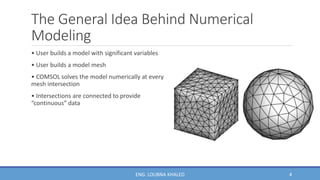
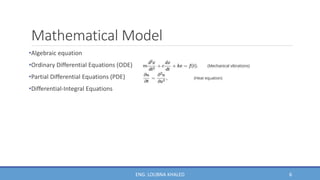
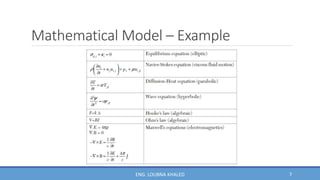
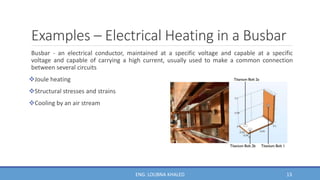
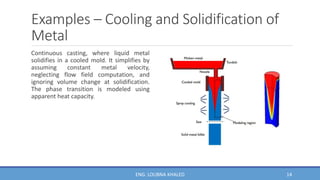
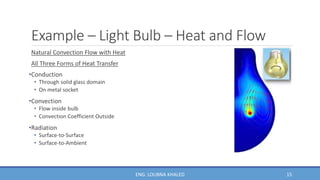
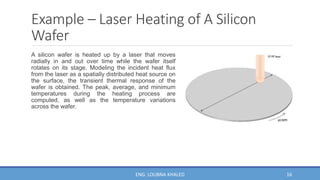
COMSOL Multiphysics is finite element analysis software that can model various physics and engineering applications, especially coupled phenomena involving multiple physical fields. It allows users to build numerical models by defining variables, building meshes, and solving models at mesh intersections. Models can represent systems using algebraic equations, ordinary differential equations, partial differential equations, or other mathematical relationships. COMSOL can then simulate these models to analyze effects like heat transfer, fluid flow, electromagnetics, and more across engineering disciplines.