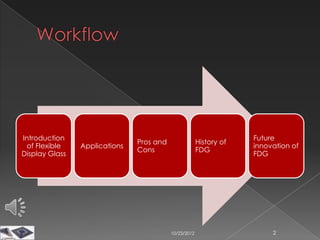
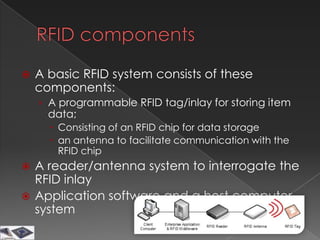
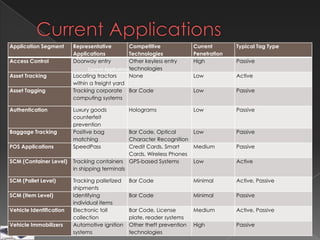
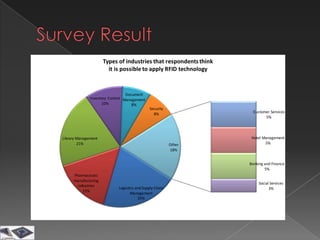
The document discusses the history, components, types, frequencies and applications of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. It describes the basic parts of an RFID system and how passive, semi-passive, and active RFID tags operate. Examples of common applications of RFID technology are also provided across various industries such as logistics, retail, transportation and more.