The document discusses the architecture of WiMAX networks, including:
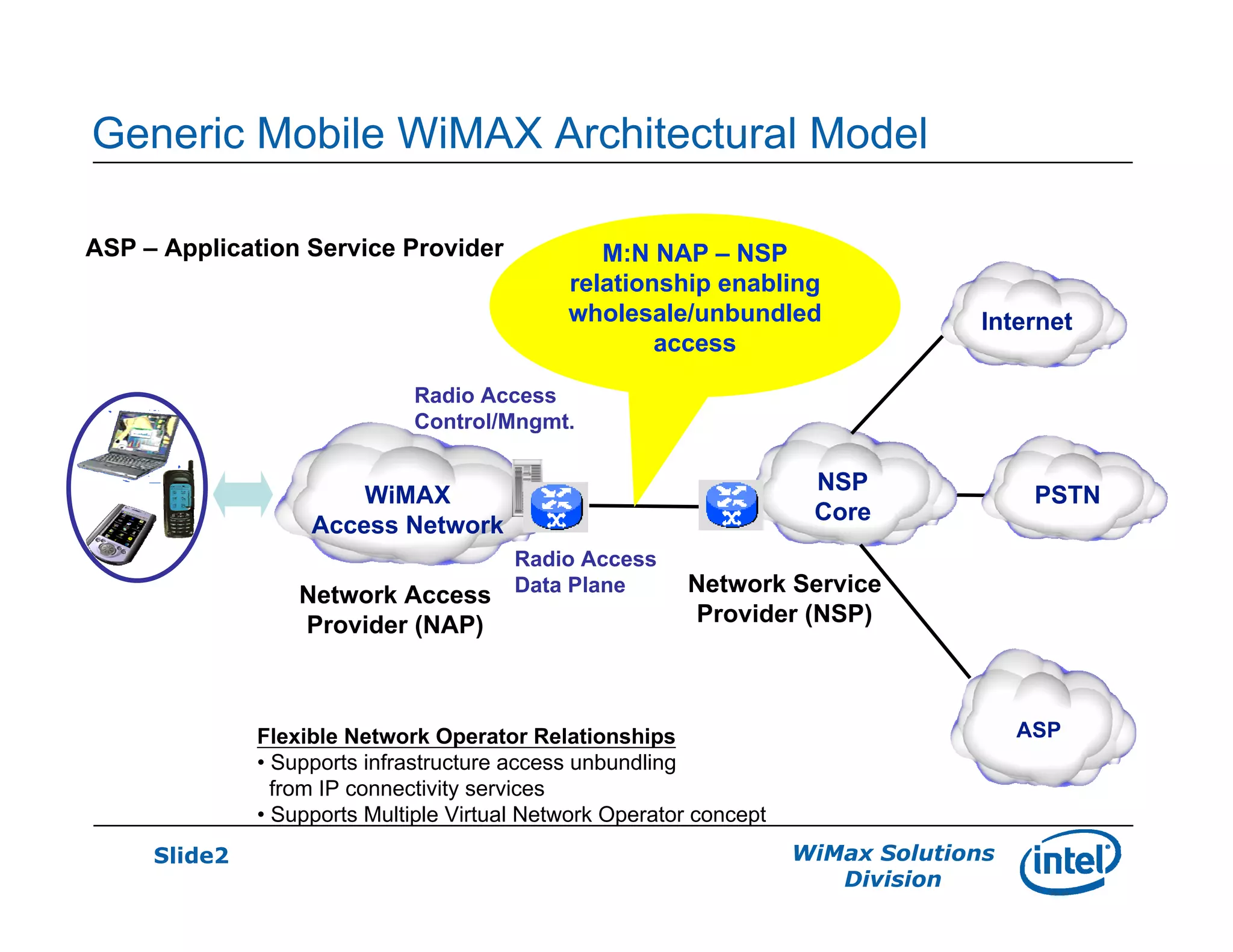
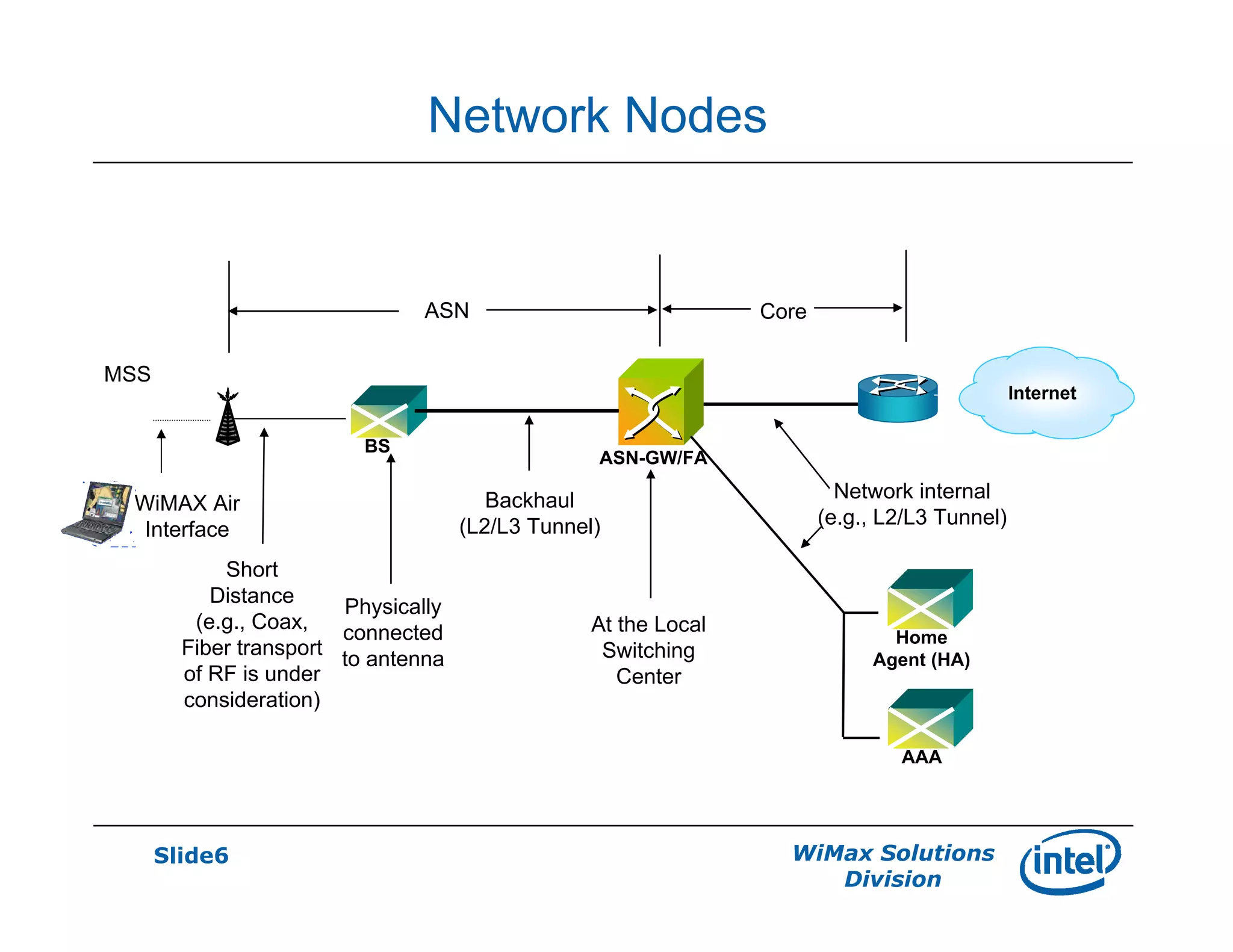
- The generic mobile WiMAX architectural model includes an access network, core network, and application service providers with flexible relationships between network operators.
