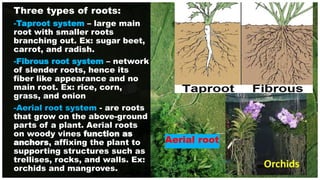
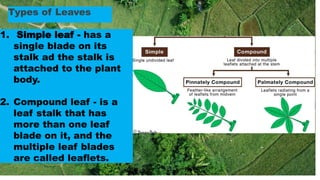
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant. There are three main root systems: taproots have a large main root with smaller roots, fibrous roots have a network of slender roots without a main root, and aerial roots grow from above-ground plant parts to provide additional support. Stems transport water and minerals between the roots and other plant parts like leaves, flowers, and fruit. Stems can be aerial, above ground, or subterranean, below ground. Leaves are made of a petiole, blade, veins and produce food for the plant through photosynthesis. There are simple leaves with one blade and compound leaves with multiple leaflets.