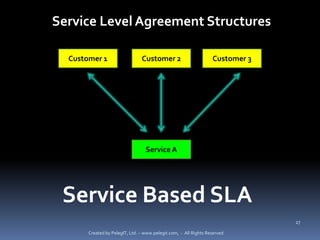
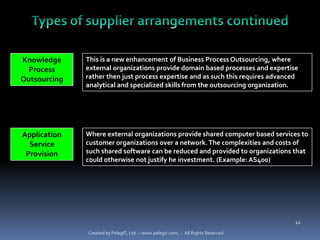
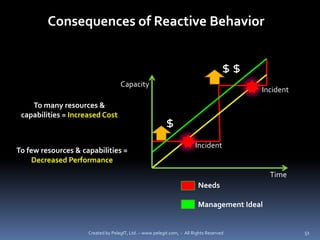
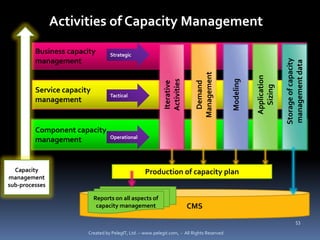
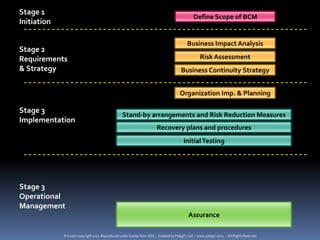
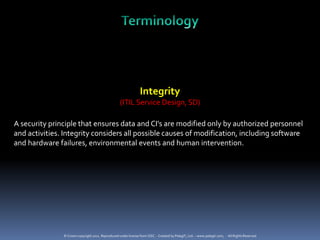
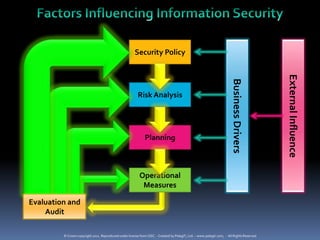
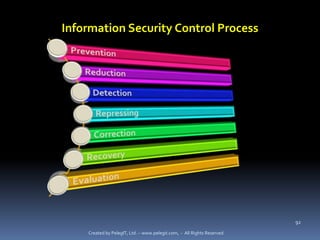
The document provides definitions and explanations of key terms related to IT service management based on ITIL best practices. It defines concepts like service level agreements, operational level agreements, underpinning contracts, service catalogs, service level requirements, service level targets, capabilities, configuration items, key performance indicators, critical success factors, availability, and maintainability. The definitions are concise explanations of each term in the context of ITIL.