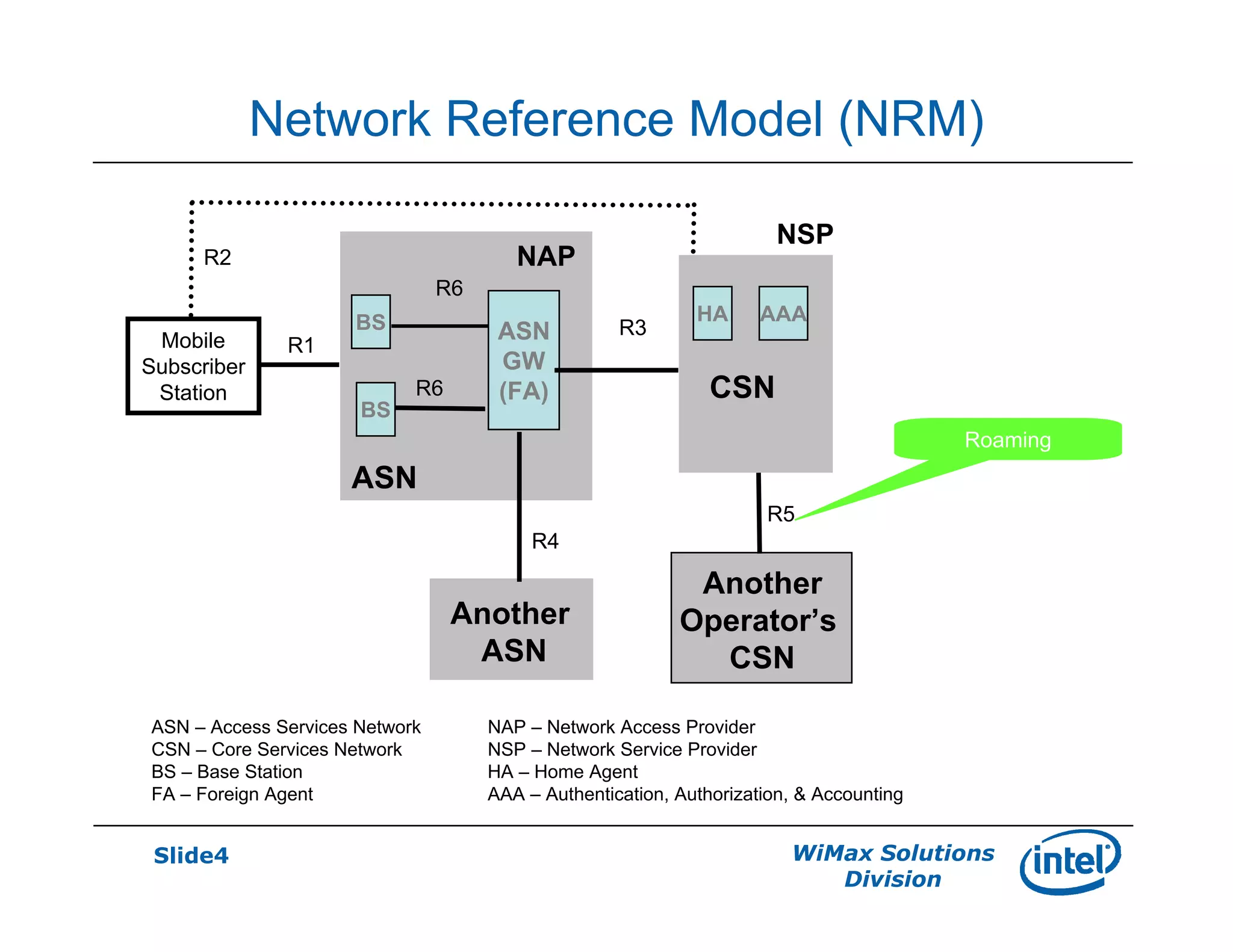
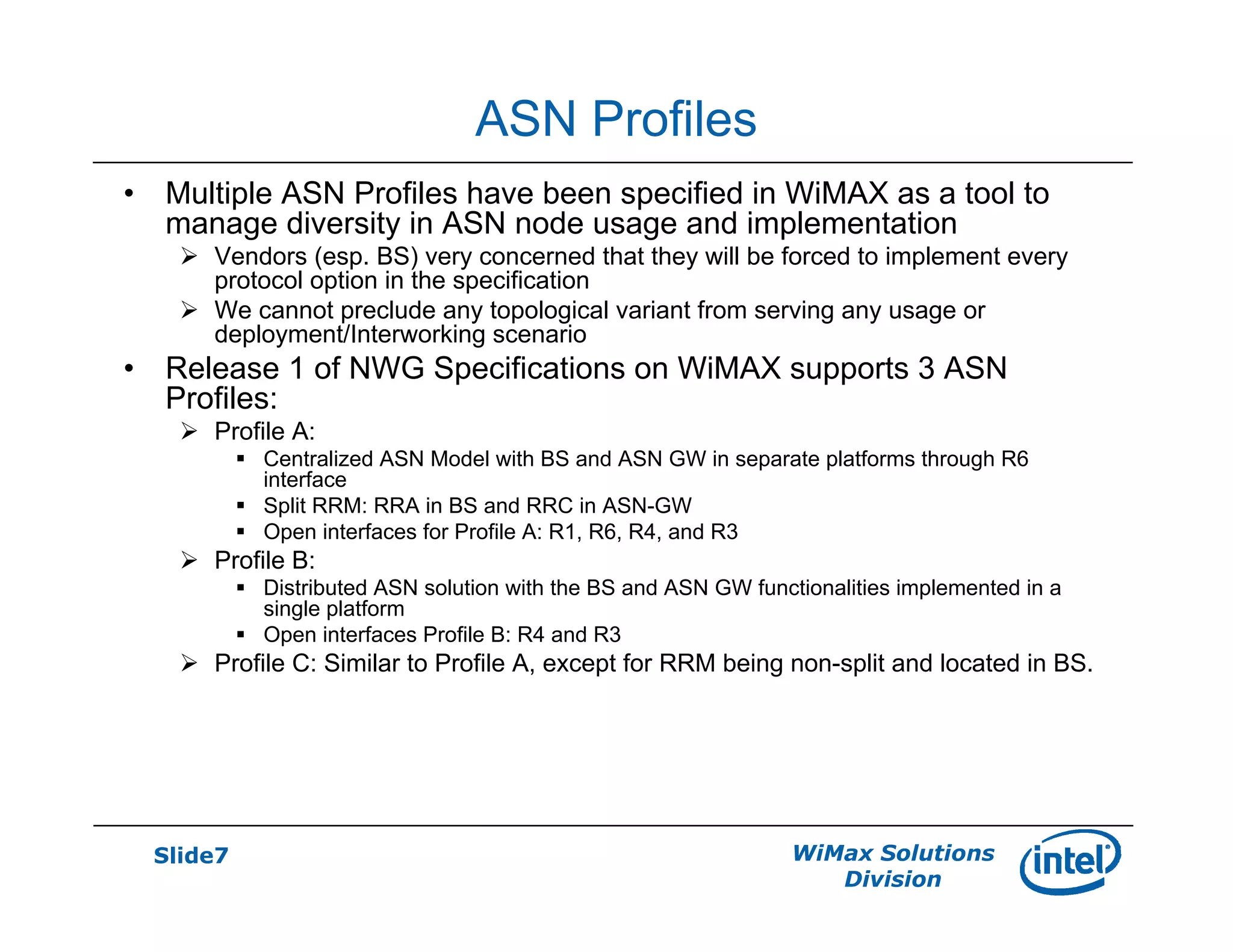
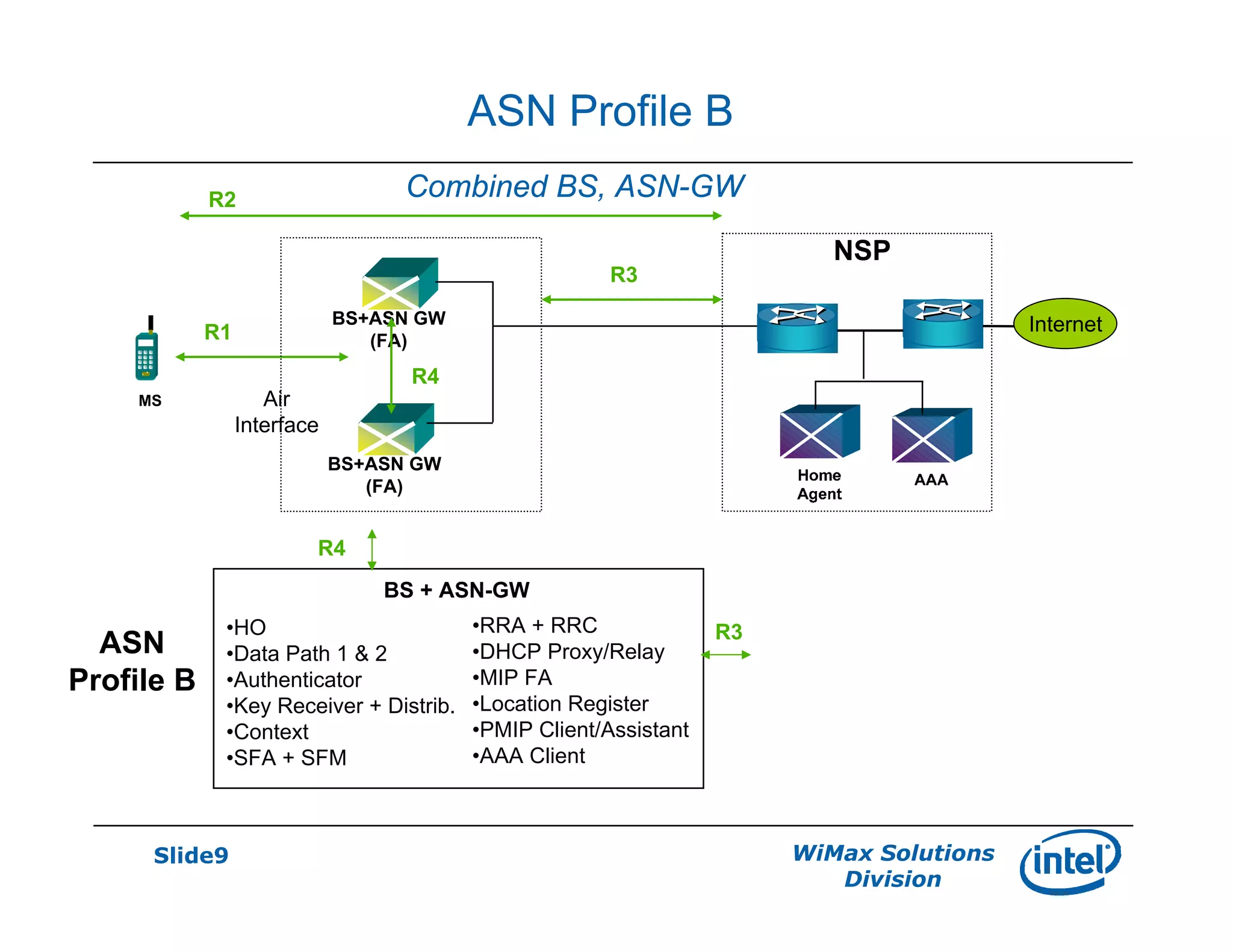
