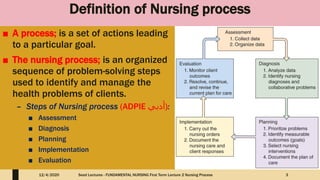
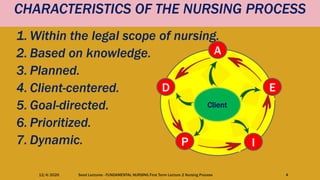
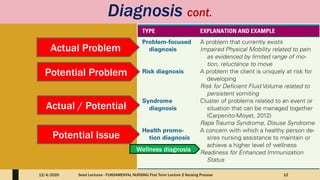
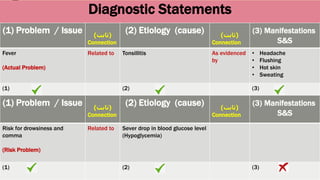
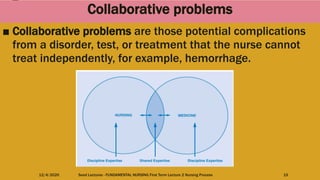
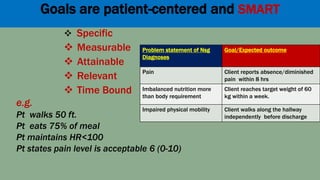
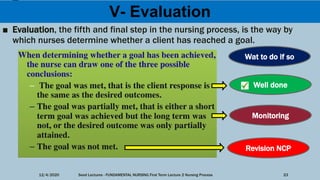
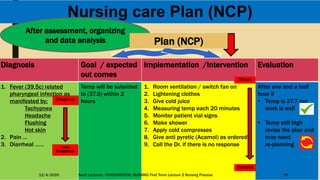
This document outlines the nursing process, which is a systematic problem-solving method used by nurses to identify and meet patients' healthcare needs. The five main steps of the nursing process are: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Assessment involves collecting patient data through health histories, physical exams, and other methods. Diagnosis identifies actual or potential health problems. Planning establishes goals and develops care plans. Implementation carries out the care plans. Evaluation assesses whether goals were met and identifies areas for improvement. The nursing process is a cyclic, continuous approach to patient care.