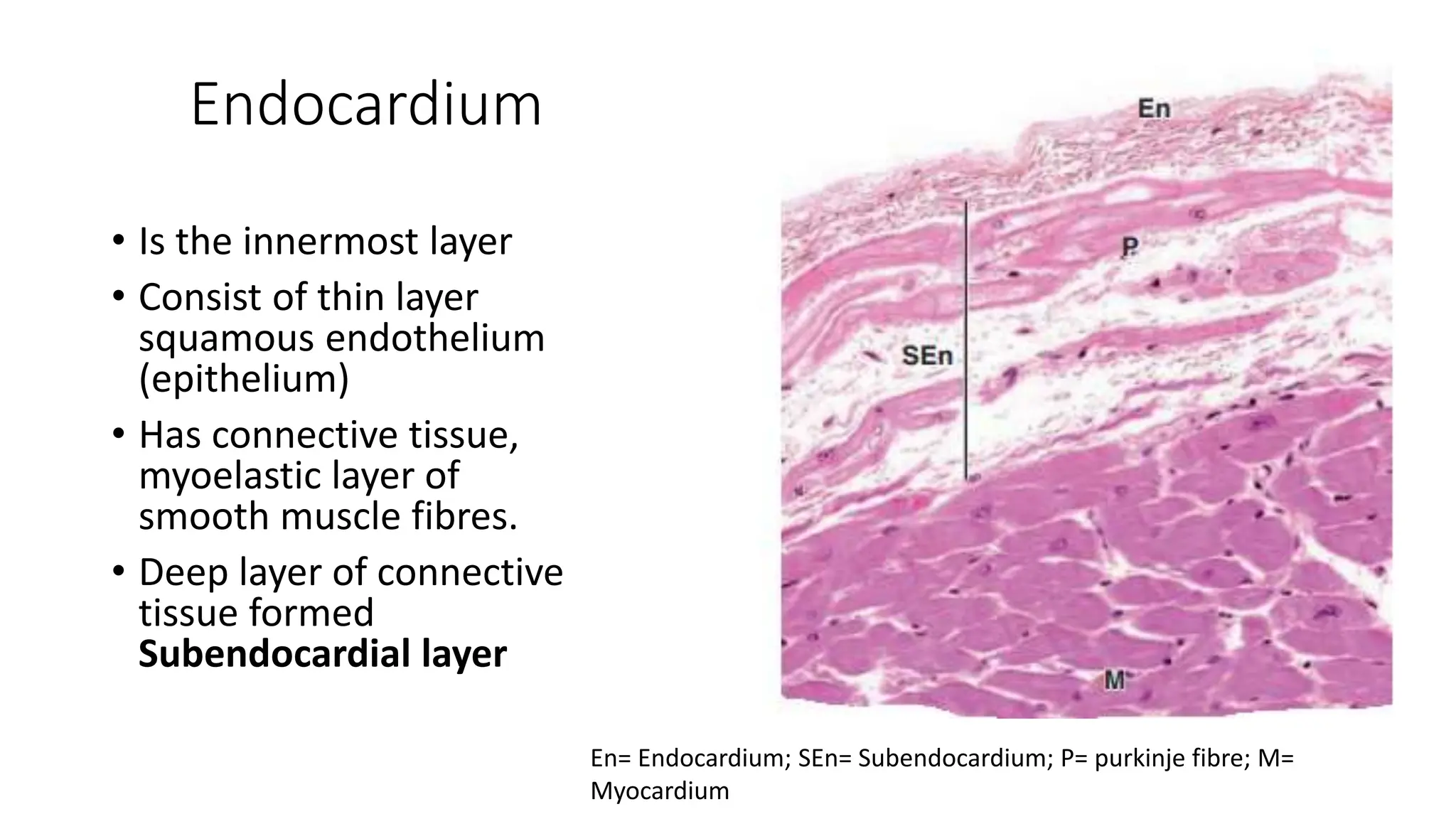
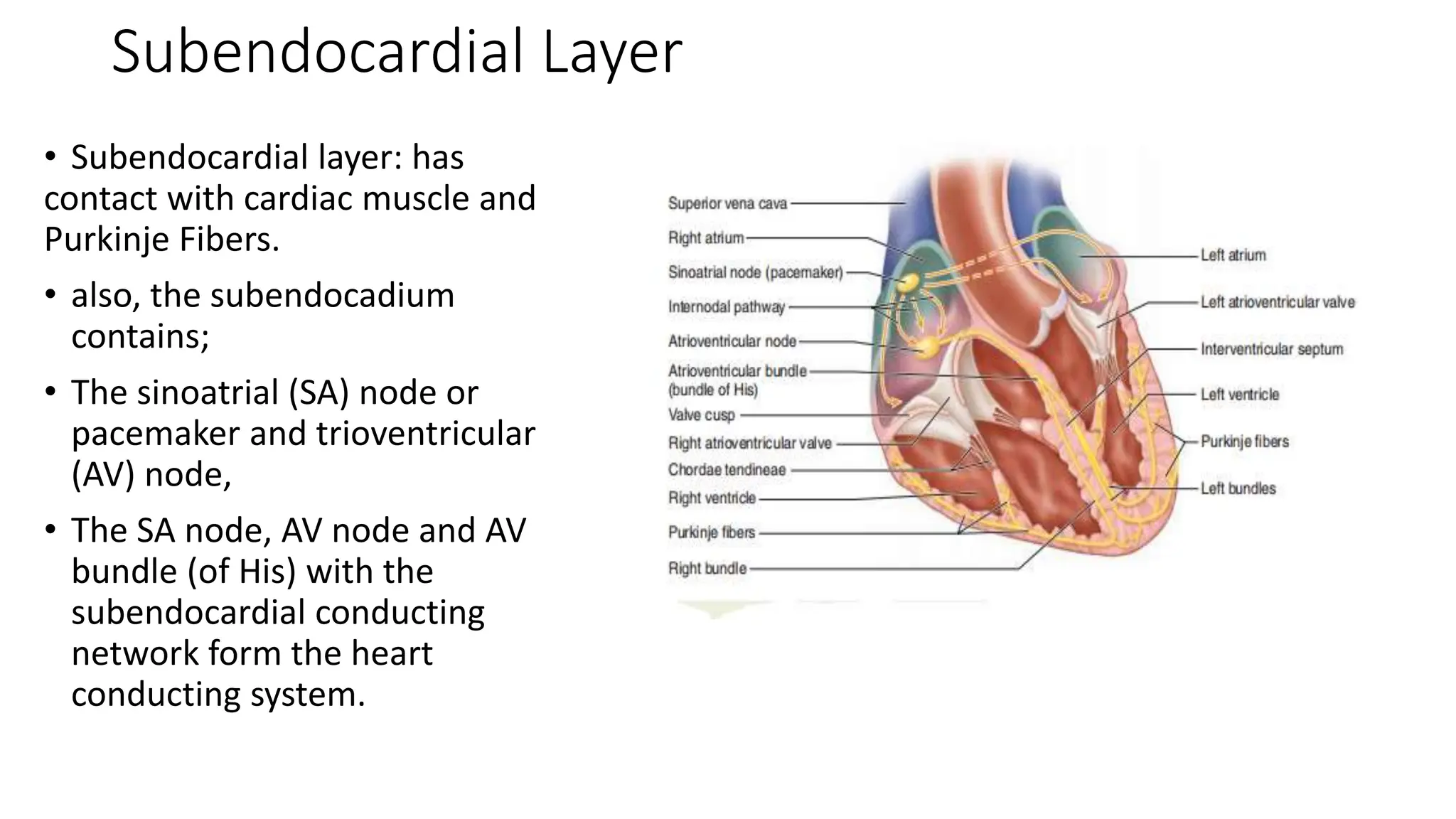
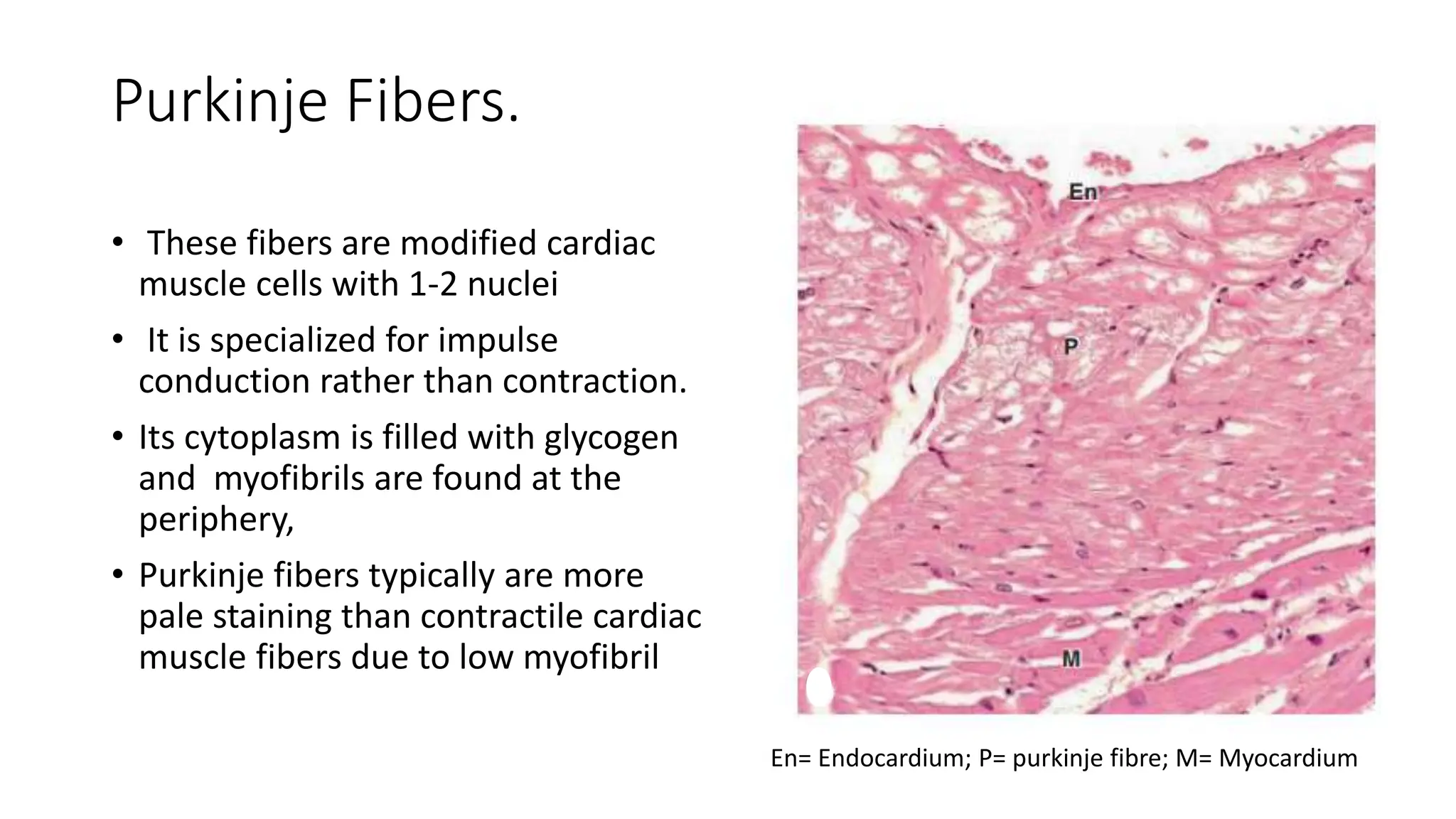
