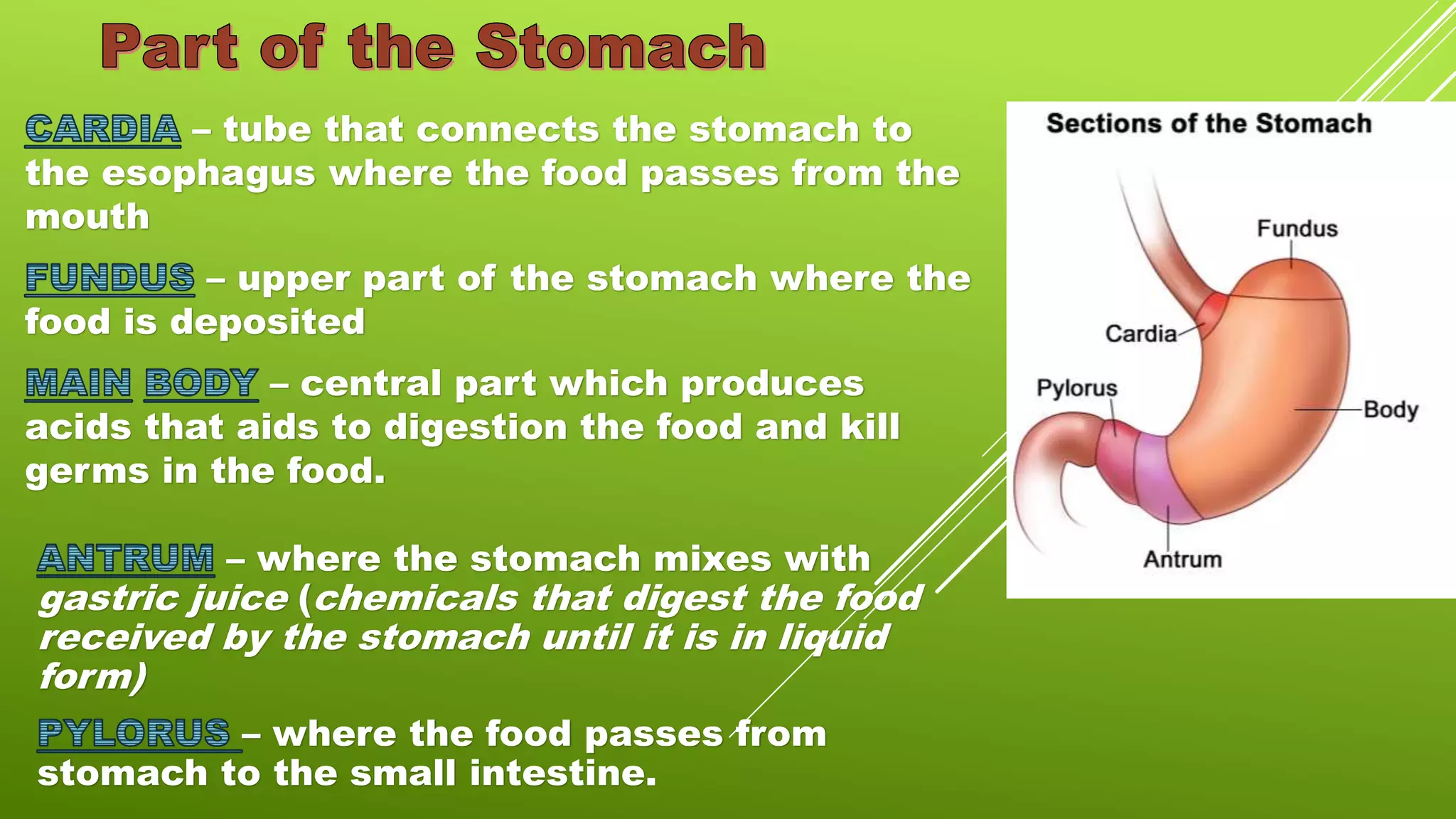
The document describes the stomach and its functions. The stomach is a baglike organ in the upper left abdomen where food stays for 3-4 hours. During this time, digestion takes place through mixing, mashing and turning food into a soupy substance that is then released to the small intestine. Not all food can be digested, and undigested waste passes to the large intestine. Common diseases of the stomach include gastritis, which causes inflammation of the stomach lining, and ulcers, which are open sores that develop on the stomach or small intestine lining. Lifestyle changes like eating slowly, not overeating, eating regularly, and drinking water can help support stomach health.