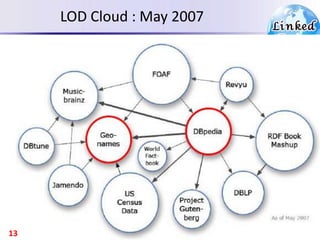
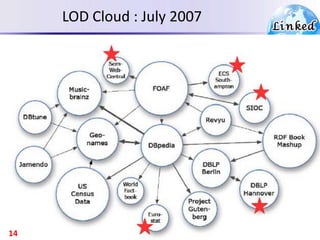
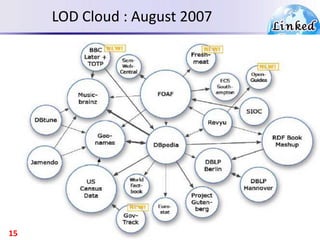
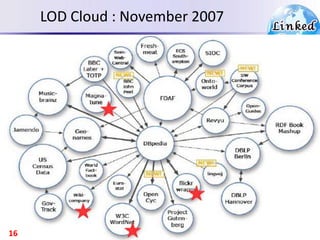
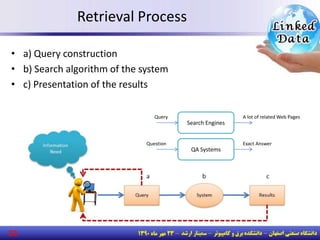
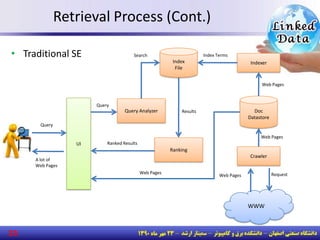
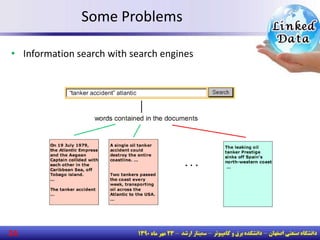
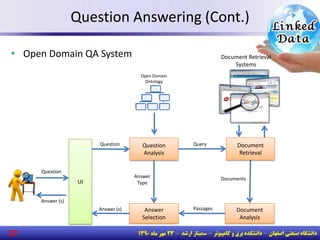
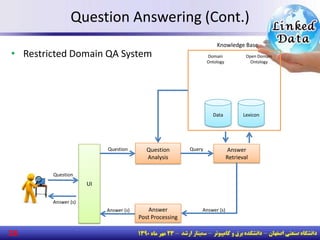
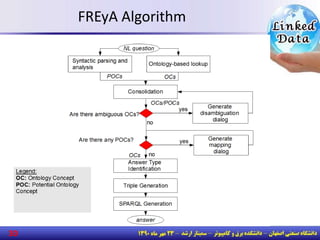
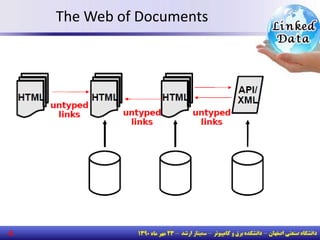
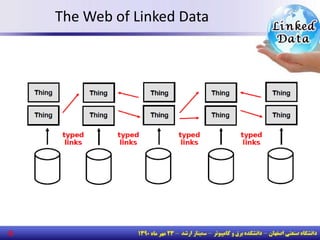
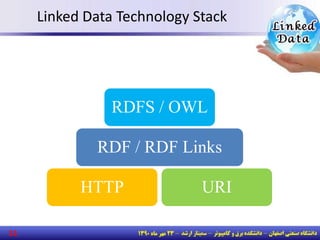
The document discusses the evolution of the web from documents to data, and introduces linked data which publishes machine-readable data on the web that is explicitly defined and linked to other datasets. It then discusses question answering systems that take natural language questions and locate answers from document collections, including both closed-domain systems with restricted knowledge bases and open-domain systems that retrieve answers from the web. The document also presents the linked data technology stack and some examples of linked open data clouds from 2007 to 2011 to demonstrate the growth of linked data on the web.






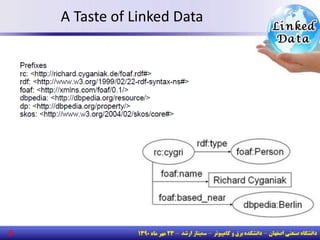

![Ontology , RDF
• Ontology provides a means to vocabularies
and link’s semantics on linked data.
• RDF provides a generic, graph-based data
model to structure and link data that
describes things
• A triple [subject, predicate, object]
– Subject: a URI
– Predicate: a URI
– Object: a URI or a string literal
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/questionansweringinlinkeddata-130923005814-phpapp01/85/Question-answering-in-linked-data-12-320.jpg)