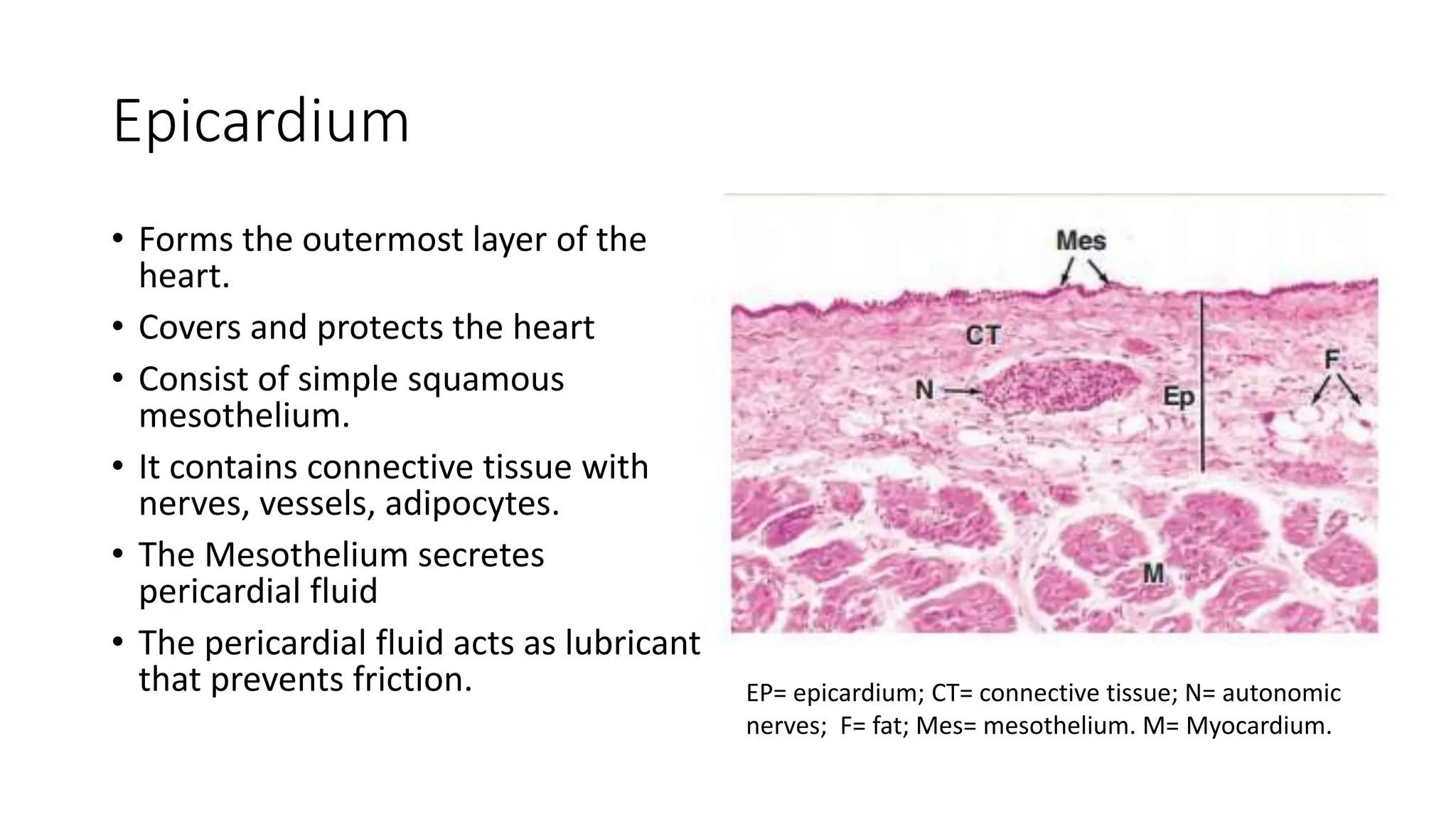
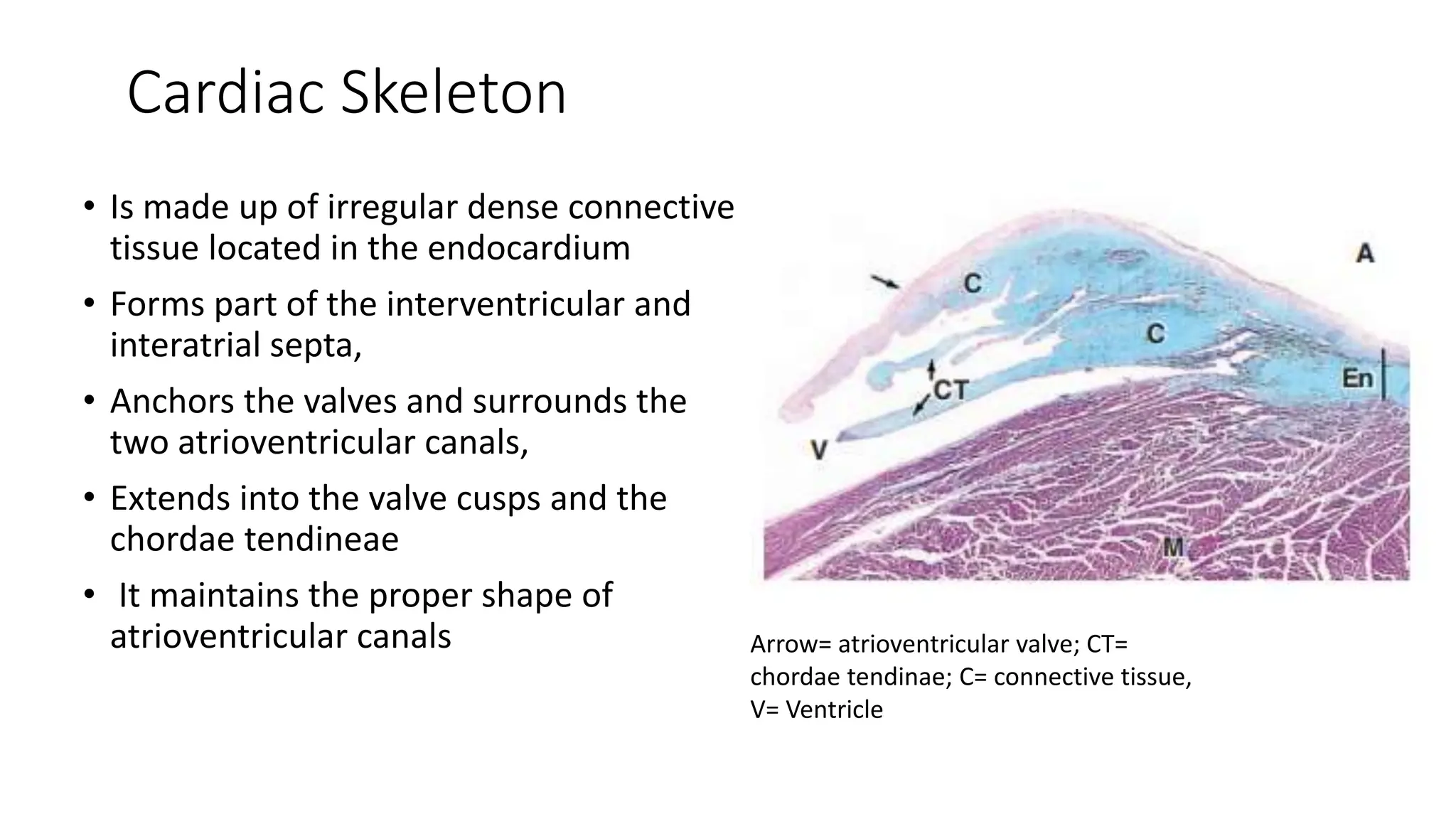
