Embed presentation
Download to read offline


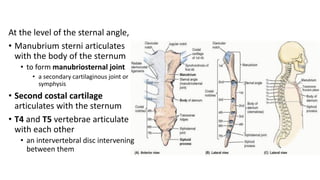
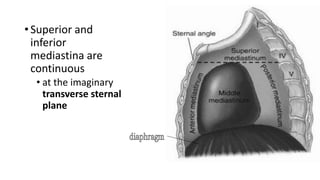
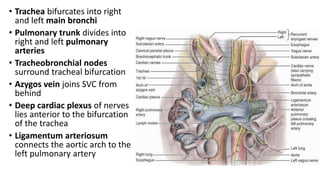


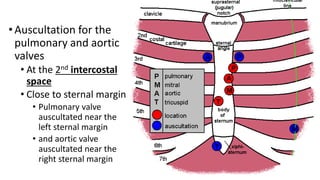
The sternal angle of Louis is an important anatomical landmark where several structures come together. At this level, the manubrium and body of the sternum articulate to form the manubriosternal joint. The trachea bifurcates into the right and left main bronchi, and the pulmonary trunk divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries. Several important blood vessels and nerves also lie at this level, including the azygos vein, deep cardiac plexus, and ligamentum arteriosum.







