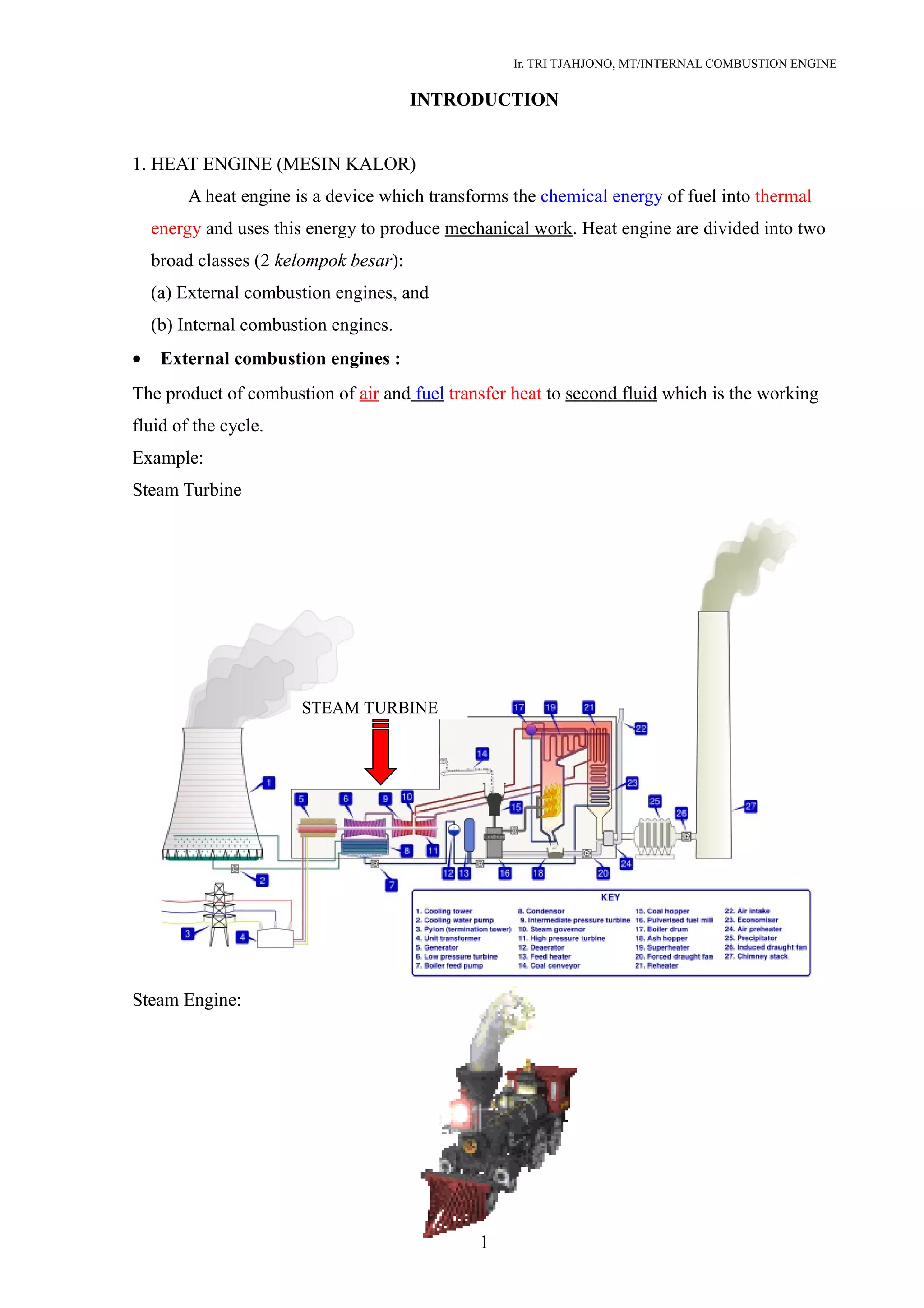
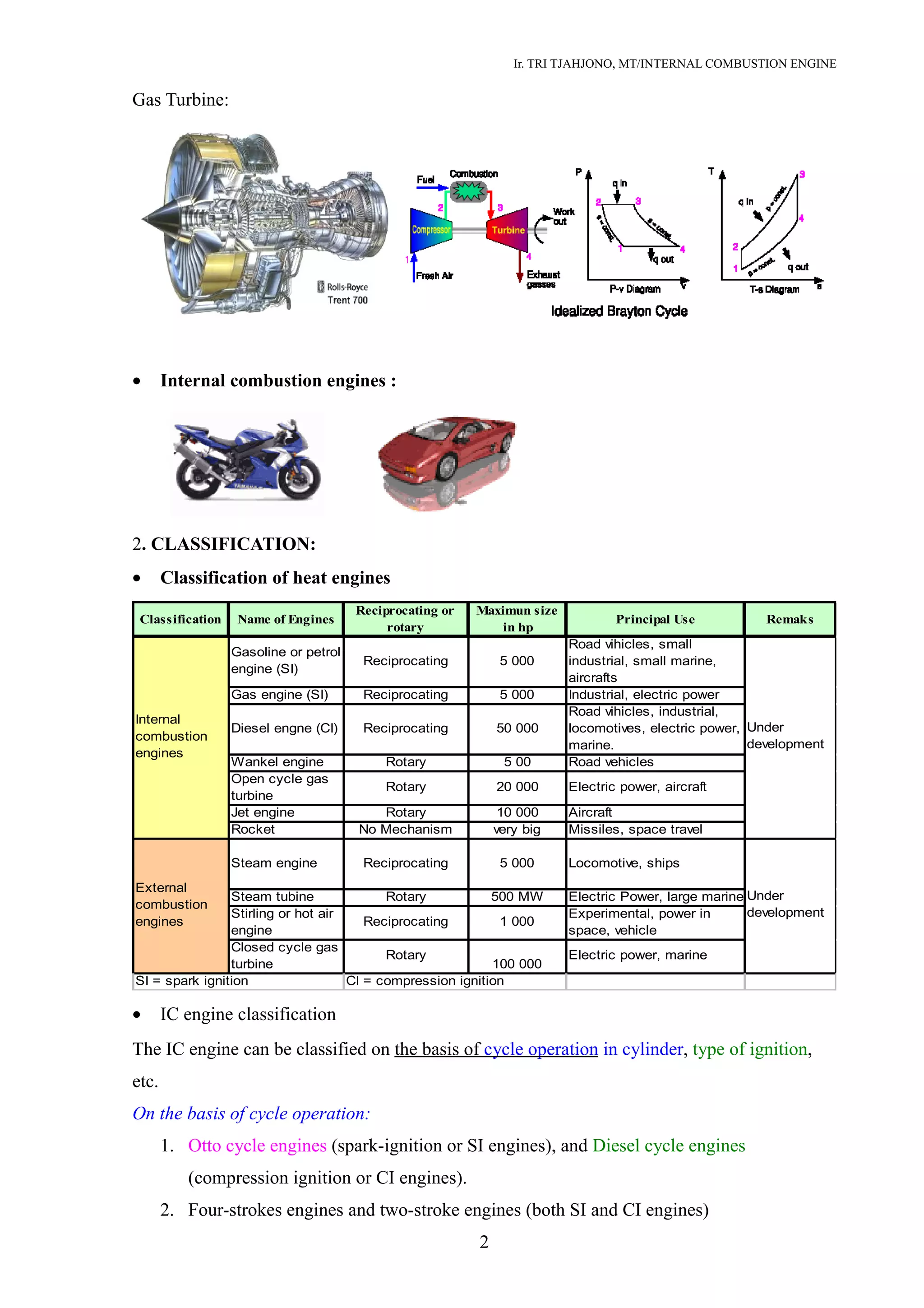
This document provides an introduction to heat engines and classifications of internal combustion engines. It begins by defining heat engines as devices that convert the chemical energy of fuel into thermal energy and then mechanical work. Heat engines are divided into external combustion engines, where combustion occurs separately from the working fluid, and internal combustion engines, where combustion occurs inside the engine itself.
