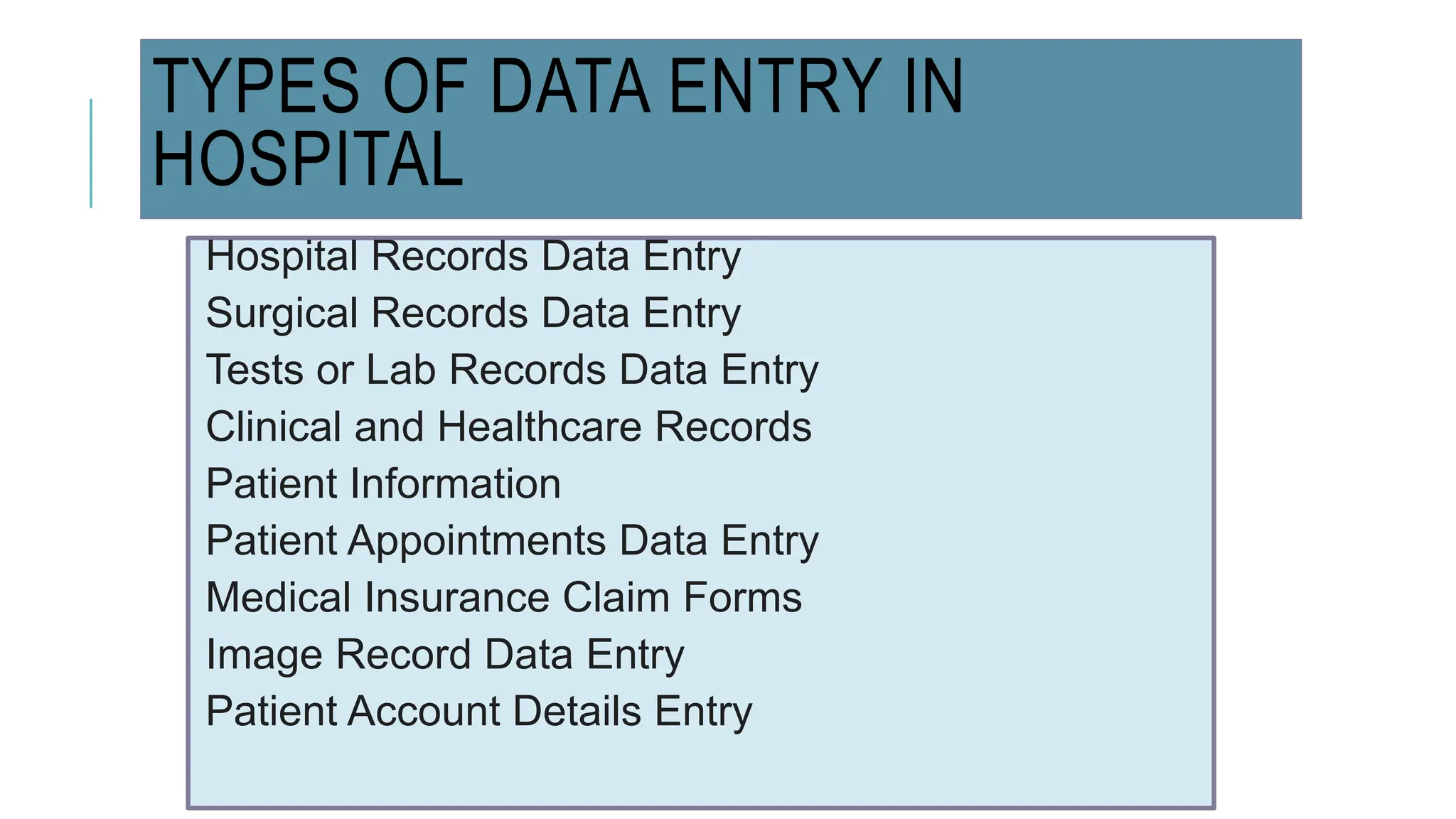
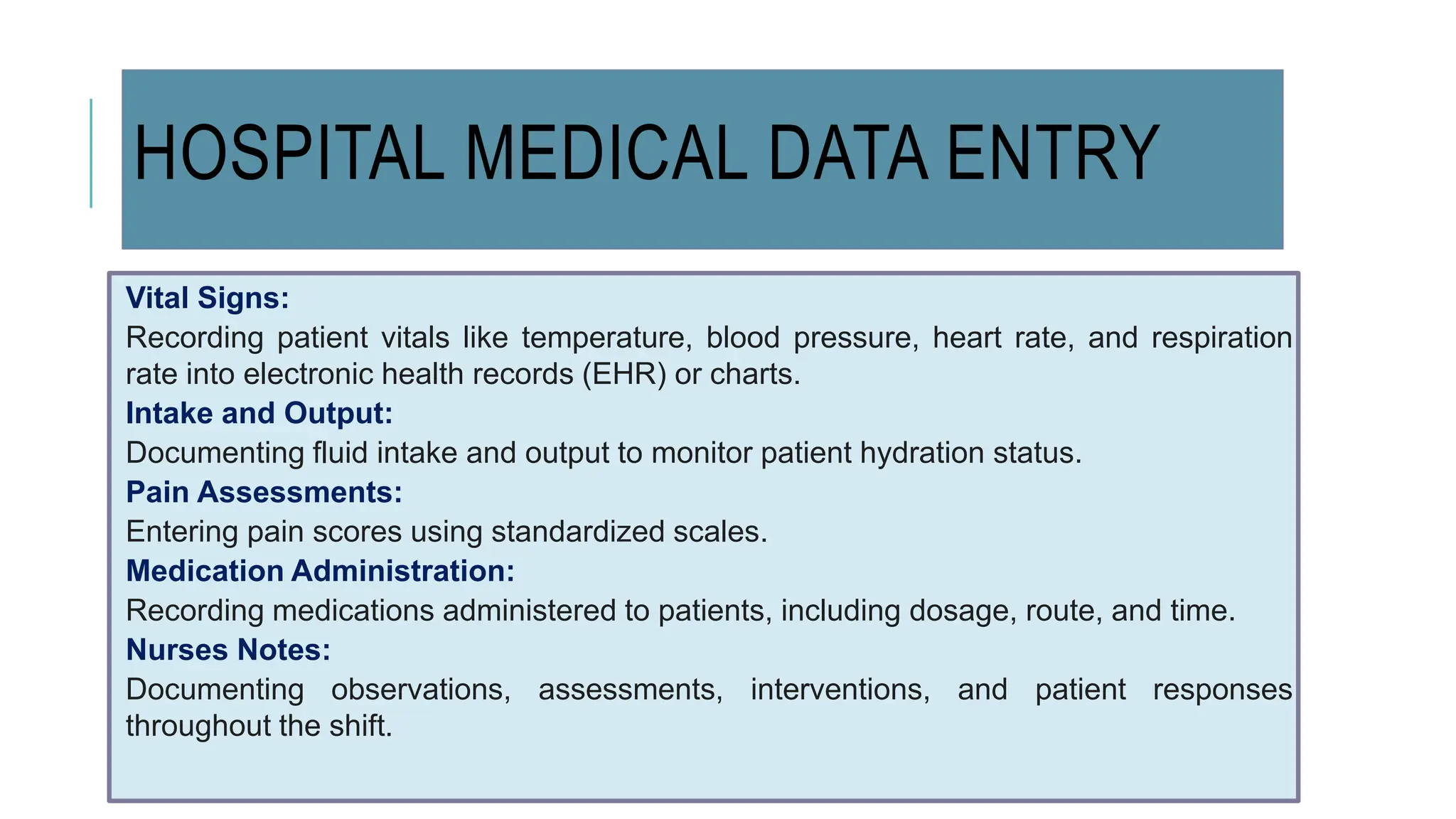
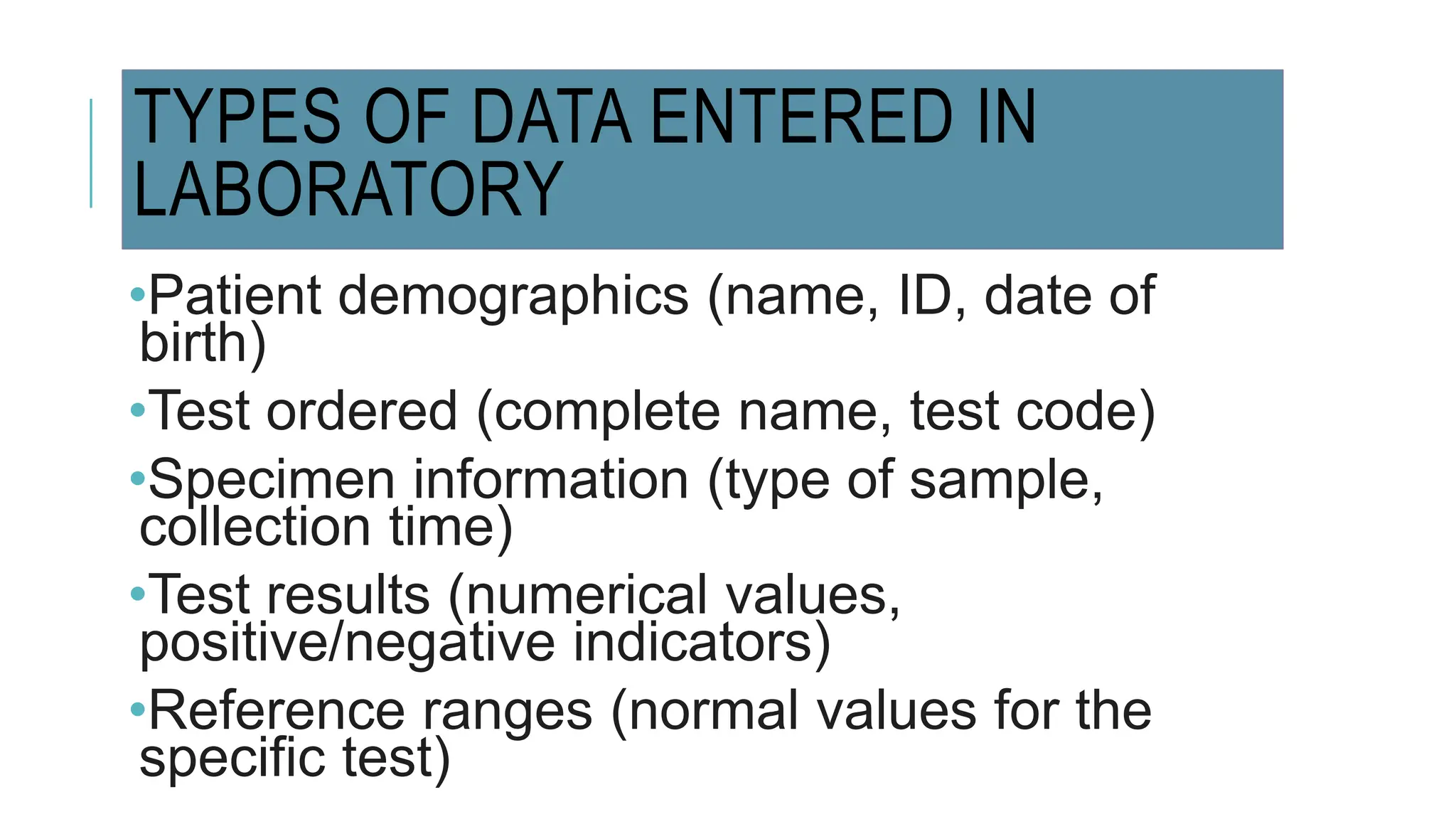