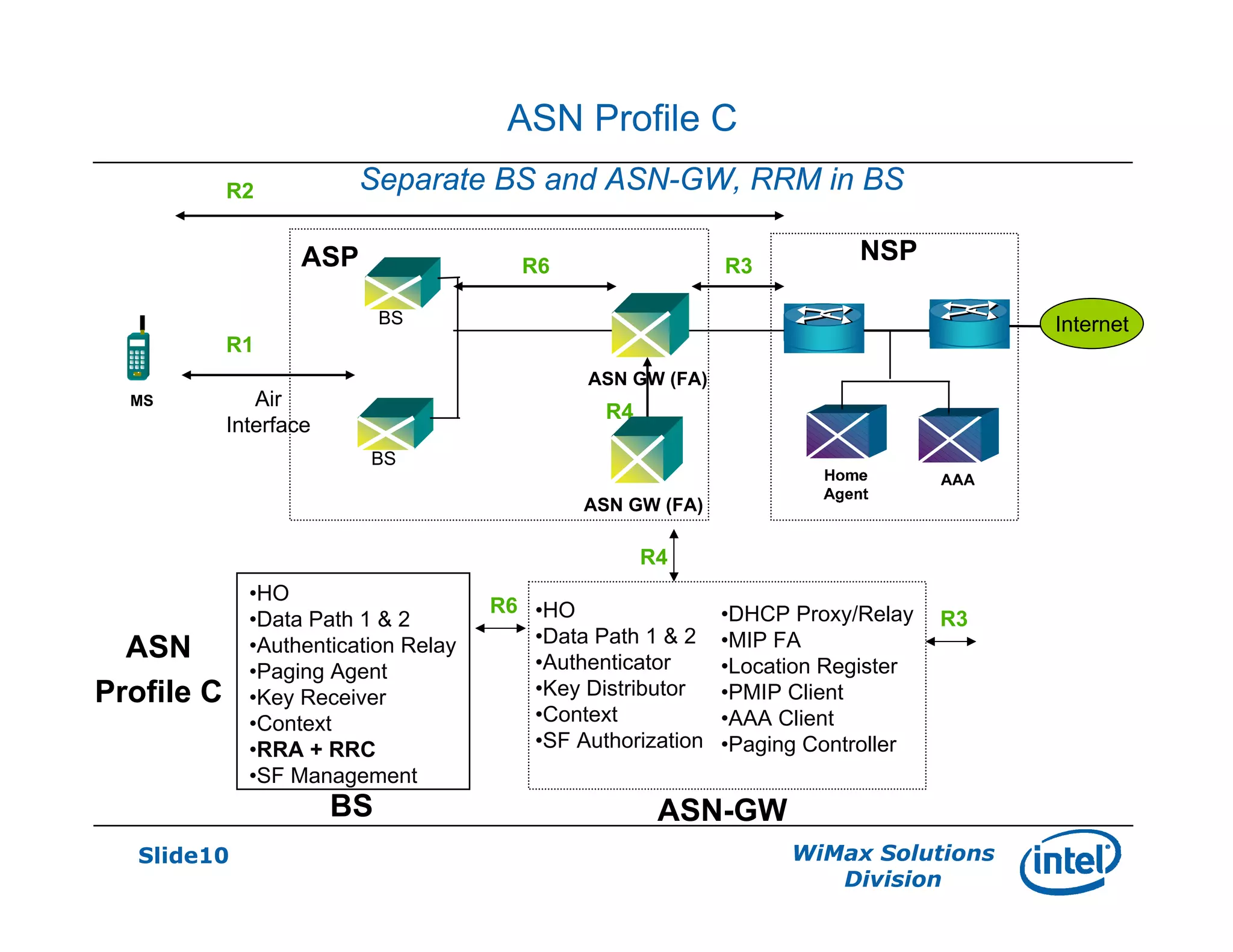
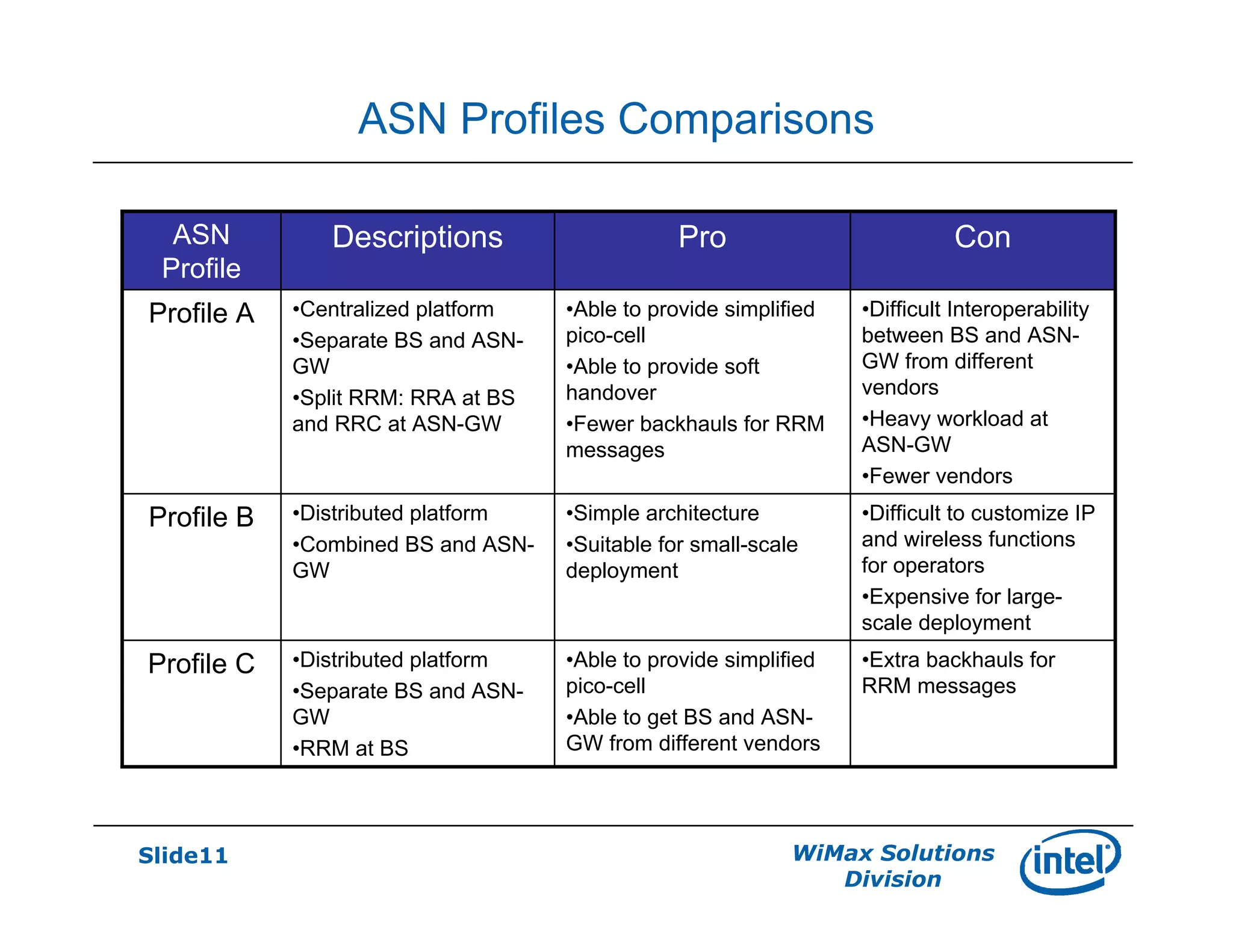
- There are three defined ASN profiles - Profile A with separate BS and ASN-GW, Profile B with combined BS and ASN-GW, and Profile C similar to Profile A but with RRM functions in the BS.
