5.4 lecture 2019
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•278 views
Chapter 5.4 Notes
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Genome size, organization,& gene regulation in prokaryotes (lac-operon)

Genome size, organization,& gene regulation in prokaryotes (lac-operon)
Similar to 5.4 lecture 2019
Similar to 5.4 lecture 2019 (20)
lecture3geneticcontrolcellreproduction-180702011658.pdf

lecture3geneticcontrolcellreproduction-180702011658.pdf
1.introduction to genetic engineering and restriction enzymes

1.introduction to genetic engineering and restriction enzymes
Development biology (rna processing and translational regulation of developme...

Development biology (rna processing and translational regulation of developme...
Chapter 20 Molecular Genetics Lesson 2 - Genes_Transcription and Translation

Chapter 20 Molecular Genetics Lesson 2 - Genes_Transcription and Translation
104 Genetics and cellular functionLearning Objective.docx

104 Genetics and cellular functionLearning Objective.docx
More from alexsong2018
More from alexsong2018 (19)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Introduction,importance and scope of horticulture.pptx

Introduction,importance and scope of horticulture.pptx
Justdial Call Girls In Indirapuram, Ghaziabad, 8800357707 Escorts Service

Justdial Call Girls In Indirapuram, Ghaziabad, 8800357707 Escorts Service
Locating and isolating a gene, FISH, GISH, Chromosome walking and jumping, te...

Locating and isolating a gene, FISH, GISH, Chromosome walking and jumping, te...
High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...

High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...
Chemical Tests; flame test, positive and negative ions test Edexcel Internati...

Chemical Tests; flame test, positive and negative ions test Edexcel Internati...
Call Girls Alandi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Alandi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry

FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry
5.4 lecture 2019
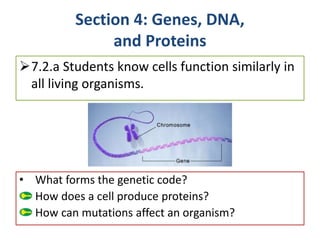
- 1. Section 4: Genes, DNA, and Proteins • What forms the genetic code? How does a cell produce proteins? How can mutations affect an organism? 7.2.a Students know cells function similarly in all living organisms.
- 2. The Genetic Code • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism's cells.
- 3. Genes and DNA • A single gene may contain anywhere from several hundred to a million or more nitrogenous bases.
- 4. Order of Bases • The order of nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long-chain molecules made of individual amino acids. • A group of three DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. – Example: CGT = alanine
- 6. How Cells Make Proteins • The production of proteins is called protein synthesis. • During protein synthesis, the cell uses information from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein. • Take place on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
- 7. The Role of RNA • A messenger must carry the genetic code from the DNA, in the nucleus, to the ribosome, in the cytoplasm. – mRNA DNA RNA sugar = deoxyribose sugar = ribose two strands one strand ATGC AUGC (uracil)
- 8. Types of RNA • Messenger RNA – RNA that copies the coded message from DNA in the nucleus and carries the message into the cytoplasm. • Transfer RNA – RNA in the cytoplasm that carries an amino acid to the ribosome and adds it to the growing protein chain.
- 9. HOW IS RNA DIFFERENT FROM DNA? Reading Checkpoint
- 10. Translating the Code 1. DNA unzips 1. One strand directs the production of mRNA. 2. RNA bases pair up with DNA bases 1. A-U, T-A, C-G, G-C 2. mRNA leaves the nucleus 1. attaches to a ribosome 2. mRNA provides the code and ribosomes move along he strand 3. tRNA attach to the mRNA 1. tRNA “reads” the code on mRNA by pairing to the three letter codes 2. tRNA also carries the specific amino acids – determined by the order of the three-letter codes on the mRNA 4. The protein molecule grows larger as each amino acid is added to the chain
- 11. During protein synthesis, the cell uses information from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein. How Cells Make Proteins
- 13. In which organelle of the cell are proteins manufactured?
- 14. WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF TRNA? Reading Checkpoint
- 15. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT THAT PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BE SO CAREFULLY ORGANIZED? Bonus Question
- 16. Mutations • Mutation – A change in a gene or chromosome. • Mutations can cause a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis. • As a result, the organism’s trait, or phenotype, may be different from what it normally would have been. • Mutations in body cells vs. sex cells
- 17. Types of Mutations • Small changes can occur during DNA replication single base substituted for another one or more bases removed from a section of DNA • Chromosomes don’t separate correctly during meiosis too many or too few chromosomes or an extra segment of chromosomes
- 18. Mutations Mutations can cause a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis. As a result, the organism’s trait, or phenotype, may be different from what it normally would have been.
- 19. Effects of Mutations • Source of genetic variety • Mutations can be harmful, helpful, or neither – Mutations are harmful if they reduce the organism’s chance for survival and reproduction. • Depends partly on environment.
- 20. WHAT ARE TWO TYPES OF MUTATIONS? Reading Checkpoint
- 21. WHAT KIND OF MUTATION MIGHT HELP AN ANIMAL SURVIVE IN A DESERT? Bonus Question