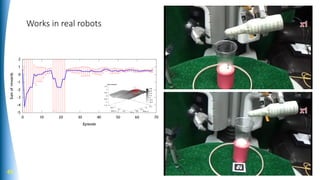
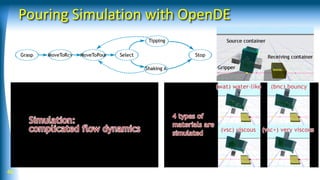
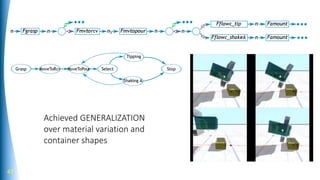
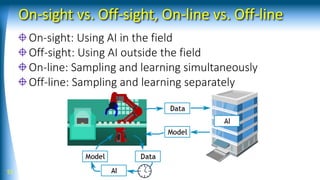
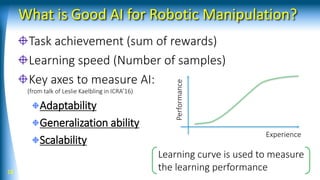
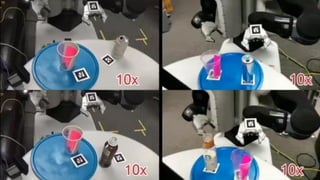
The document summarizes a talk on AI-based robotic manipulation. It introduces the speaker's work using AI for robotic tasks. Some key challenges in robotic manipulation are handling variations in objects, situations, and tasks. Deep reinforcement learning is discussed as a promising approach, though it still faces difficulties with simulation biases and lack of generalizable skills. The talk argues that a hybrid model-based and model-free reinforcement learning approach using a library of reusable skills could help with generalization. While progress is being made, many breakthroughs are still needed in areas like perception, integration of structured knowledge, and hybrid reinforcement learning approaches before human-level robotic manipulation is achieved.




















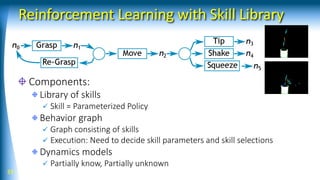
![Pouring Behavior with Skill Library
Skill library
flow ctrl (tip, shake, …), grasp, move arm, …
State machines (structure, feedback control)
Planning methods
grasp, re-grasp, pouring locations,
feasible trajectories, …
Optimization-based approach
Learning methods
Skill selection Table, Softmax
Parameter adjustment
(e.g. shake axis) Optimization (CMA-ES)
Improve plan quality Improve value functions25 [Yamaguchi et al. IJHR 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-25-320.jpg)






![Model-based RL vs. Model-free RL
34
[Reinforcement Learning]
[Direct Policy Search] [Value Function-based]
[Model-based]
[Model-free]
RL RL SL
[Dynamic Programming][Optimization]
Planning
depth
Learning
complexity
[Policy] [Value Functions] [Forward Models]What is
learned
0 1 N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-34-320.jpg)
![Model-free is tend to obtain better performance
35
[Kober,Peters,2011] [Kormushev,2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-35-320.jpg)

![Model-based is suffered from simulation biases
37
Simulation bias: When forward models are inaccurate (usual when
learning models), integrating the forward models causes a rapid
increase of future state estimation errors
cf. [Atkeson,Schaal,1997b][Kober,Peters,2013]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-37-320.jpg)
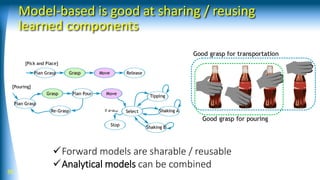
![Model-based is good at generalization
38
input
output
hidden
- u
update
FK ANN
Learning inverse kinematics of android face
[Magtanong, Yamaguchi, et al. 2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-38-320.jpg)
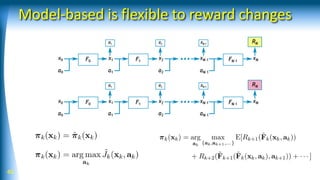
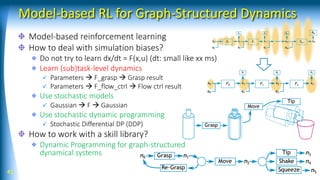
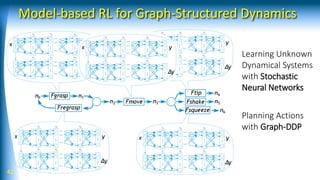
![43 [Yamaguchi and Atkeson, ICRA 2016]
Stochastic Neural Networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-43-320.jpg)
![44
Graph-DDP
[Yamaguchi and Atkeson, Humanoids 2015, 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rsj18-180423121453/85/AI-based-Robotic-Manipulation-44-320.jpg)