ask: [[Category:A]][[p3::category:B]] or [[ p.p1.p2 :: <q>[[Category:D]] or [[p1::<q>[[SomePage]]</q>]]</q> || !v || <q>[[Category:E]]</q> ]] }} _result(x) :- _tmp0(x). _tmp0(x) :- A(x), p3(x,x0), x0=category:B . _tmp0(x) :- p(x,x2), p1(x2,x3), p2(x3,x1), _tmp9(x1). _tmp9(x1) :- _tmp12(x1). _tmp12(x1) :- D(x1). _tmp12(x1) :- p1(x1,x4), x4=SomePage. _tmp9(x1) :- x1!=v. _tmp9(x1) :- E(x1).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009-09-24researchsummary-091006134944-phpapp02/75/Towards-Linked-Ontologies-and-Data-on-the-Semantic-Web-62-2048.jpg)