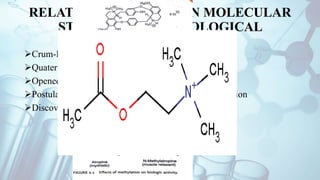
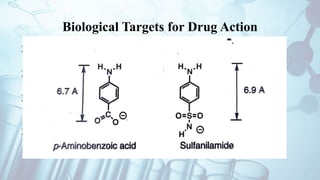
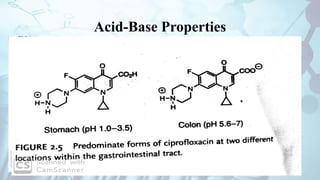
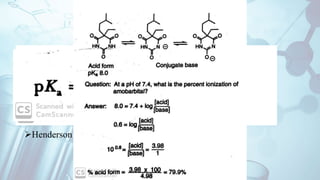
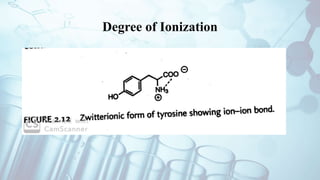
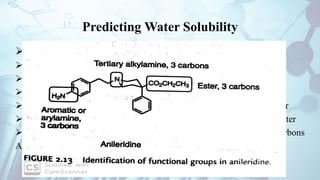
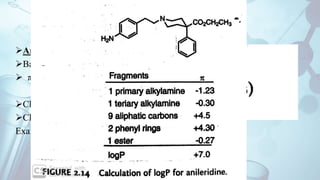
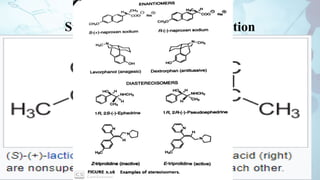
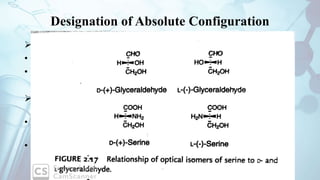
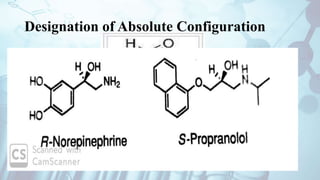
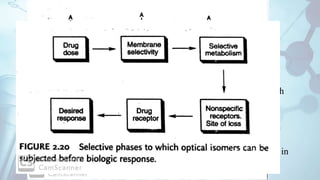
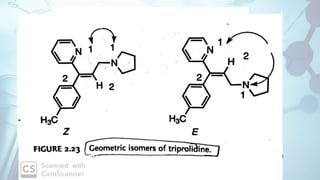
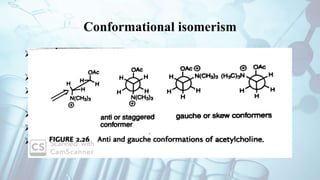
The document discusses the relationship between a drug's molecular structure and its biological activity. It covers key topics like how functional groups contribute to a drug's pharmacological effects, the role of receptors in drug selectivity and action, and how physicochemical properties like acidity and stereochemistry impact solubility, binding to targets, and a drug's overall activity. It provides examples to illustrate these structure-activity principles, which were established through seminal findings like Crum-Brown and Fraser's work with quaternary ammonium compounds and the discovery of acetylcholine by Loewi and Navrati.