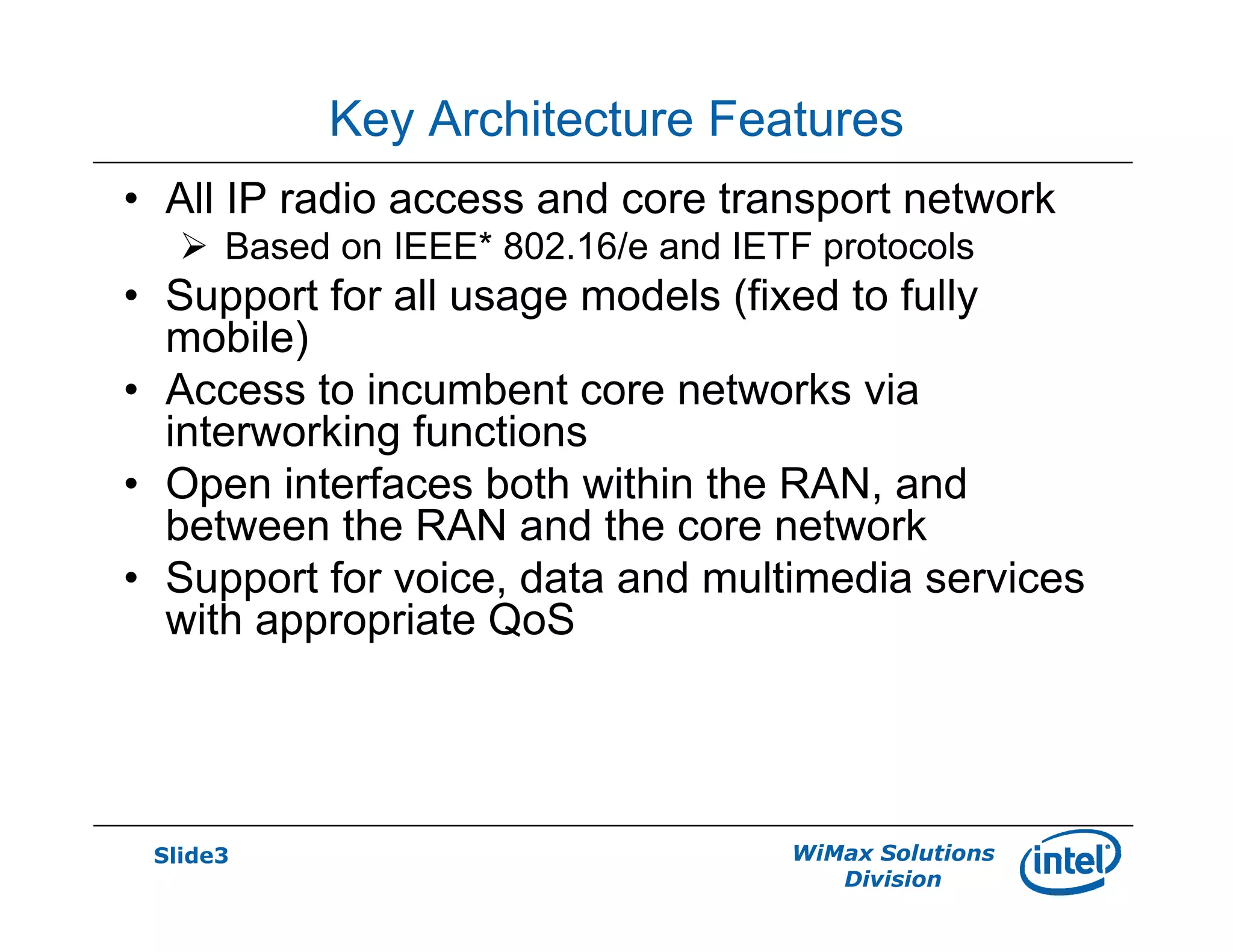
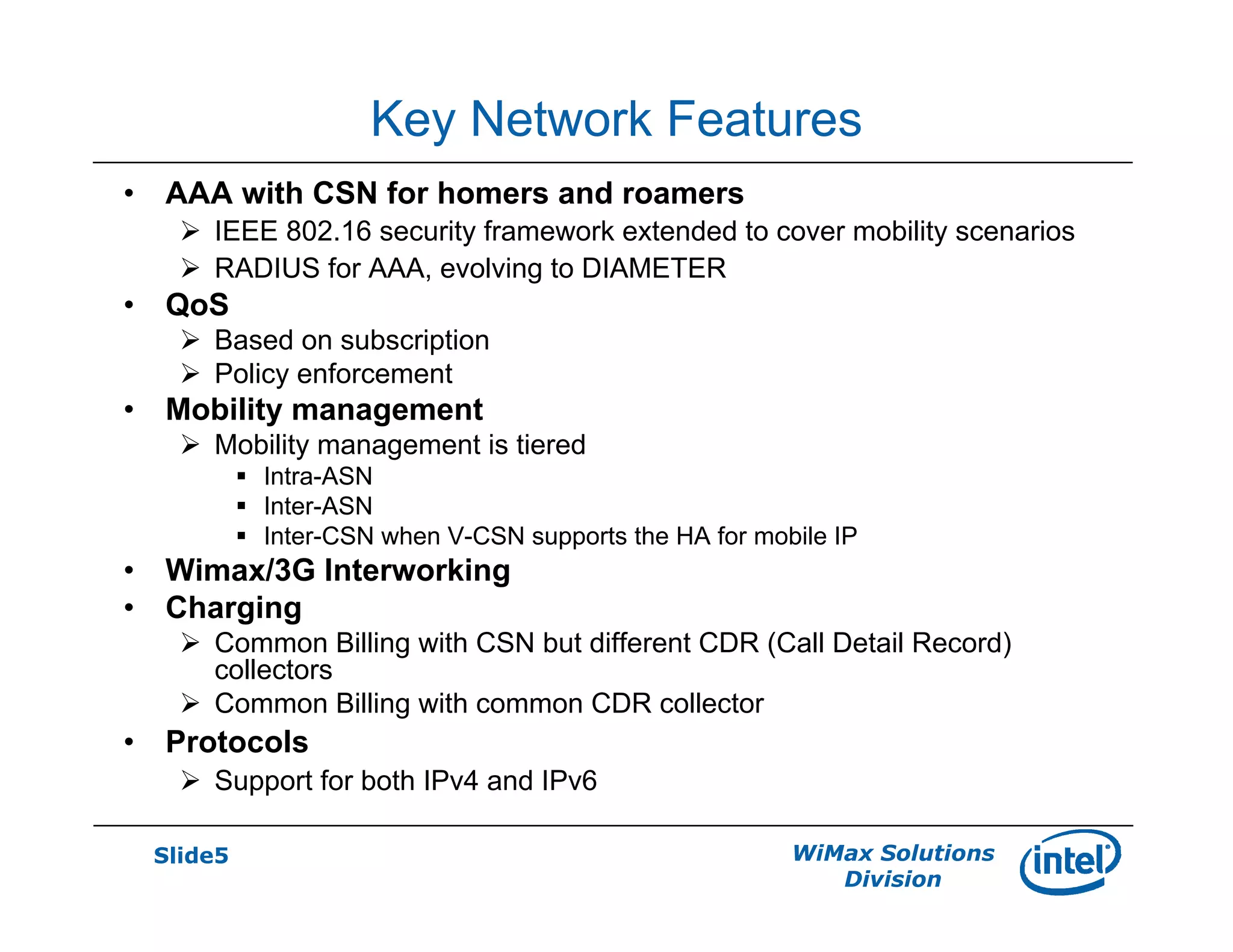
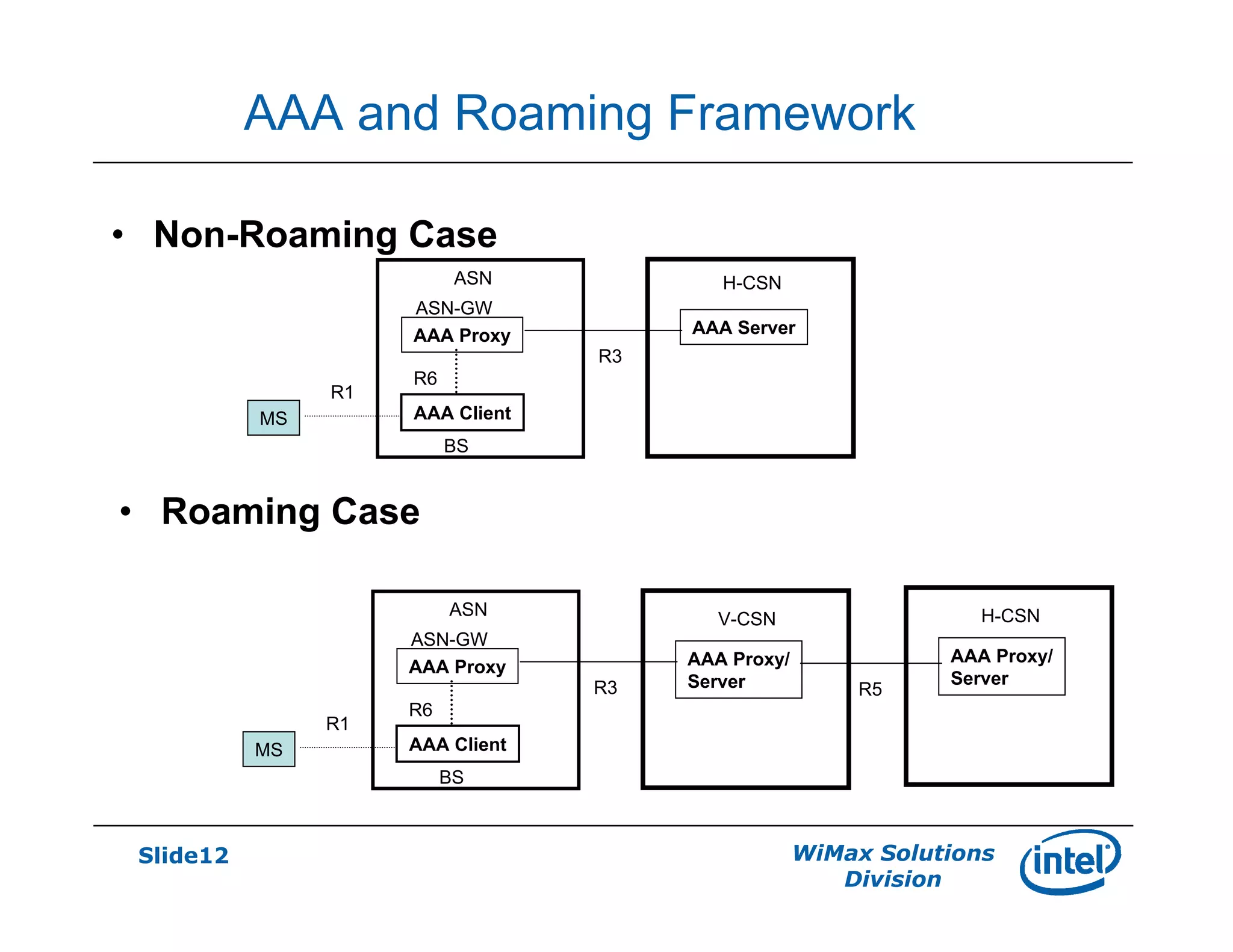
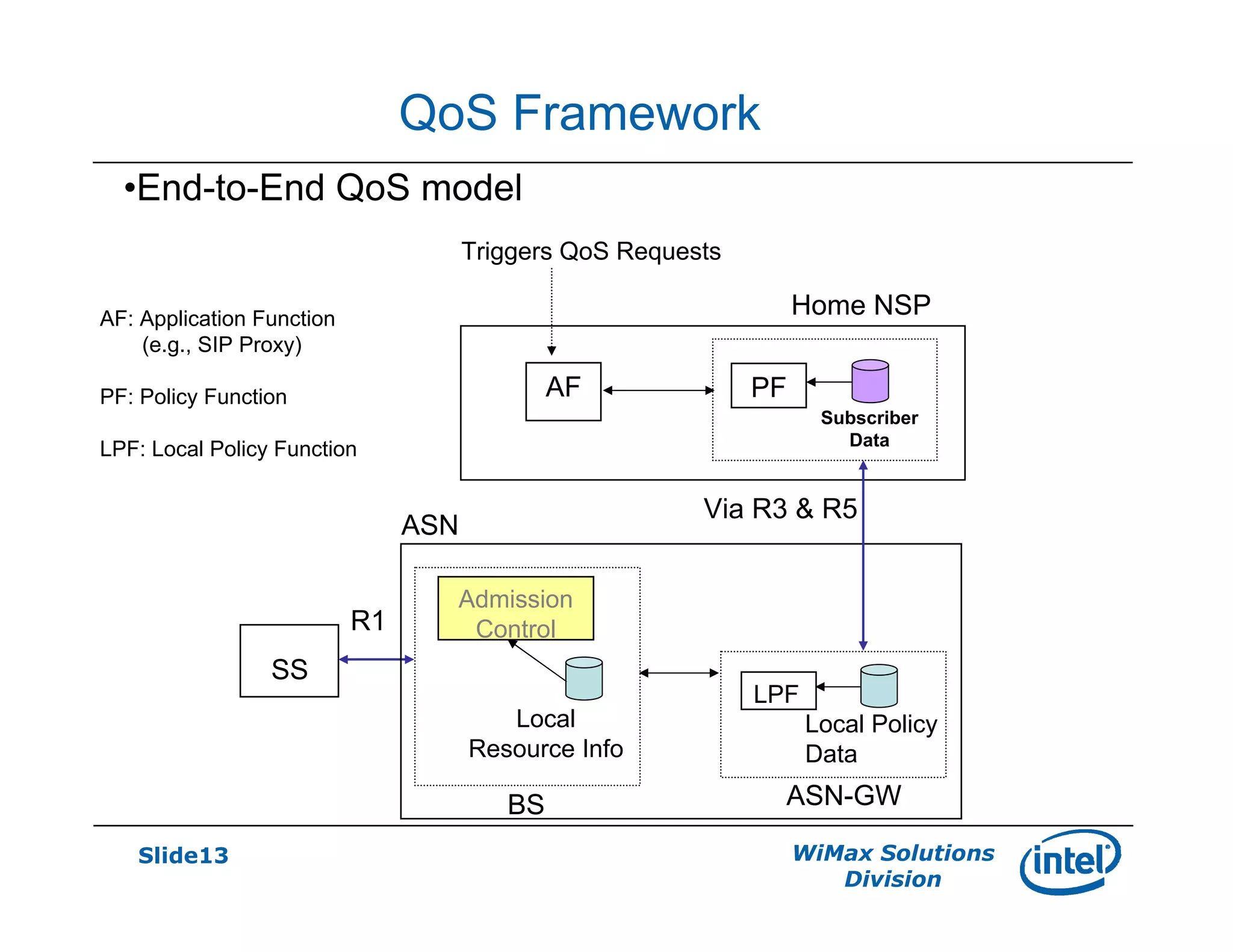
