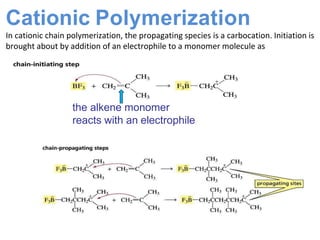
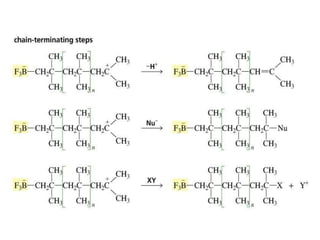
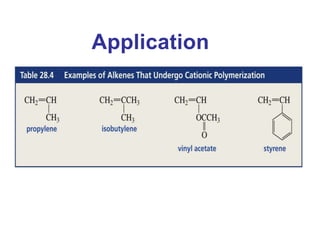
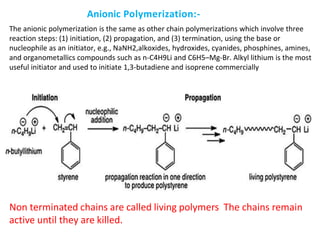
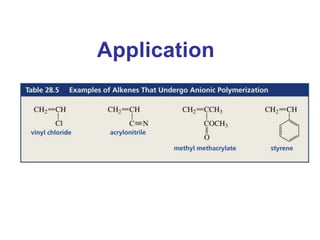
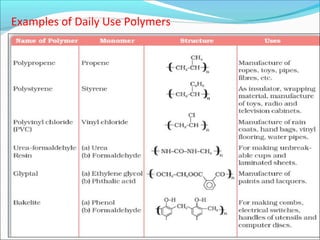
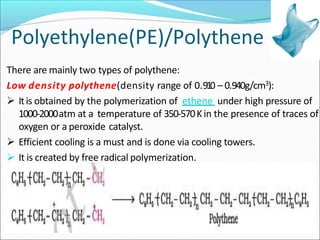
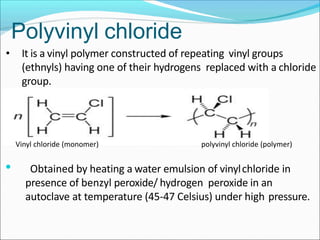
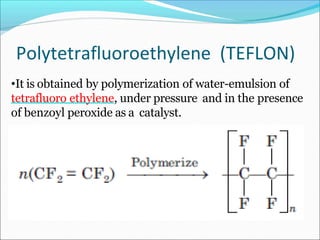
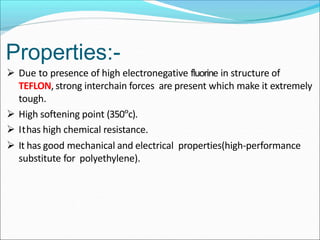
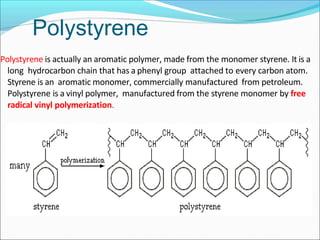
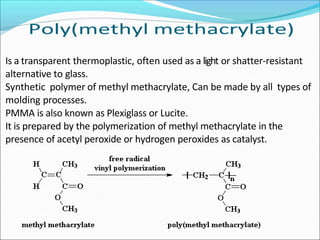
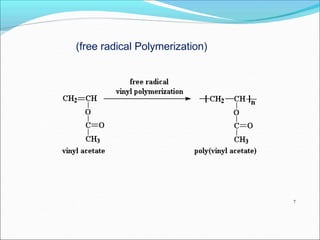
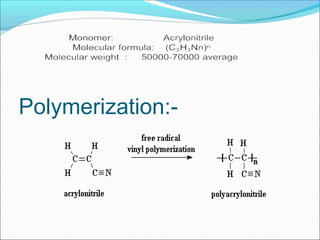
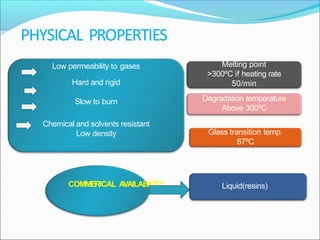
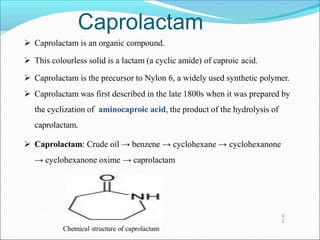
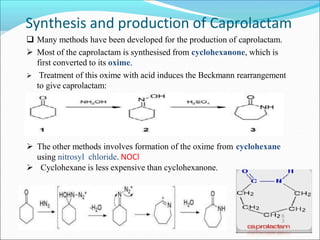
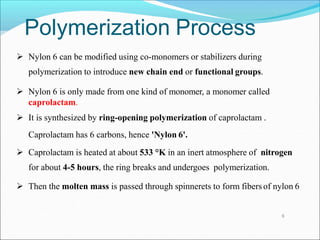
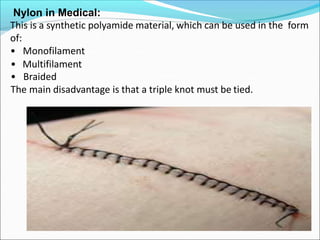
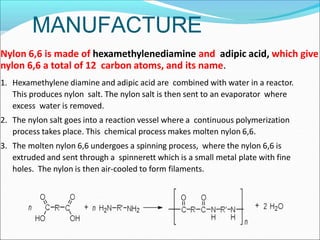
