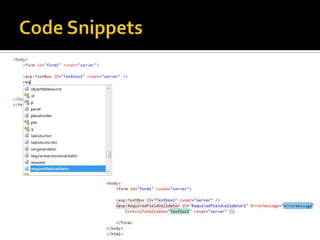
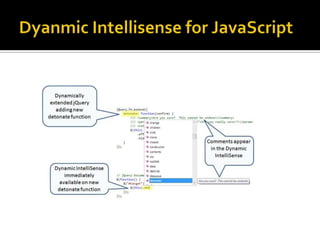
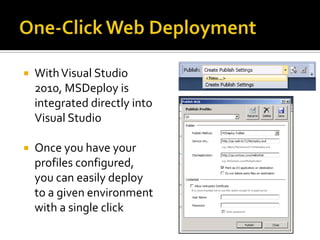
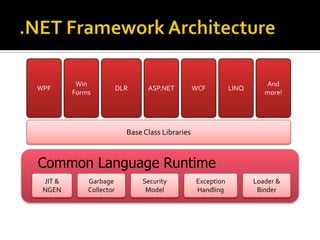
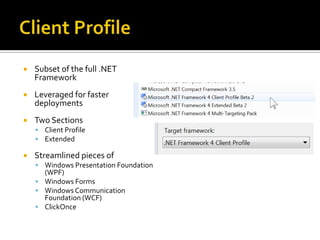
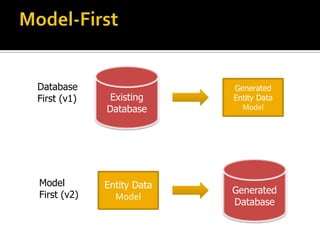
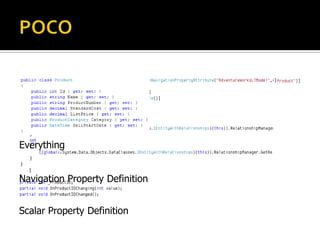
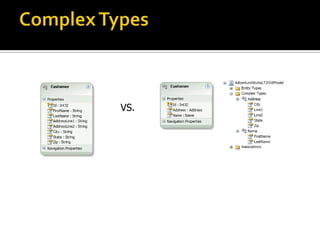
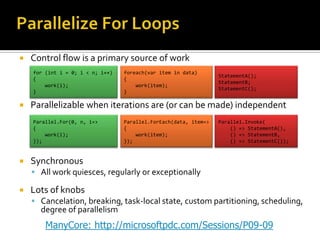
This document describes several new features and improvements in Visual Studio 2010 across various areas such as debugging, parallelism, web development, and extensibility. Some key highlights include improved debugging tools for breakpoint labeling, searching and importing/exporting, a redesigned threading window, support for debugging mini-dumps, and enhancements to web, SharePoint and ASP.NET MVC tooling.