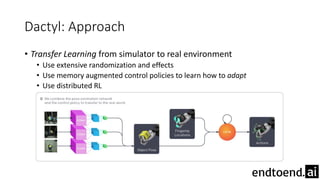
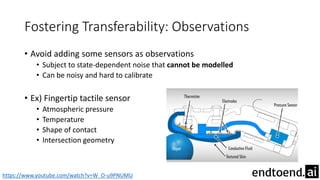
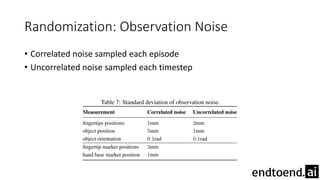
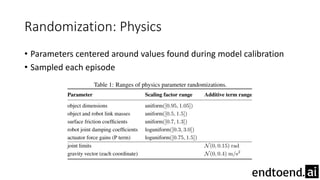
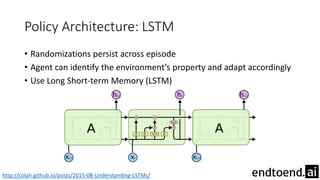
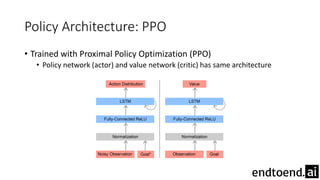
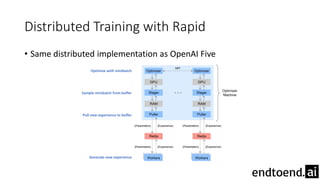
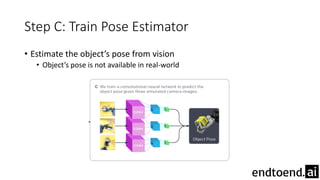
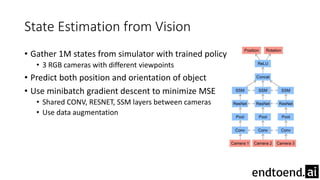
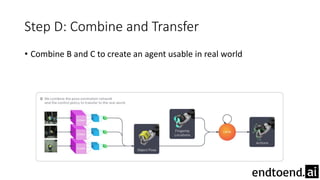
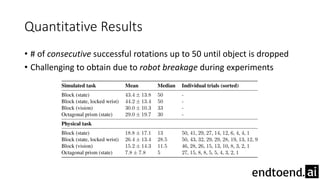
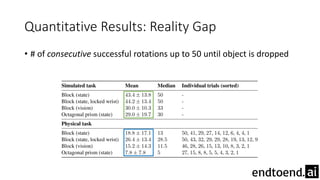
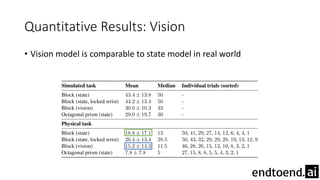
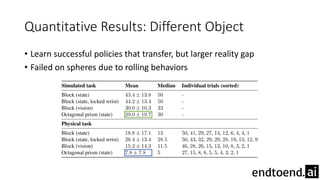
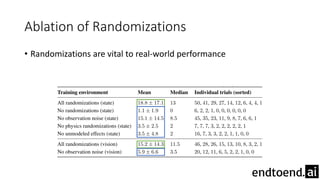
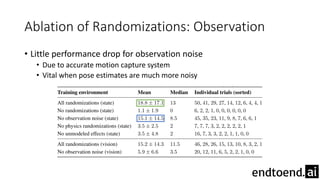
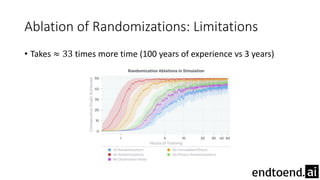
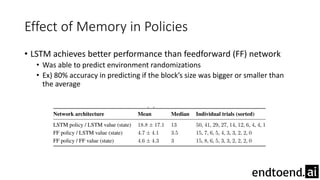
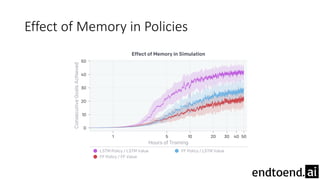
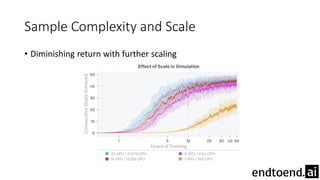
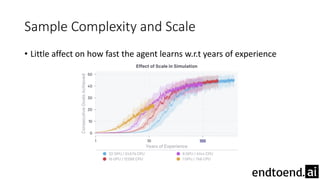
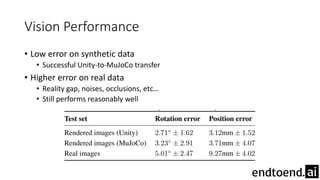
This document summarizes research on training a robot hand to perform dexterous in-hand manipulation tasks. The researchers used a simulation environment to generate large amounts of training data and trained a policy using reinforcement learning and domain randomization. They found the policy could transfer to controlling a real robot hand to successfully reorient objects, even generalizing to new objects. Key aspects that improved transferability included randomizing the simulation, using memory in the policy network, and training a vision model to estimate object pose without sensors.