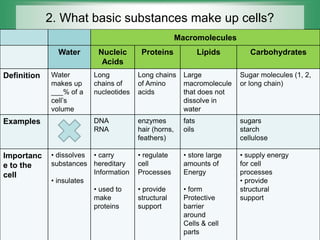
Cells are the smallest unit of life and all living things are composed of one or more cells. The three main components that make up cells are macromolecules, water, and nucleic acids. Macromolecules include proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates which provide structure, store energy, carry out functions, and act as protective barriers. Water makes up 70% of a cell's volume and is important for dissolving substances and insulation. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA carry hereditary information and help regulate cell processes.