1) Polymers are large molecules formed from the combination of small molecules called monomers through a process called polymerization.
2) Polymerization is initiated by a reactive site on a monomer that is produced using an initiator. This allows monomers to add onto a growing polymer chain.
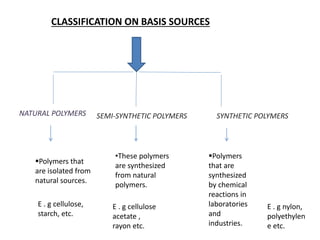
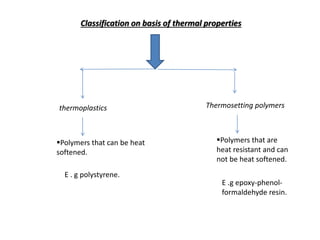
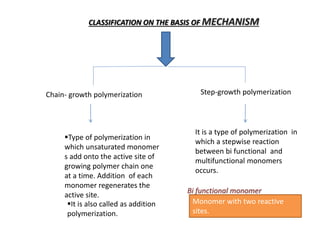
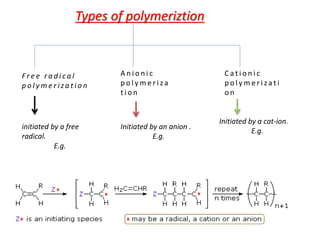
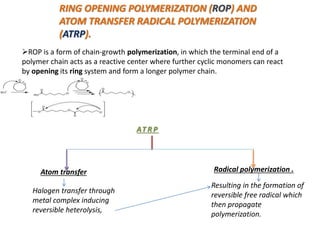
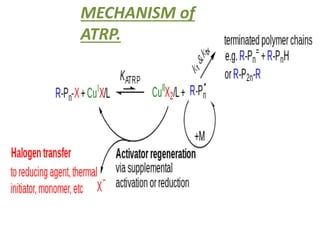
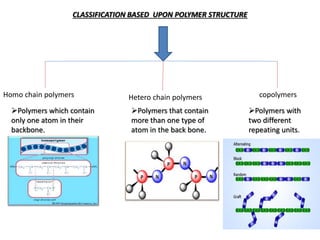
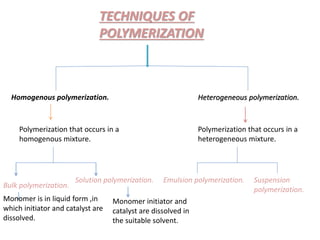
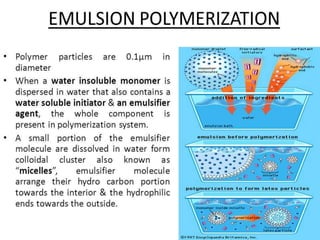
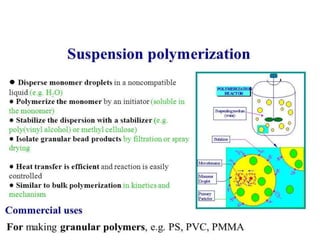
3) Polymers are classified based on their source, thermal properties, polymerization mechanism, and structure. Some examples of polymerization mechanisms discussed are chain-growth, step-growth, free radical, anionic, and cationic polymerization.