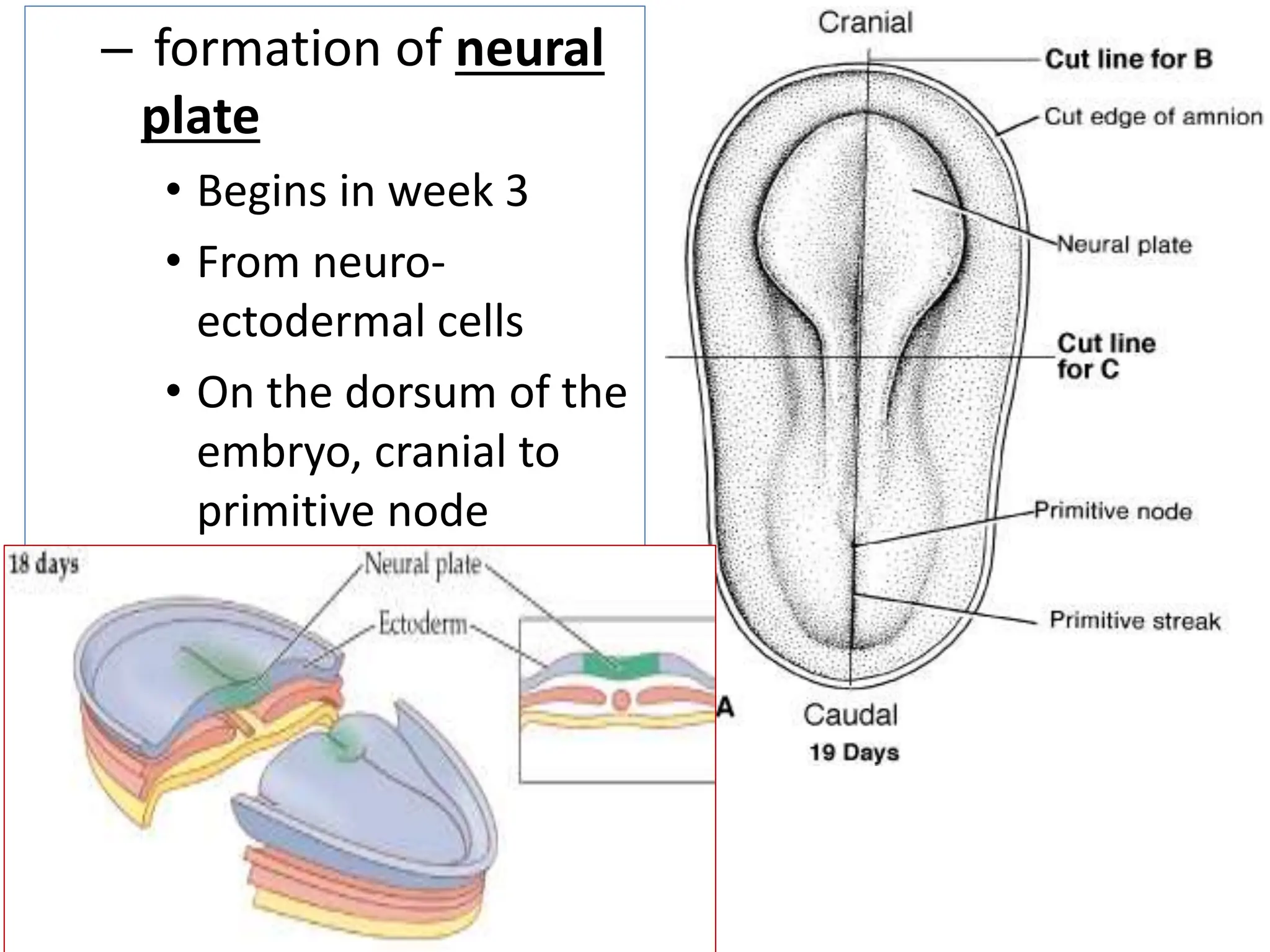
The document summarizes the process of neurulation during embryonic development. It involves the formation of the neural plate from neuroectodermal cells, which then folds to form the neural groove and neural folds. The neural folds then fuse together beginning in the cervical region, leaving two openings (neuropores) that close sequentially. The fused neural tube will eventually form the brain and spinal cord. Defects in neurulation can result in neural tube defects such as anencephaly, spina bifida, and rachischisis.