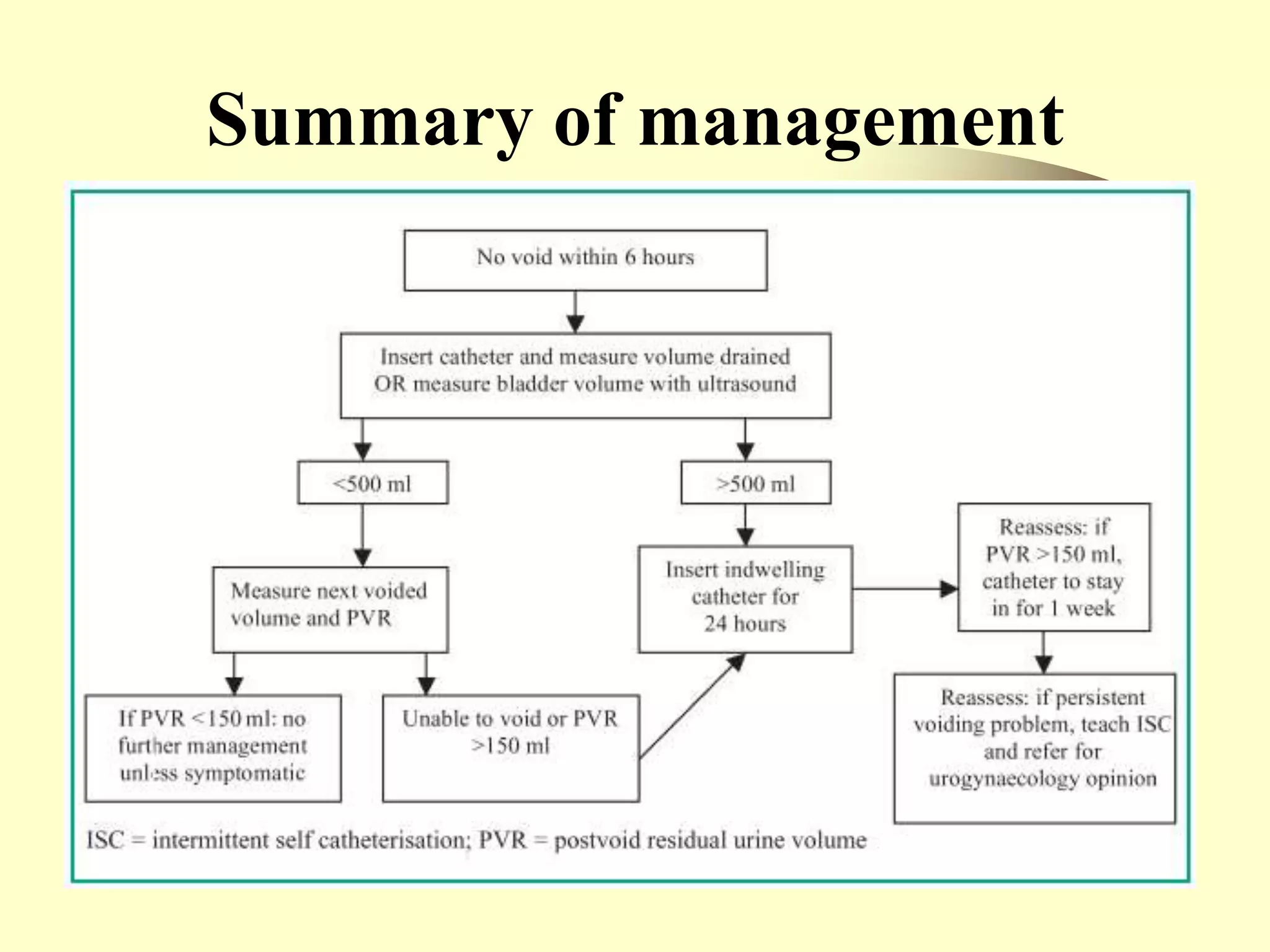
Postpartum voiding dysfunction and urinary retention is common after delivery and can lead to complications if not properly managed. Risk factors include instrumental delivery, epidural analgesia, prolonged labor, and large birth weight. Pathophysiology may involve nerve damage during delivery and physiological changes causing a hypotonic bladder. Management includes encouraging voiding every 2-3 hours during labor, offering an indwelling catheter for 6 hours after an epidural, and measuring voided volumes and post-void residuals to identify retention. Treatment involves catheterization, pelvic floor exercises, analgesia, and clean intermittent self-catheterization if needed.