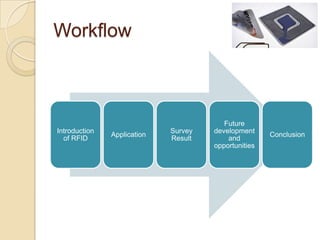
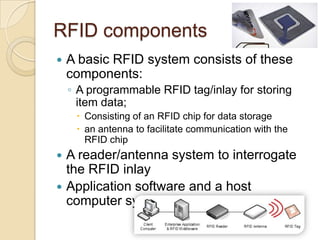
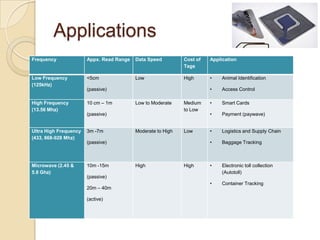
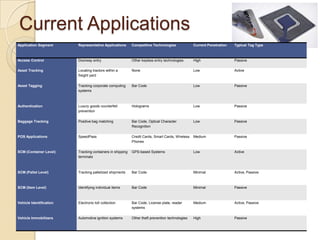
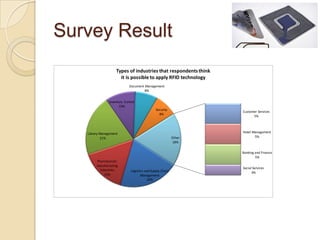
RFID technology uses radio waves to electronically identify objects. It consists of tags that store data, readers that interrogate tags, and application software. There are passive, semi-passive, and active tags. Common applications include access control, asset tracking, supply chain management, and electronic toll collection. A survey found potential industries for RFID include document management, inventory control, library management, logistics, and security. Further development opportunities exist in medical and library uses. RFID provides contactless reading, stores more data than barcodes, and allows updating tag data, but costs remain higher than barcodes and signals can be blocked by some materials.