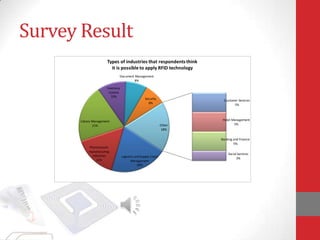
The document discusses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, including its components, types of RFID tags, current applications such as supply chain management and electronic toll collection, the results of an online survey on potential applications, and future development opportunities in areas such as medical uses and library management. RFID offers advantages over barcodes such as contactless reading and ability to hold more data, but costs remain higher and standards are still being developed.