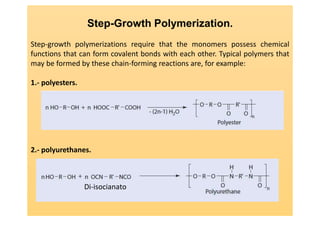
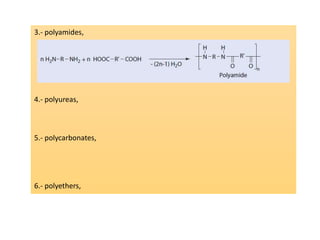
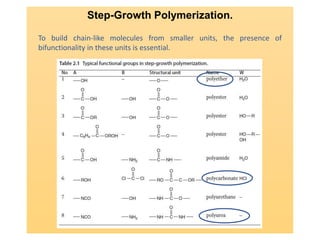
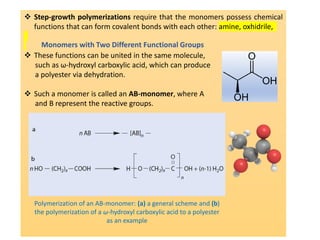
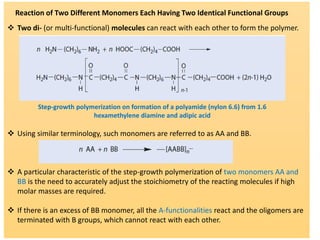
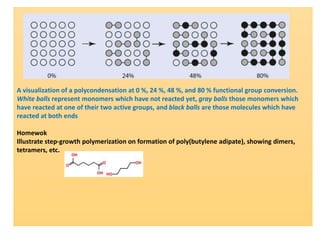
Step-growth polymerization requires monomers with reactive functional groups like amines, carboxylic acids, or alcohols that can form covalent bonds to build polymeric chains. Common polymers formed through step-growth include polyesters, polyurethanes, polyamides, and polycarbonates. The monomers must be bifunctional, containing two different reactive groups, like a carboxylic acid and alcohol that can undergo condensation polymerization to form the polymer backbone. The stoichiometry of the bifunctional monomers must be carefully controlled to achieve high molar masses.