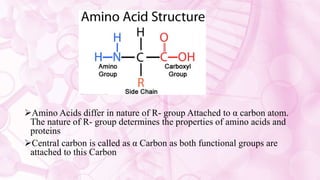
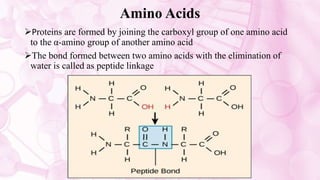
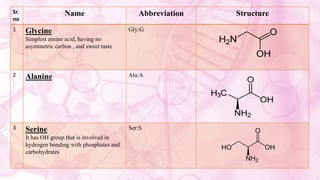
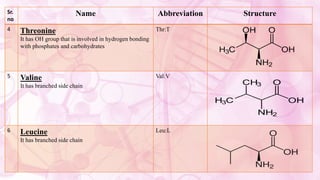
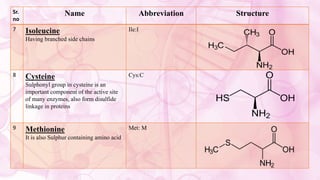
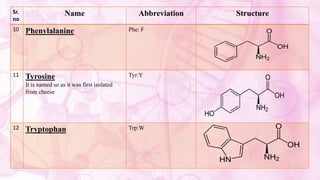
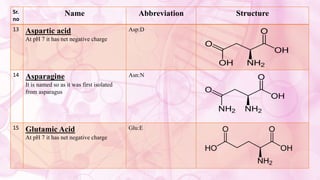
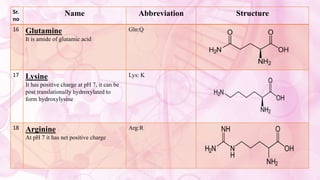
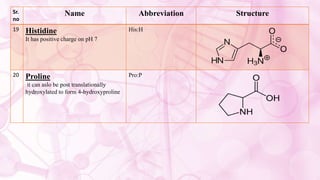
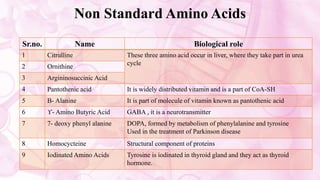
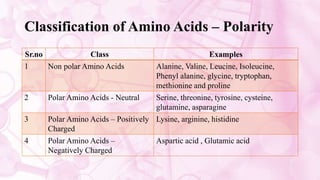
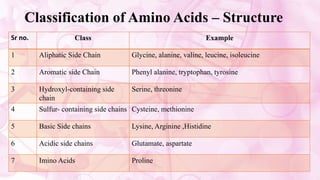
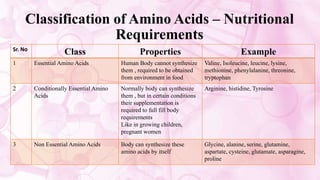
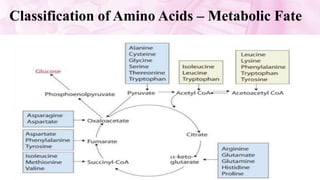
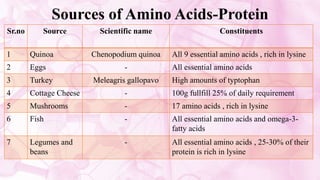
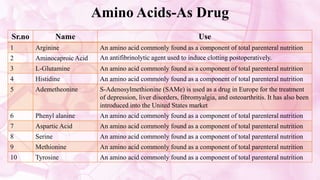
This document discusses amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. It defines amino acids as having both a carboxyl group and an amine group. There are 20 standard amino acids that commonly occur in proteins. Amino acids differ in their R groups, which determine the properties of amino acids and proteins. Proteins are formed by linking amino acids through peptide bonds formed by the elimination of water. The document also classifies amino acids based on polarity, structure, nutritional requirements, and metabolic fate. It discusses amino acid sources from foods like quinoa and eggs. Some amino acids are also used as drugs to treat conditions like depression and liver disorders. The document concludes with describing an extraction method for free amino acids from tomato