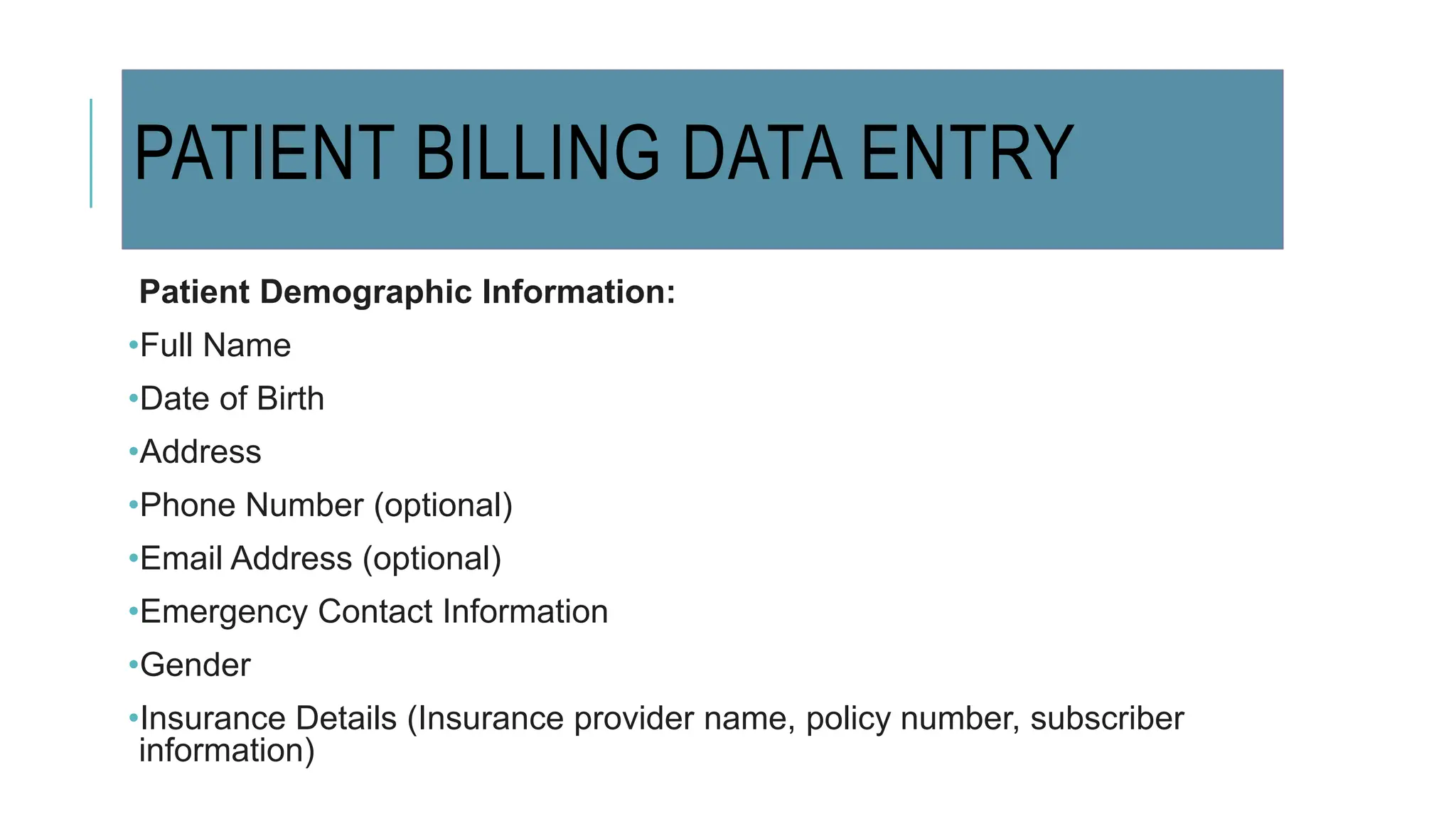
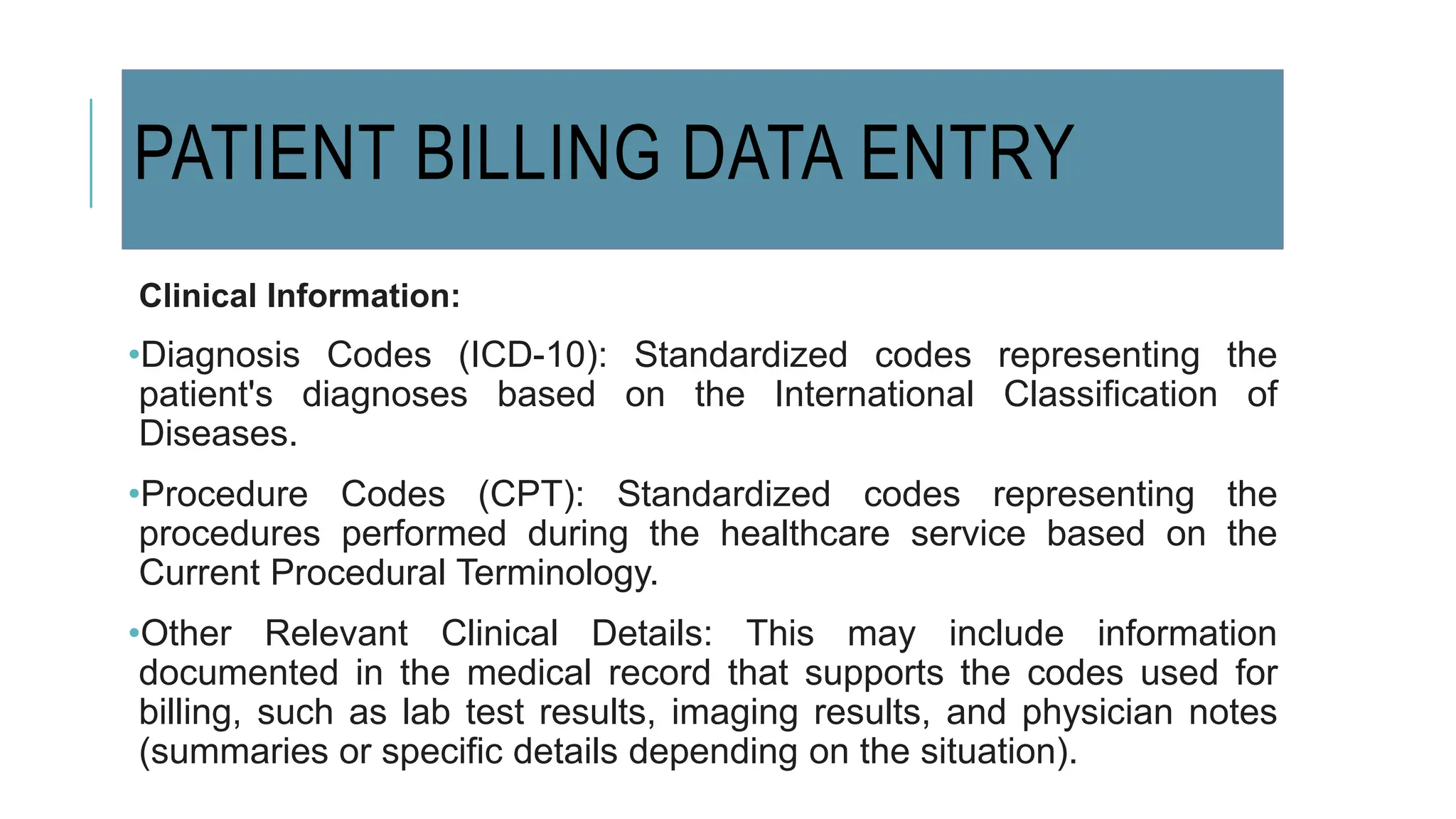
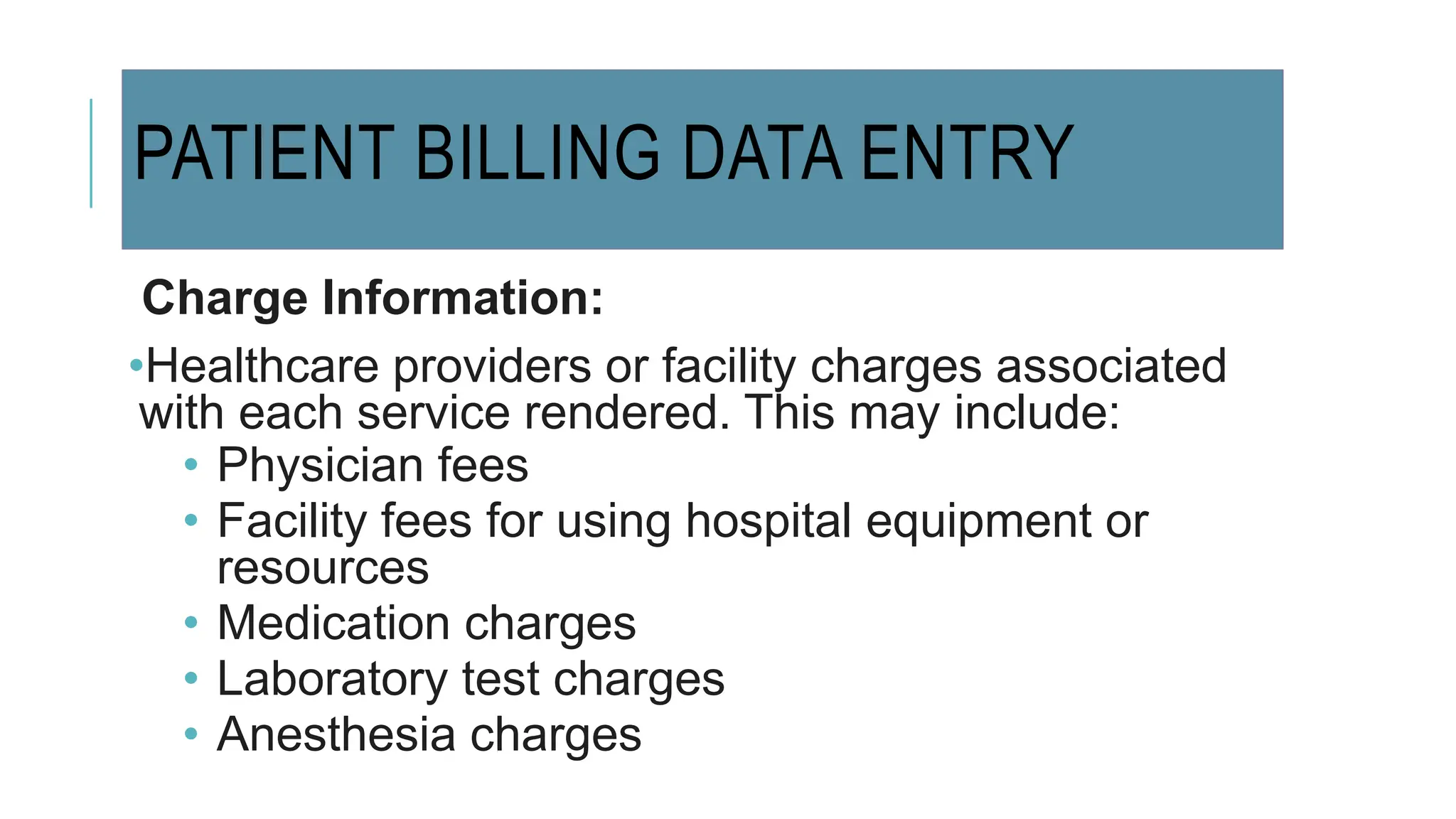
Data entry in hospitals involves electronically capturing essential patient and operational information to enhance care, streamline administration, and minimize errors. It includes various types of data such as patient demographics, medical history, clinical records, and billing information, with specific procedures for surgical and laboratory data entry. The process contributes to improved communication, accurate record-keeping, and efficient billing practices.