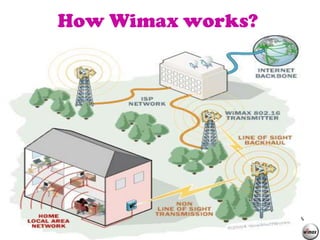
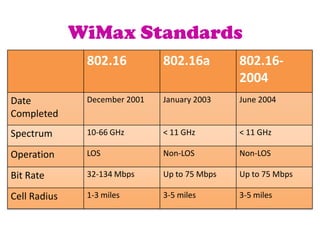
WiMAX is a wireless technology that provides broadband connections over long distances. It uses radio waves in the 2-11 GHz range to transmit data, allowing it to provide coverage over large areas of up to 50 km from the base station. WiMAX was developed to provide wireless internet access similar to cable or DSL but over longer distances and in more rural areas. It allows for speeds of up to 70 Mbps and can support both fixed and mobile broadband applications. While WiFi is better suited for short range indoor use due to its lower power and speeds of up to 54 Mbps.