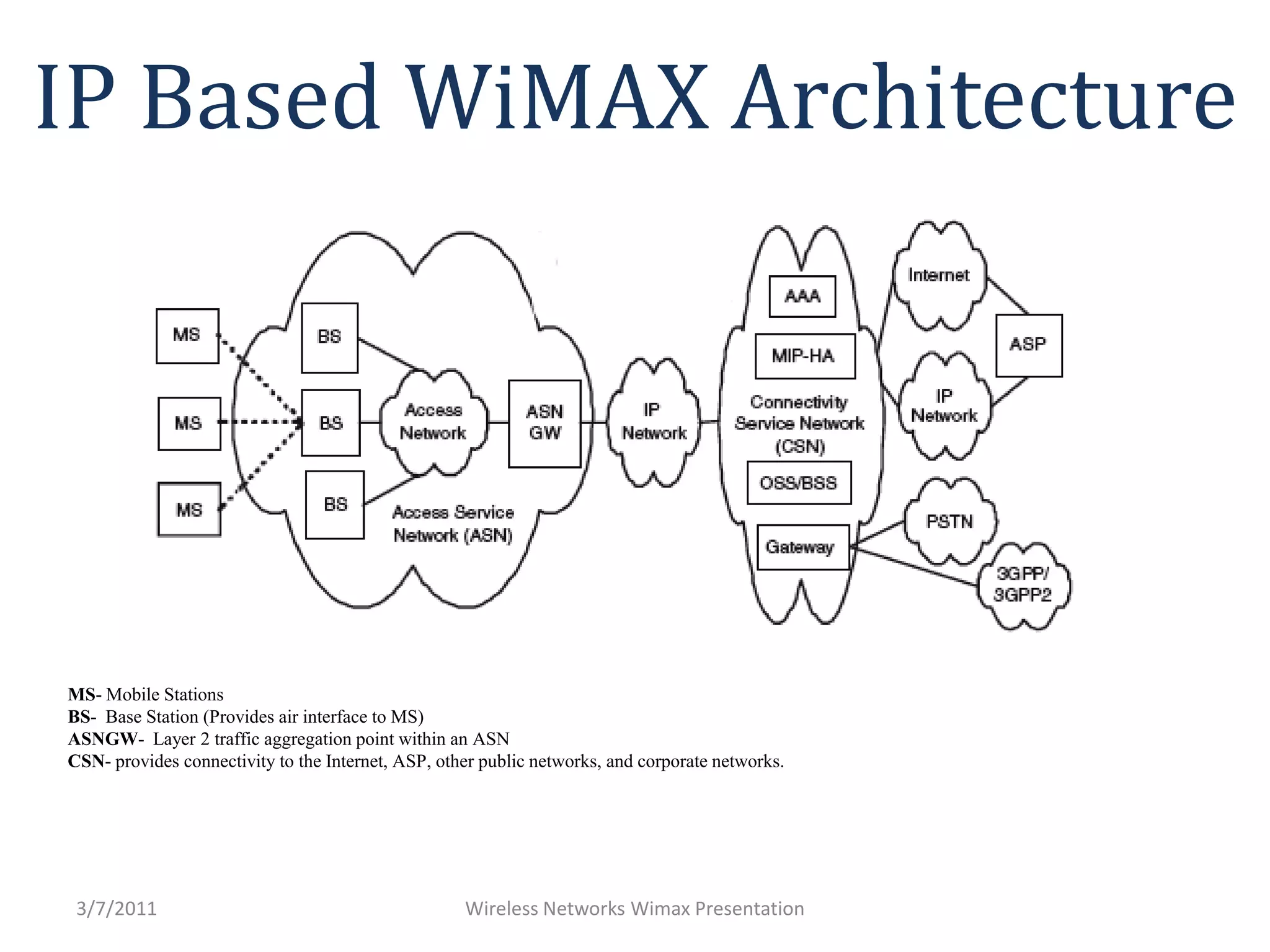
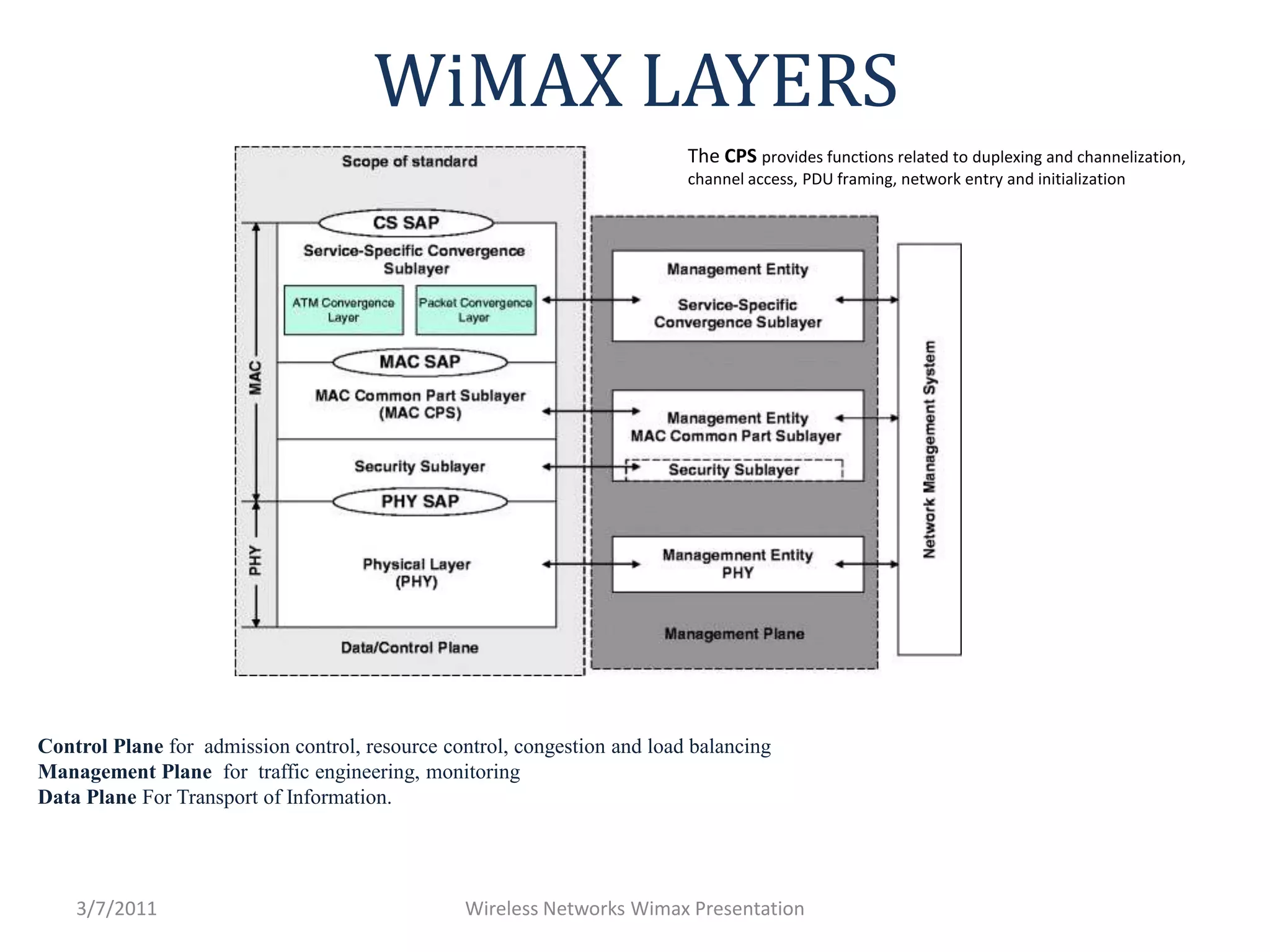
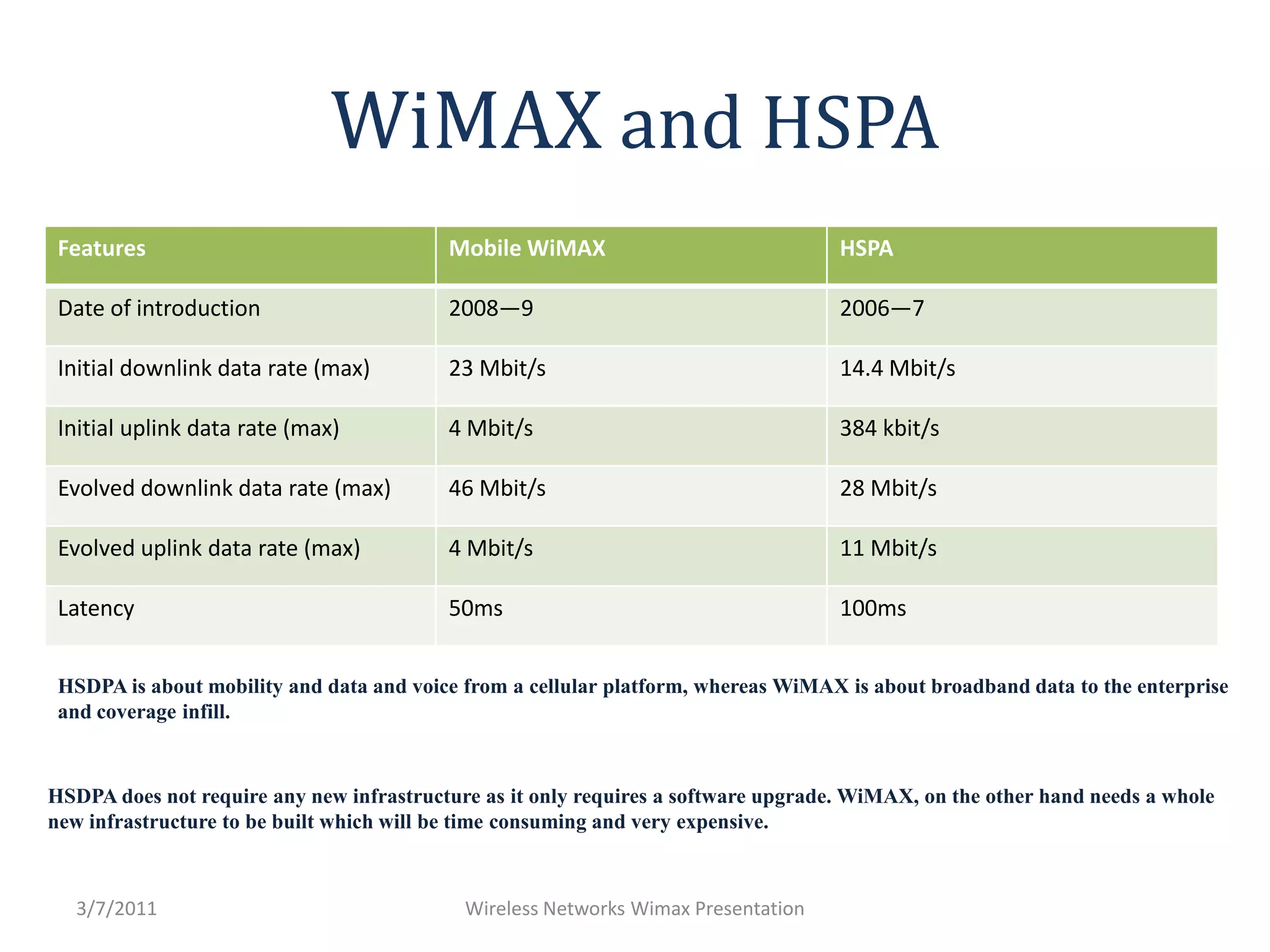
WiMAX uses OFDM and smart antennas to improve performance. It provides QoS and improved security. The architecture includes mobile stations, base stations, an access service network gateway for traffic aggregation, and a connectivity service network for internet/network access. WiMAX antennas can be omnidirectional, sectoral, or panel designs. The protocol layers include the control, management, and data planes. OFDMA dynamically allocates bandwidth across frequency channels. While HSPA focuses on cellular mobility and data/voice, WiMAX provides broadband data through a new infrastructure.