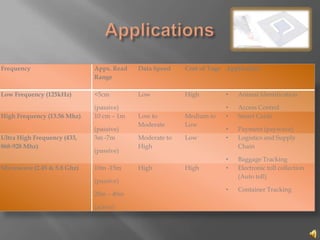
The document discusses RFID technology, including its components, frequency ranges, tag types, and applications in various industries. A survey was conducted to gather opinions on possible RFID applications from small and medium enterprises. The document concludes that RFID provides benefits like contactless reading and holding more data than barcodes, but also has limitations like higher costs compared to barcodes and potential signal interference from some materials.