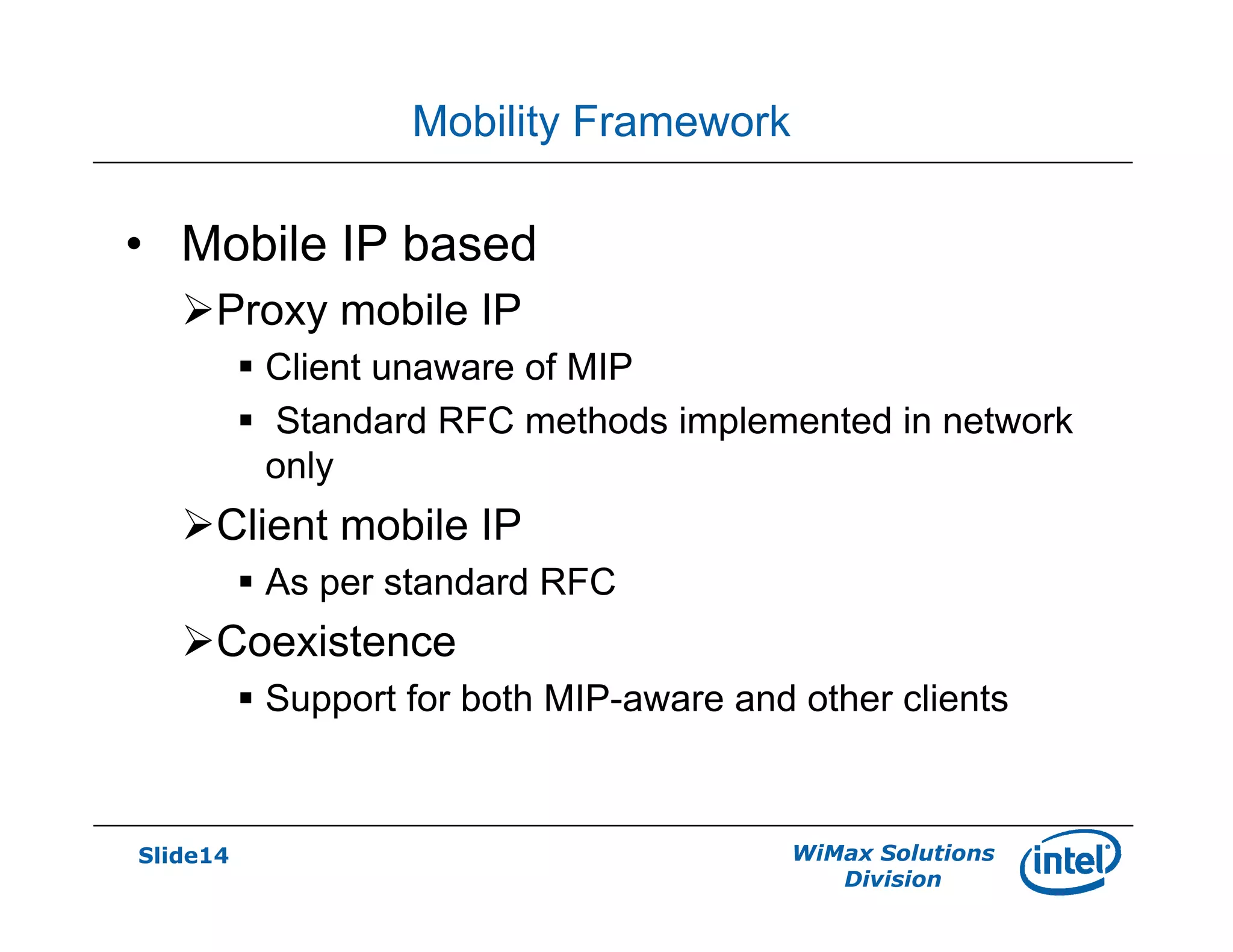
- Key network features discussed include AAA and roaming frameworks, QoS framework, and