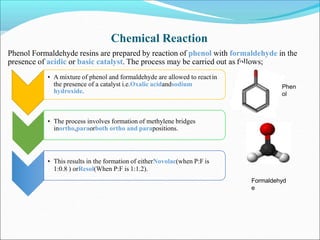
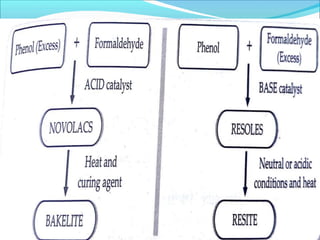
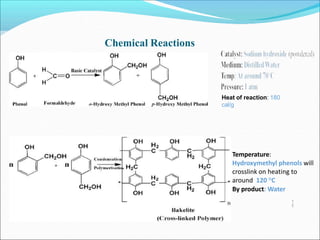
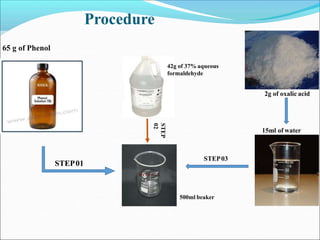
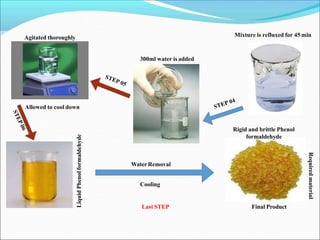
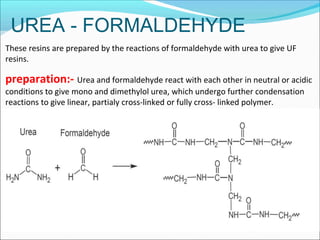
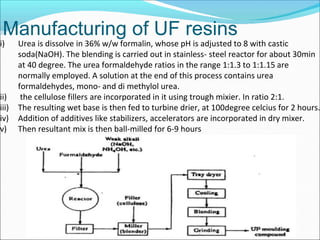
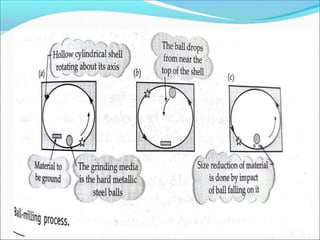
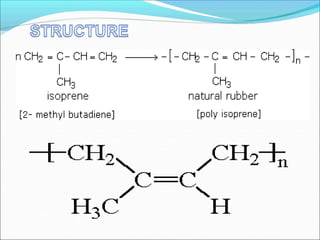
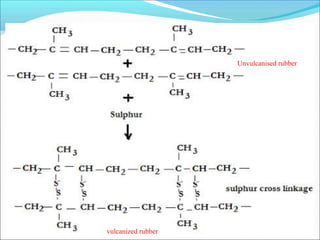
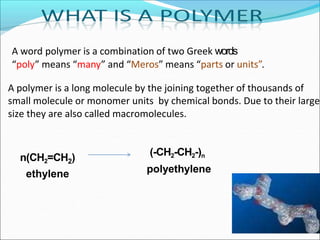
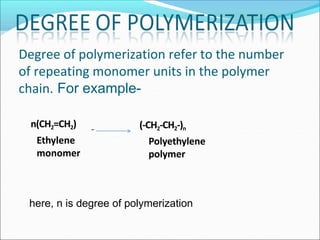
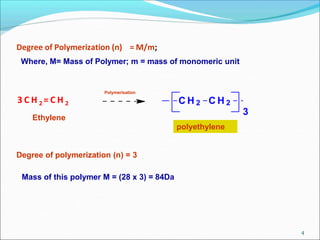
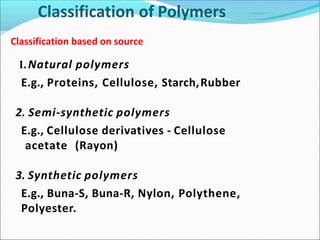
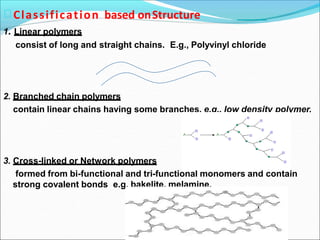
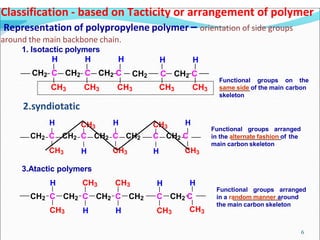
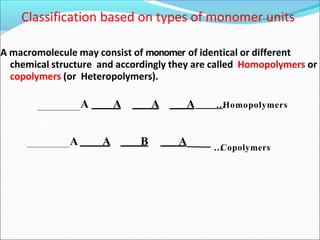
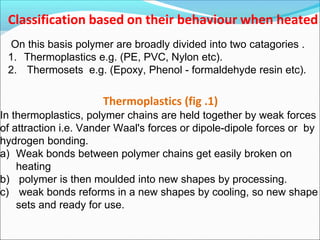
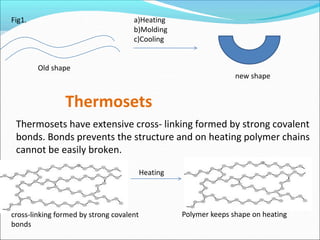
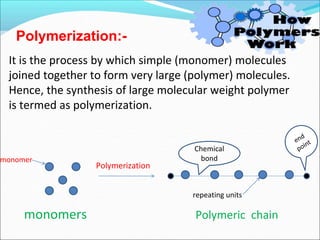
