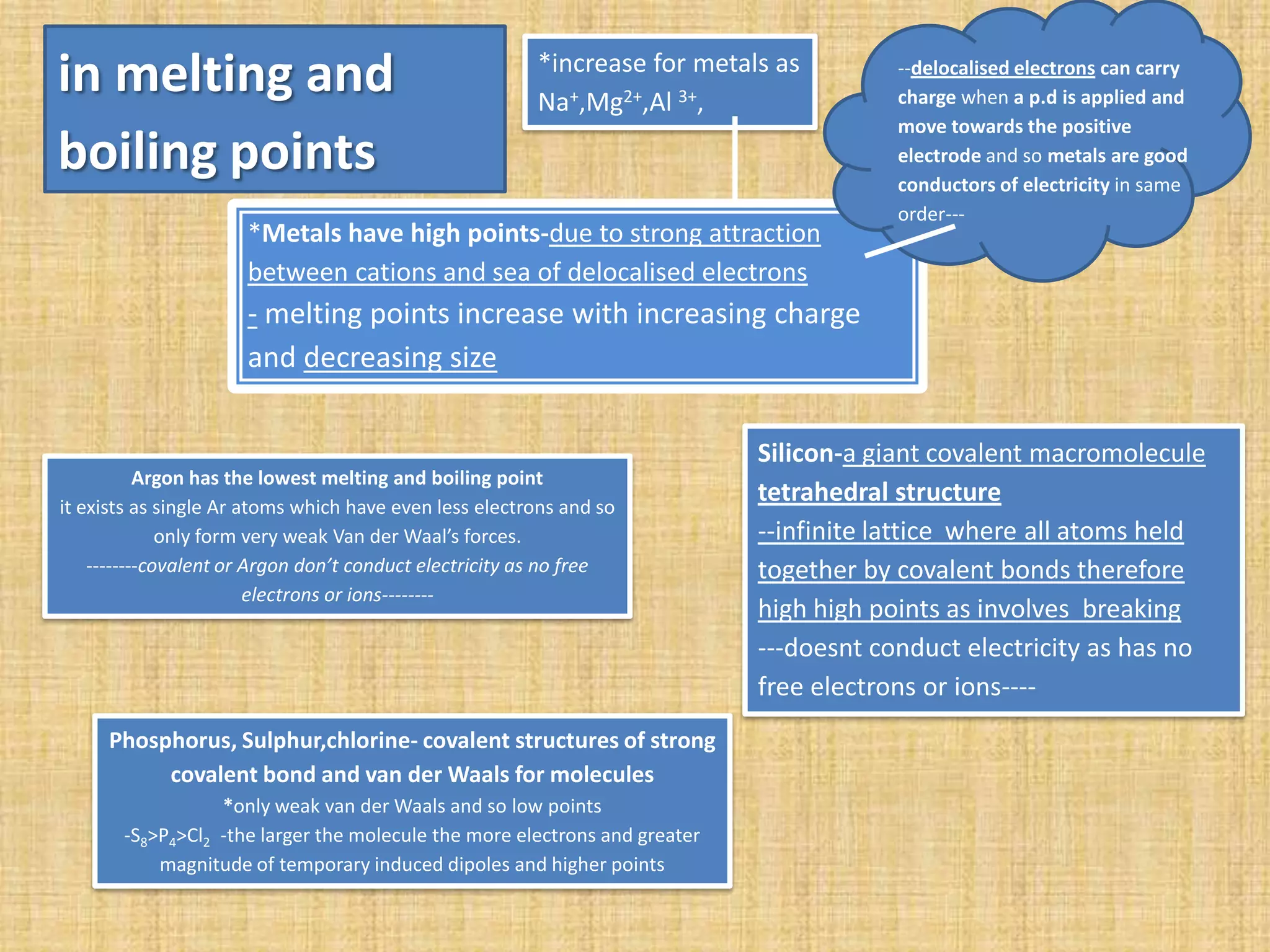
The periodic table arranges elements in order of increasing atomic number. Elements are placed in blocks based on their outer electron configurations (s, p, d, f). Elements in the same group have similar properties due to their outer shell electrons. Properties trend periodically across periods and groups due to changing nuclear charge and electron shielding. Metals generally have high melting points due to delocalized electrons, while nonmetals have covalent or weak van der Waals bonding and lower melting points. Ionization energy increases down groups and across periods as it is harder to remove electrons.