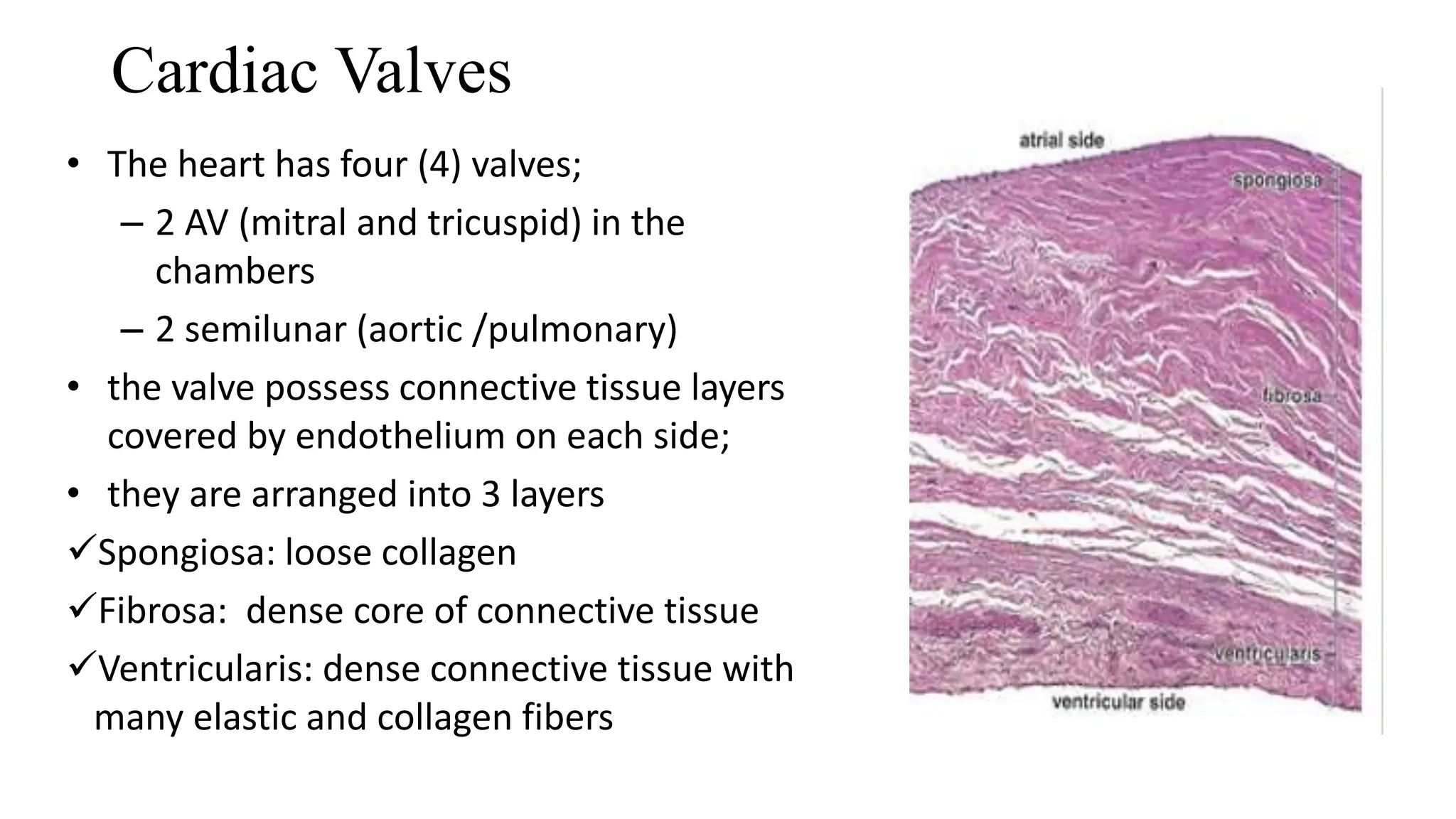
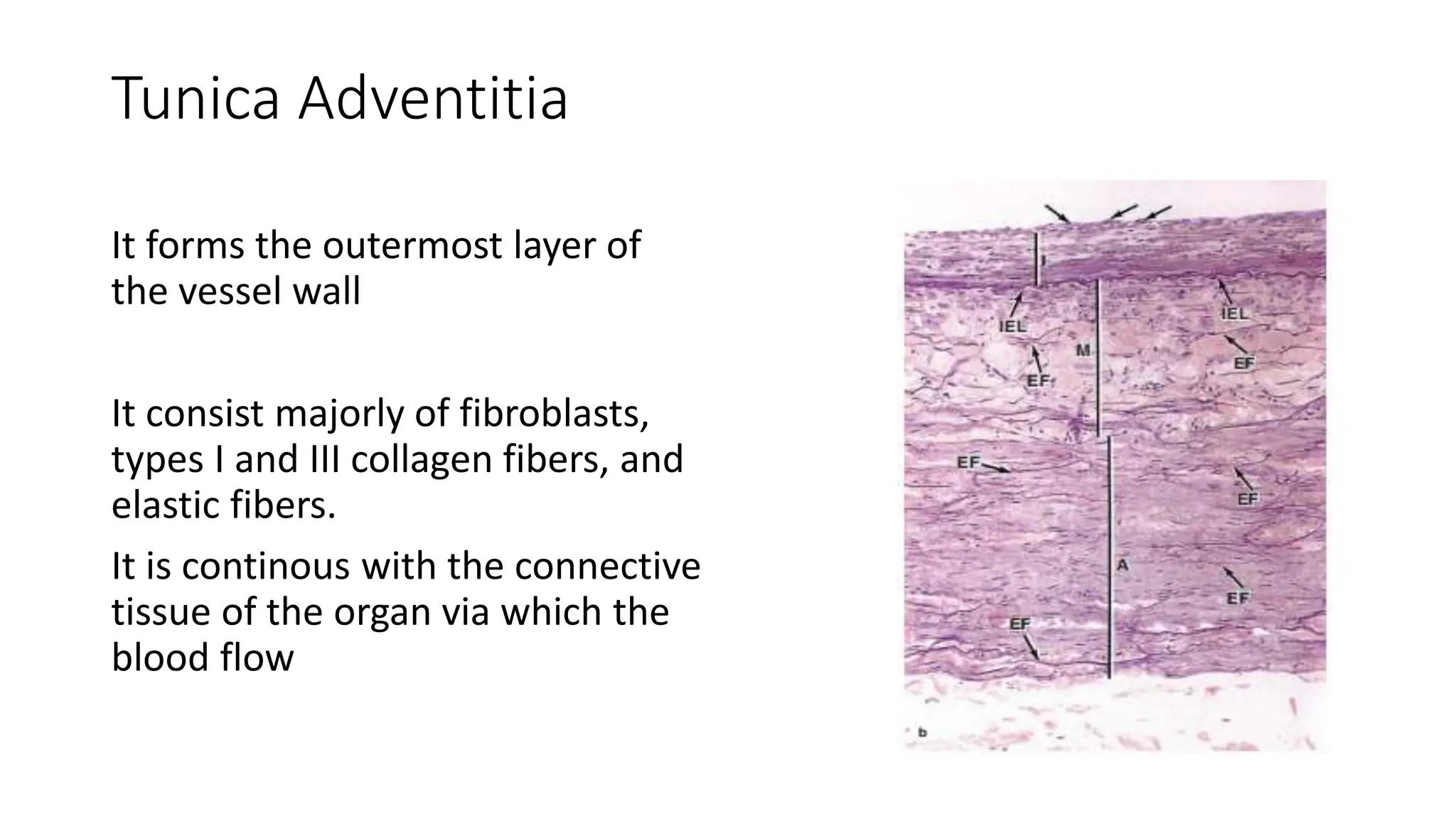
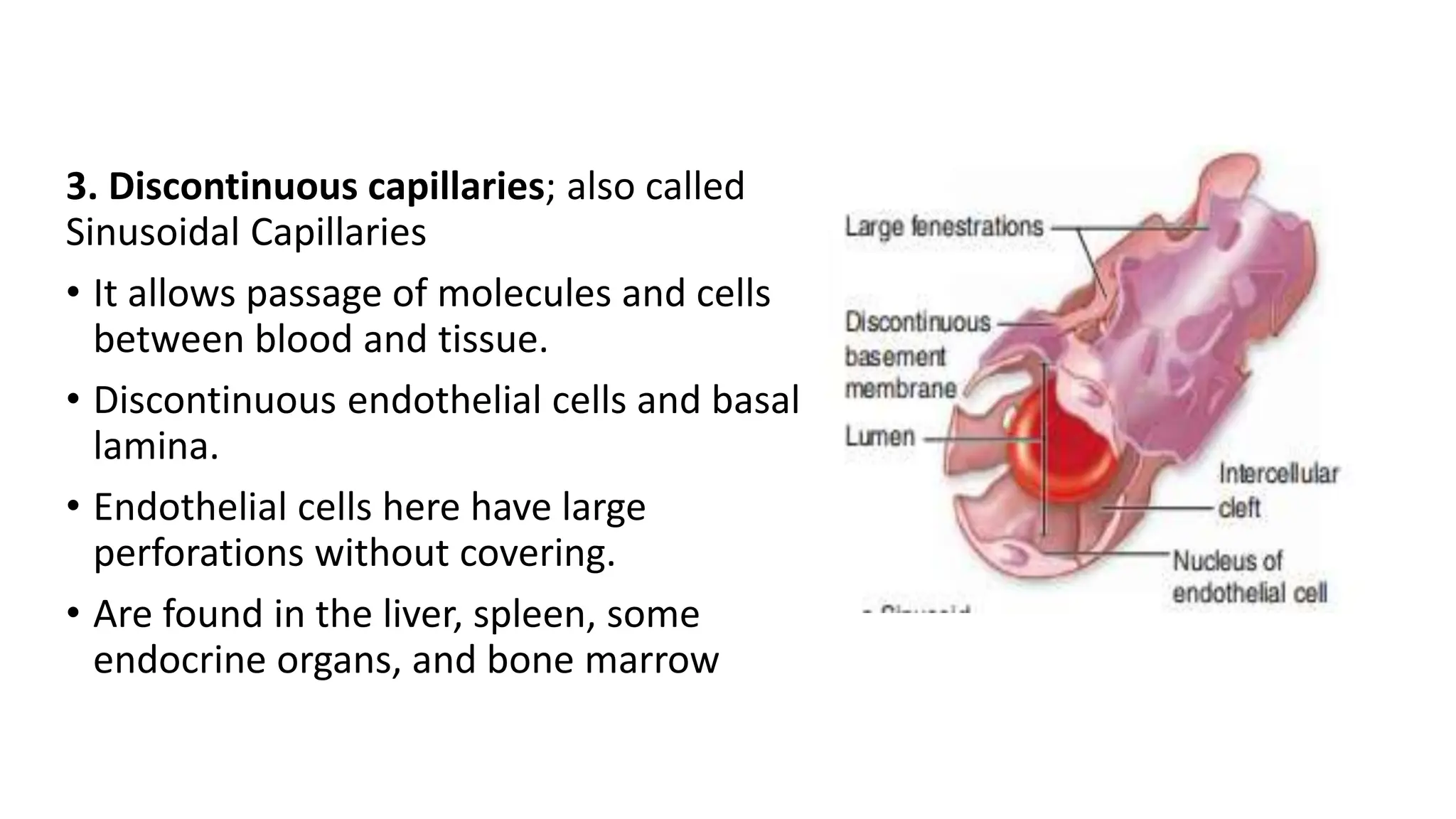