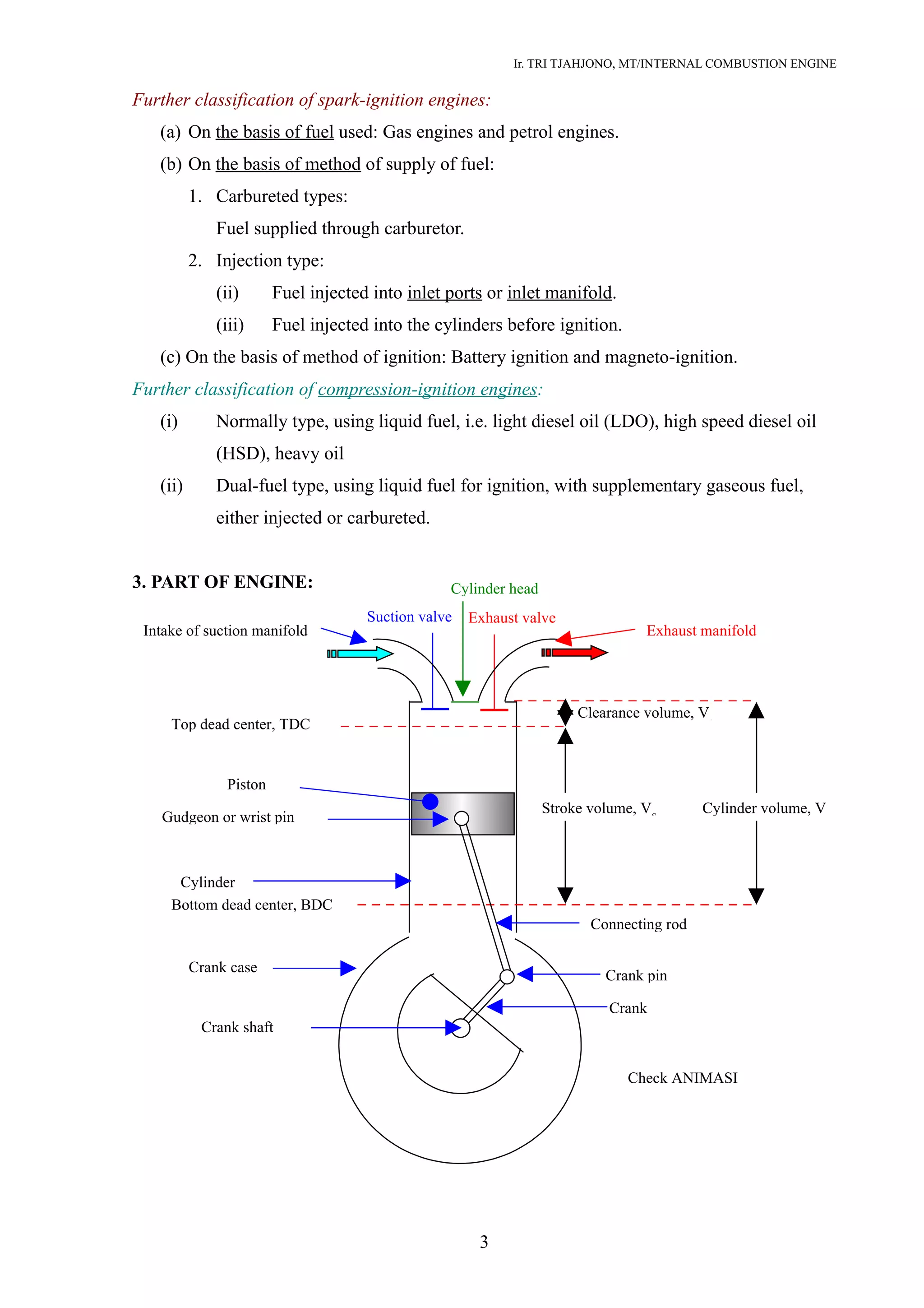
The document then classifies internal combustion engines based on their cycle of operation (Otto vs diesel), number of strokes, fuel and ignition type. Key internal combustion engine components like the cylinder, piston, valves and crankshaft are also defined. Comparisons are made between 4-stroke and 2-stroke engines as well as spark ignition and compression ignition engines in terms