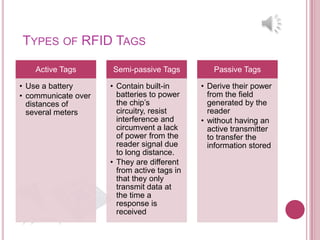
1) RFID uses radio frequencies to electronically identify objects. Tags carry data like serial numbers that readers can access without line of sight.
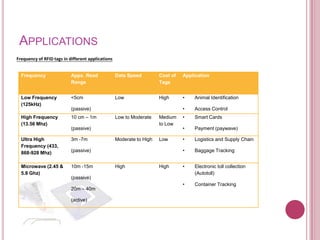
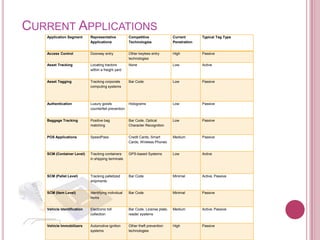
2) RFID has applications in access control, asset tracking, supply chain management, and electronic toll collection.
3) A survey found that respondents saw potential RFID applications in document management, inventory control, library management, and logistics. Further development is needed in medical uses and library management to realize more benefits.