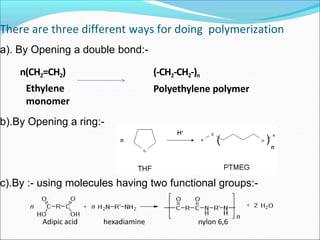
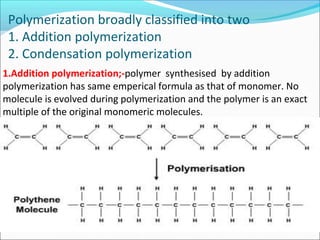
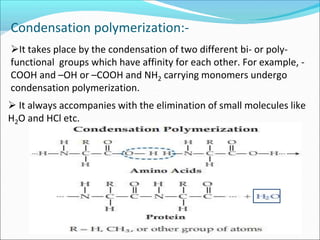
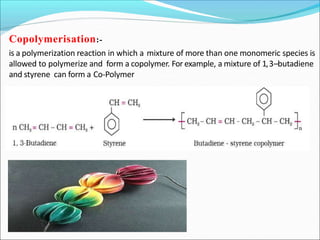
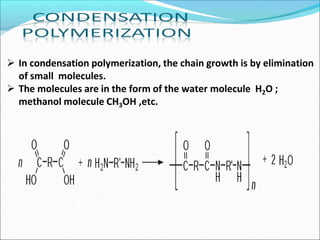
This document provides information about polymers and polymerization. It defines a polymer as a long molecule formed by joining thousands of small monomer units through chemical bonds. The degree of polymerization refers to the number of repeating monomer units in the polymer chain. Polymers can be classified based on their source, structure, tacticity, monomer units, end uses, conductance, environmental impact, and behavior when heated. The two main types of polymerization are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Examples of daily use polymers like polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, nylon, bakelite etc. are also discussed along with their properties and applications.