mobility framework based on mobile IP or proxy mobile IP.
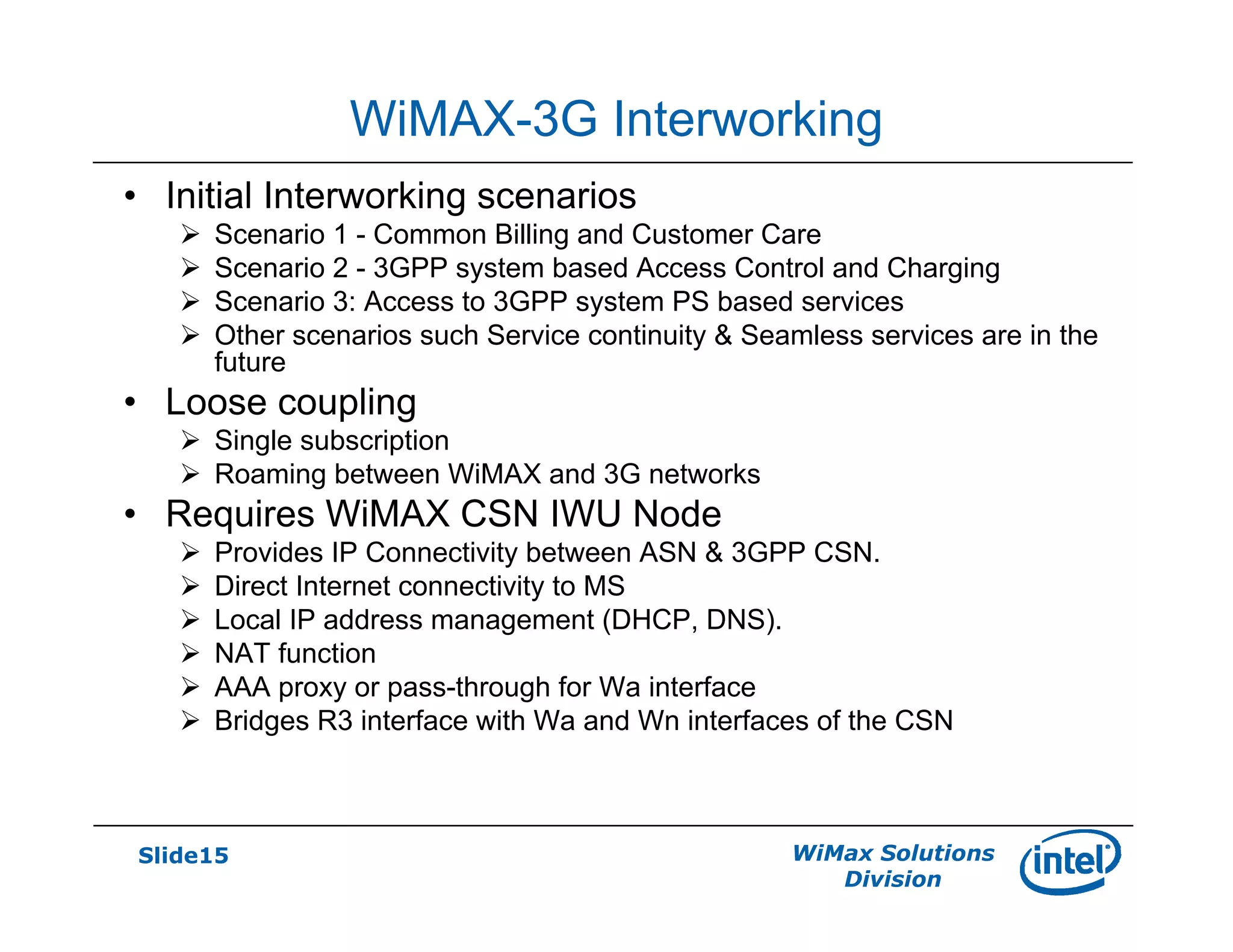
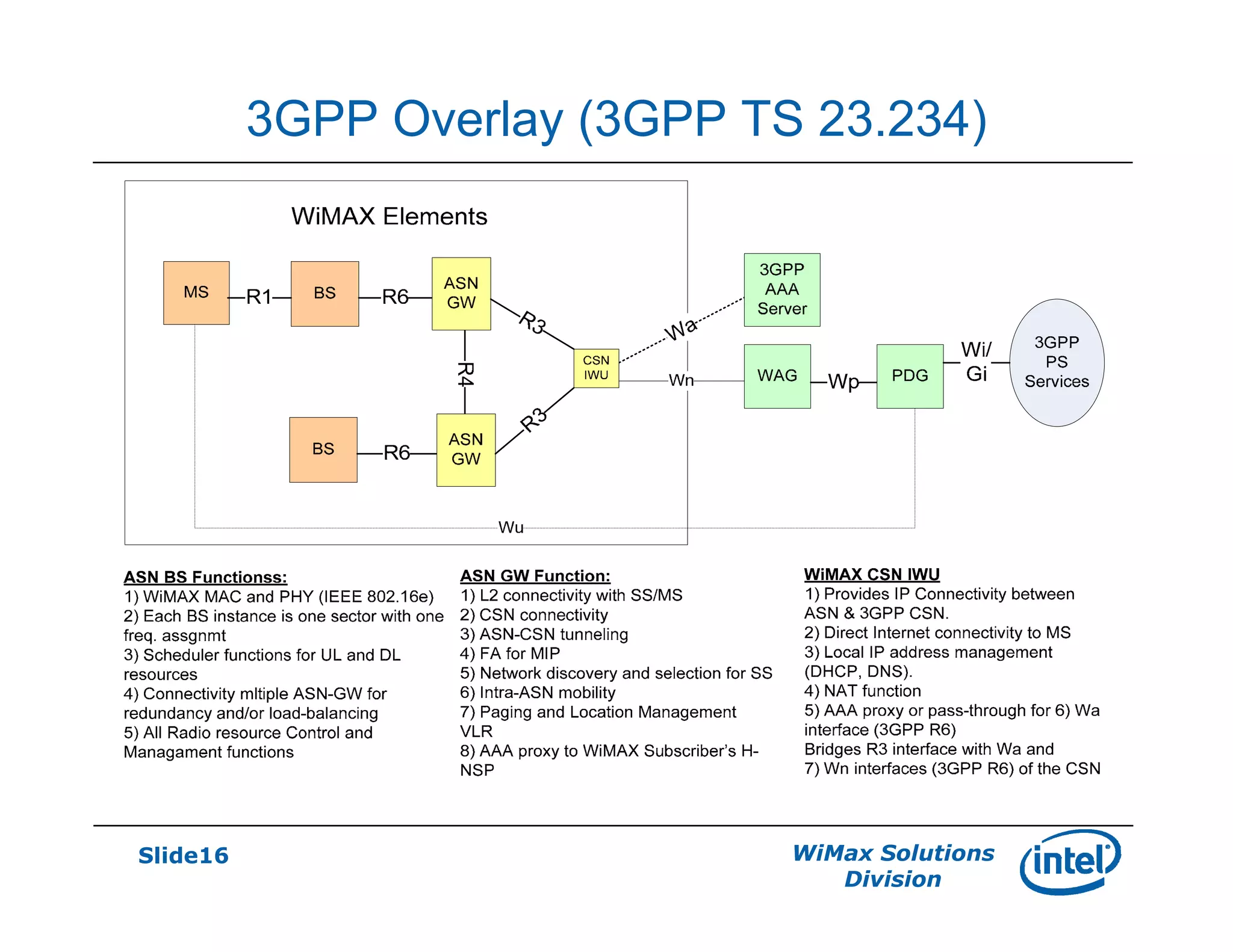
