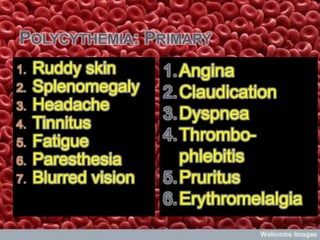
This document provides a summary of disturbances in oxygenation carrying mechanisms and transportation facilities. Specifically, it discusses issues related to disruptions in blood circulation and oxygen delivery. Key points include that disturbances can occur in the blood itself as well as the vessels and mechanisms that transport blood and oxygen throughout the body. Maintaining proper functioning of these critical systems is essential for health.