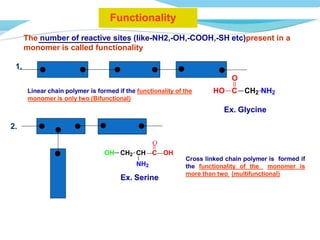


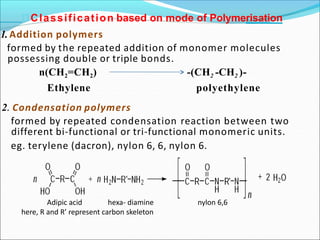
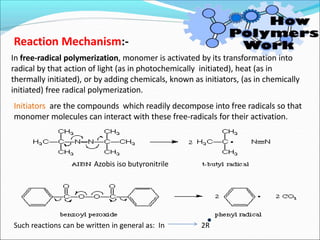

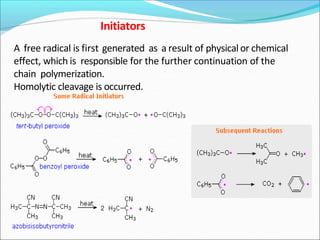
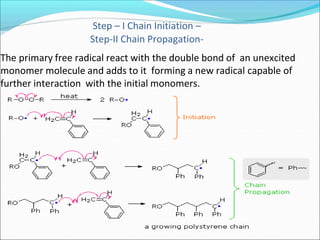
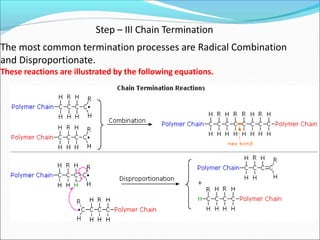
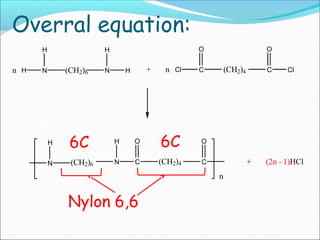
![It involves a repetitive condensation reaction between two bi- function monomer.
Example:- formation of Nylon 6,6
n HOOC(CH2)4COOH +nH2N(CH2)6NH2
[-N-(CH2)6-N-C(CH2)4-C-]n
H O
O
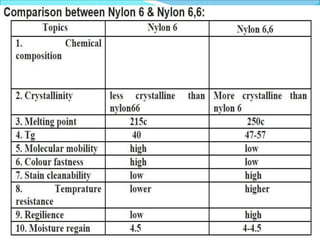
Nylon6,6
Step Growth polymerization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4polymerbt1011674199439-231012021204-c2e81e72/85/unit-4-polymer-BT101_1674199439-pptx-26-320.jpg)