Embed presentation
Download to read offline






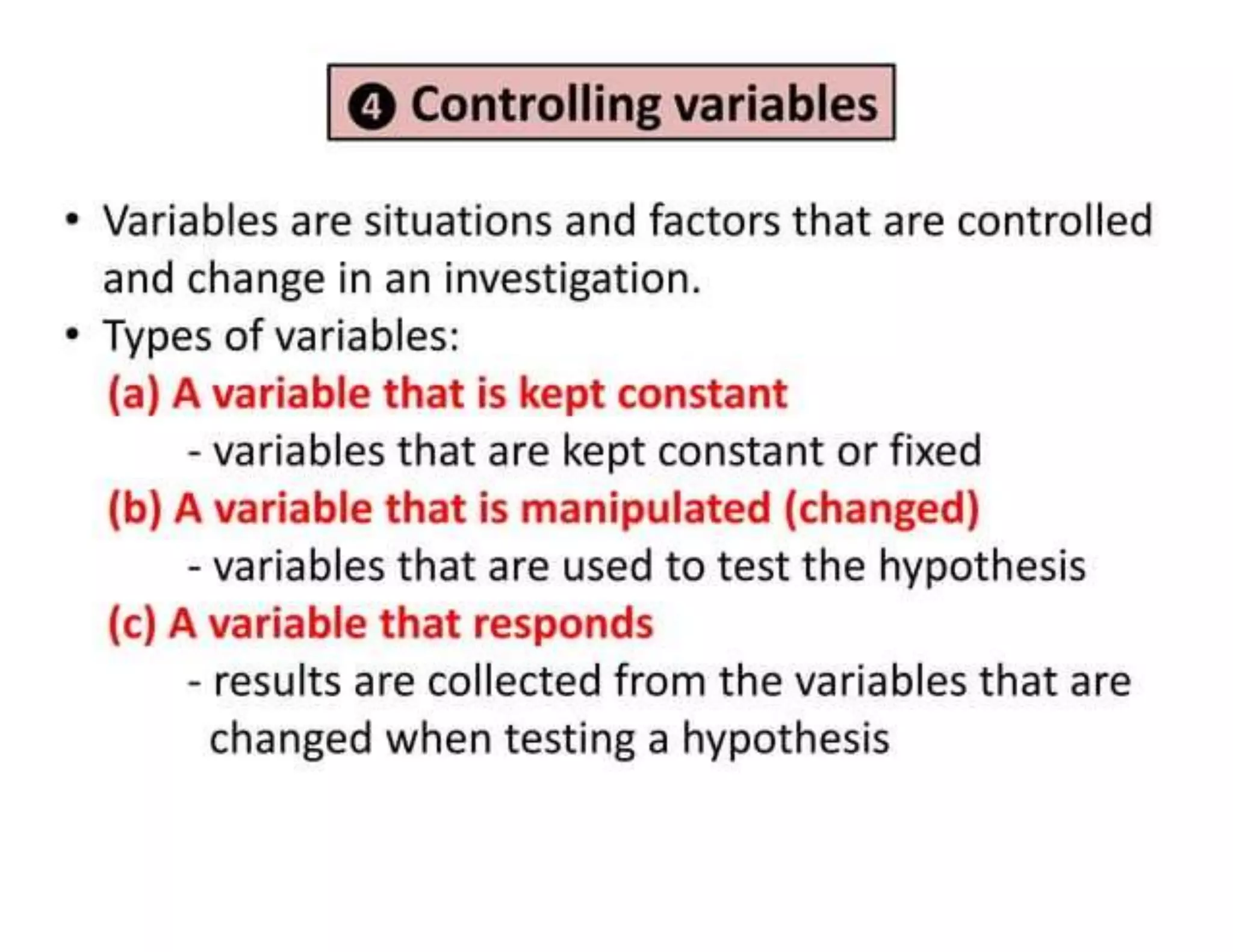




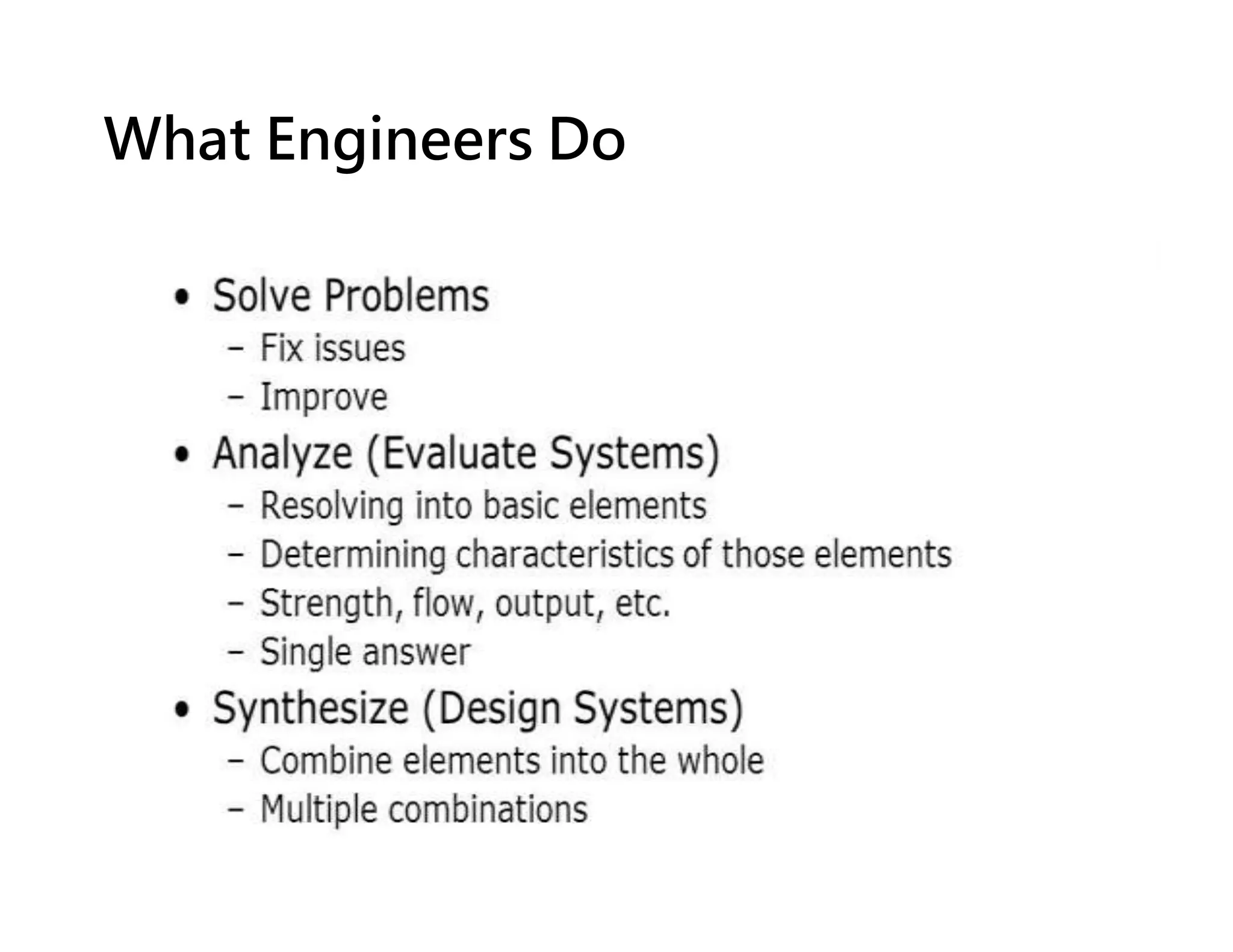


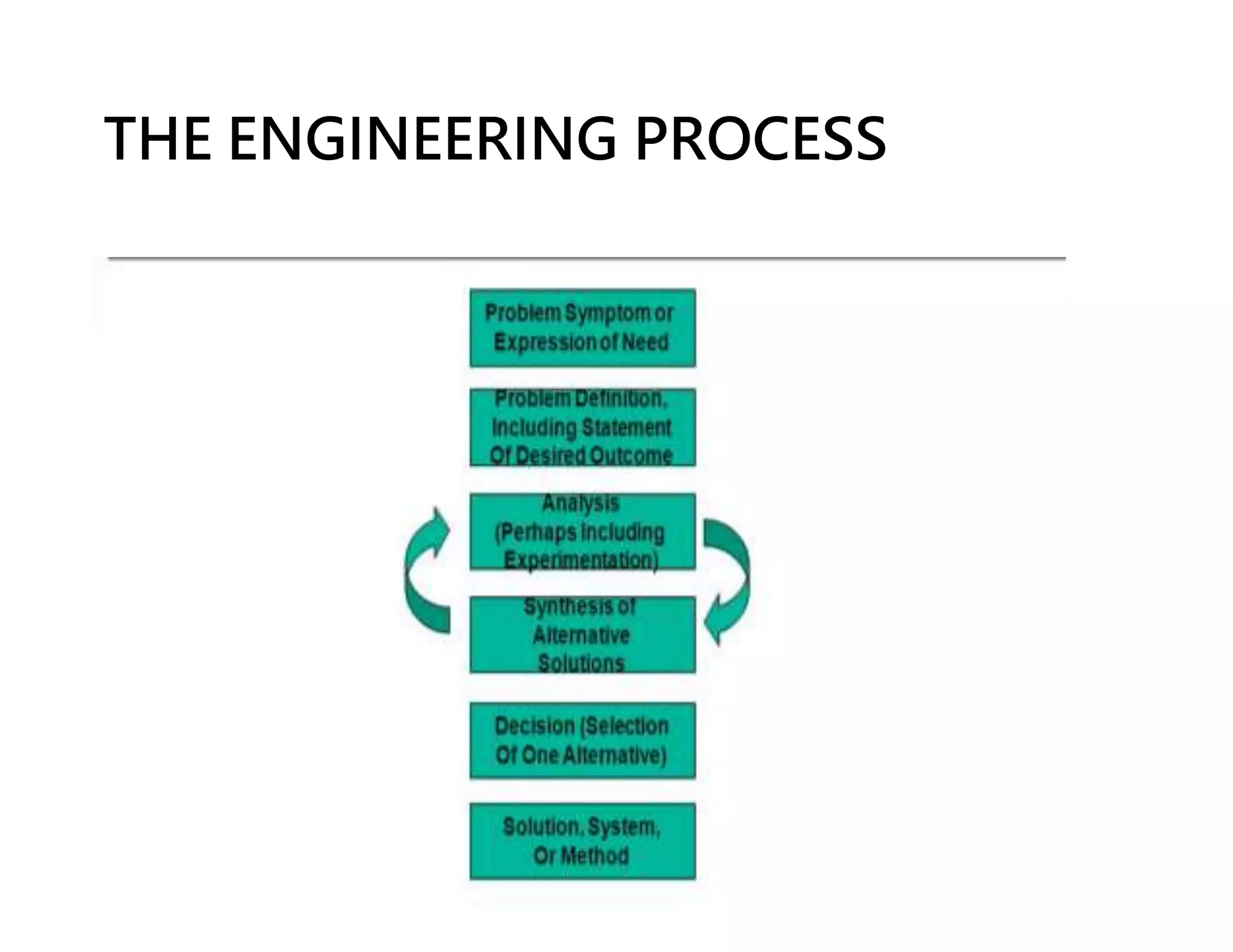

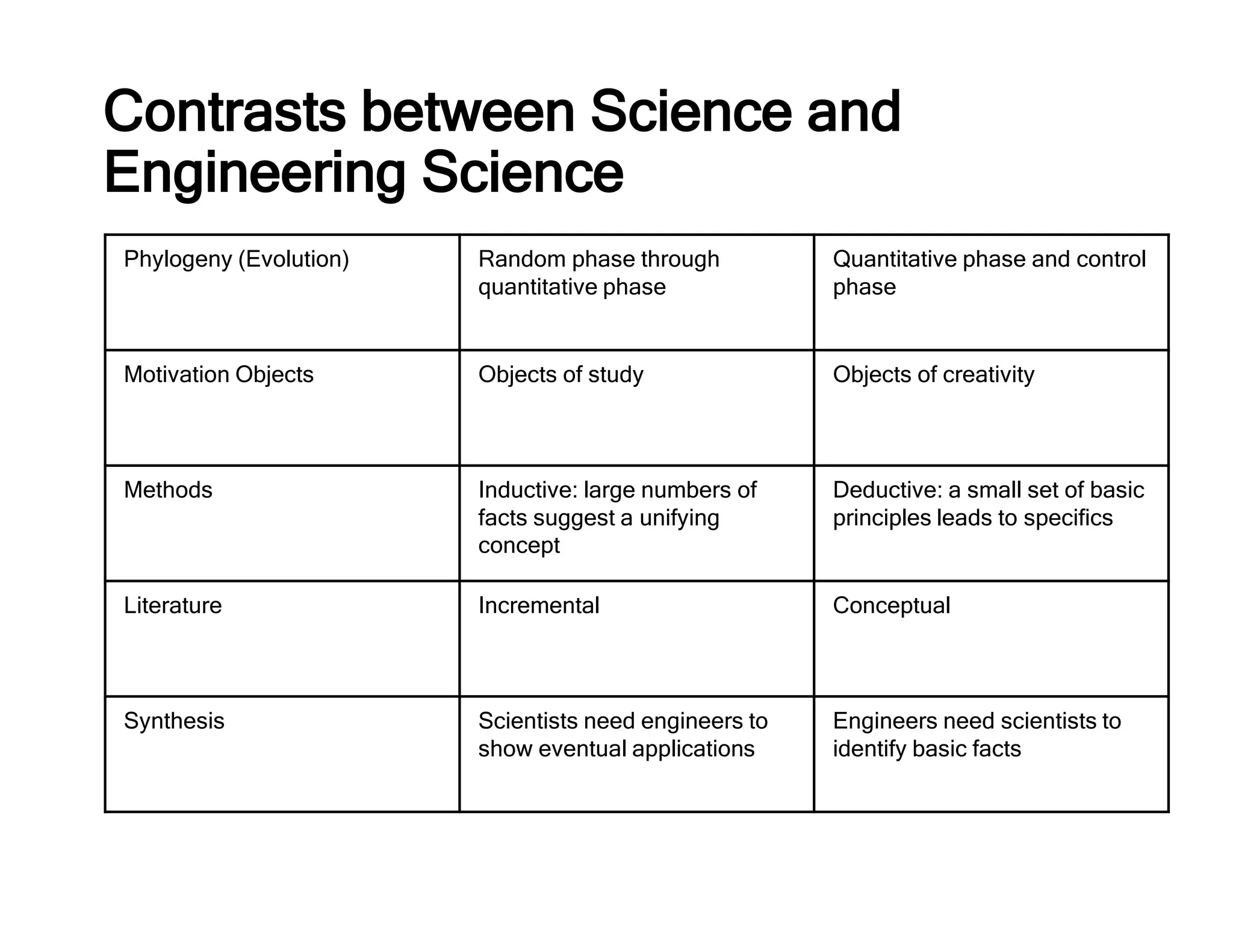
Science is the observational and experimental study of the natural world to understand its structure and behavior. It follows a specific methodology and aims to explain phenomena through facts and principles. Engineering applies scientific knowledge and mathematics to solve problems. Engineers look for new information that can be applied through a process that contrasts with science by focusing on controlled design rather than discovery. Both fields are interconnected, with scientists providing basic facts and engineers applying them through new technologies.

