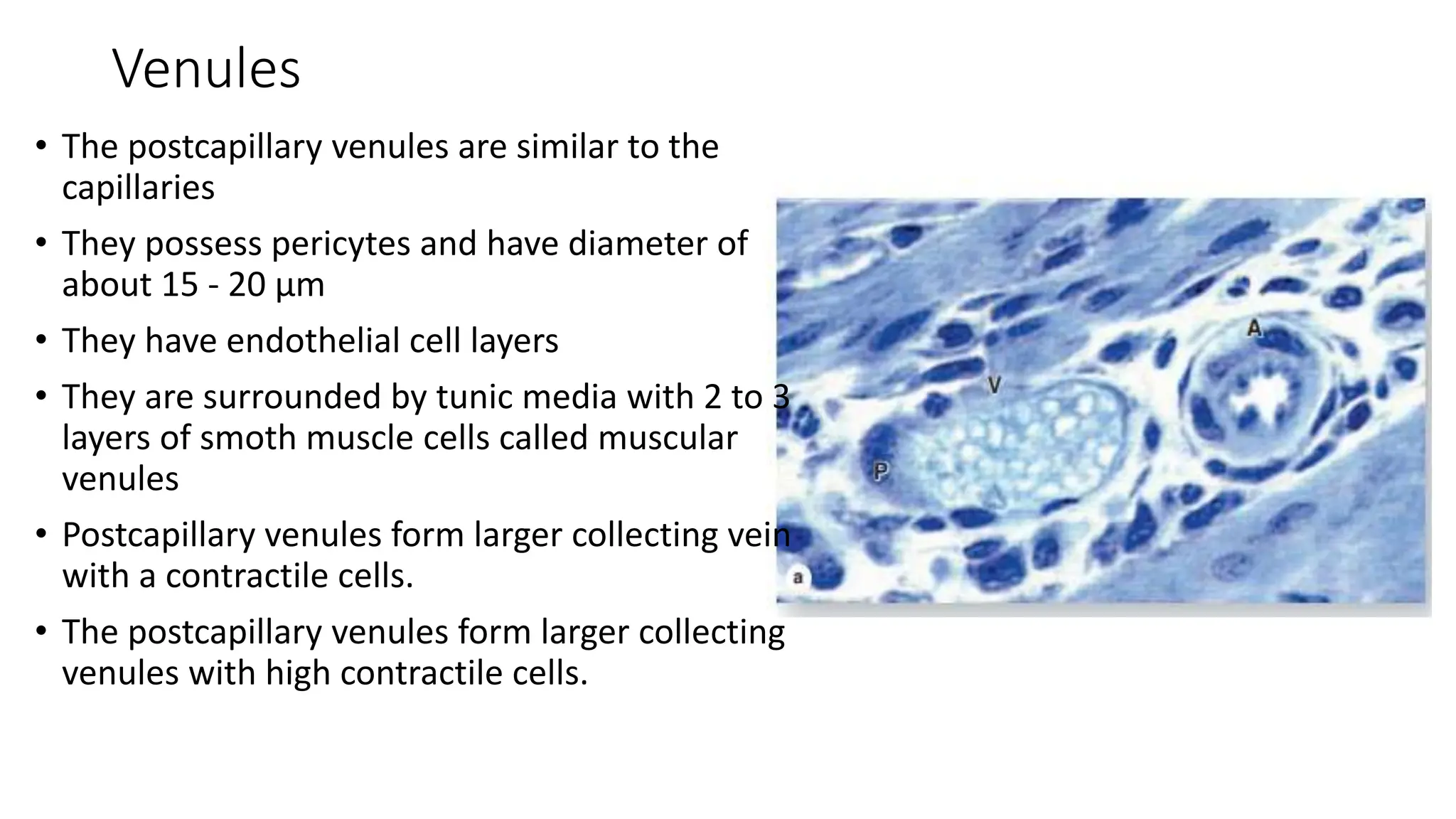
The document details the histology of the cardiovascular system, outlining the structure and function of the heart, blood vessels, and the lymphatic system. It describes the layers of the heart (endocardium, myocardium, epicardium), types of blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), and their respective layers and functions, as well as the classification of these vessels. Additionally, it discusses clinical correlations such as atheroma and their implications for cardiovascular health.