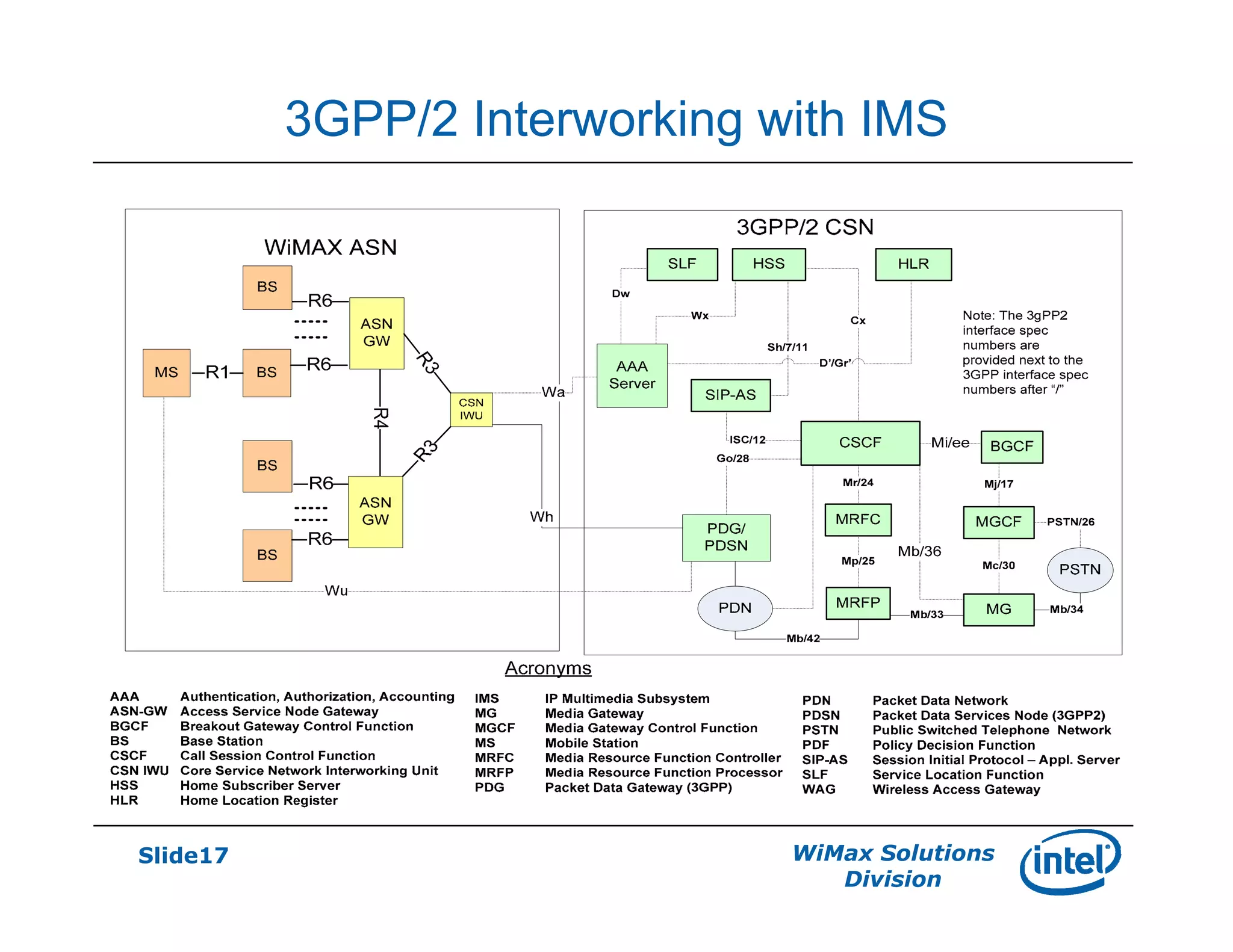
- Interworking with 3G networks is also described, including common billing scenarios and using a WiMAX CSN I